Understanding the ECG Test and Its Procedure
Know about the ECG test, why it is done, how it is performed, types, diagnosis, and understanding of ECG results. Learn about the tips for a healthy heart.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 5th Sep, 2025

Introduction
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, painless test that measures the electrical activity of your heart. It helps doctors detect heart problems, monitor heart health, and guide treatment. If you or a loved one has been advised to get an ECG, you may have questions about what it is, how it’s done, and why it’s important.
This article will explain everything in simple terms—what an ECG is, how it works, what to expect during the test, and how to interpret the results.
What Is an ECG Test?
An ECG records the electrical signals produced by your heart with each heartbeat. These signals help doctors check:
- Heart rate (how fast or slow your heart beats).
- Heart rhythm (whether your heartbeat is regular or irregular).
- Signs of heart disease, such as blocked arteries or past heart attacks.
- Effectiveness of heart medications or devices (like pacemakers).
Since the test is quick, non-invasive, and risk-free, it’s often used for routine check-ups or emergency heart evaluations.
Consult a Cardiologist for Personalised Advice
Why Is an ECG Done?
Your doctor may recommend an ECG if you experience:
- Chest pain (possible heart attack or angina).
- Irregular heartbeat (palpitations)—feeling like your heart is racing, fluttering, or skipping beats.
- Shortness of breath, dizziness, or fatigue (signs of poor heart function).
- History of heart disease (to monitor heart health).
- Before surgery (to assess heart risk).
An ECG can detect conditions like:
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms).
- Coronary artery disease (blocked heart arteries).
- Heart attack (past or current).
- Heart muscle thickening (hypertrophy).
How Is an ECG Performed?
Before the Test
- No special preparation is needed.
- Avoid heavy exercise, caffeine, or smoking before the test, as they can affect results.
- Wear loose clothing for easy access to your chest, arms, and legs.
During the Test
- You’ll lie down on an exam table.
- A technician will place small, sticky electrode patches on your chest, arms, and legs.
- These electrodes connect to an ECG machine, which records your heart’s electrical signals.
- You’ll need to stay still and breathe normally for about 5-10 minutes.
- The test is completely painless—you won’t feel anything.
After the Test
- The electrodes are removed, and you can resume normal activities immediately.
- A doctor will analyse the ECG report and discuss the results with you.
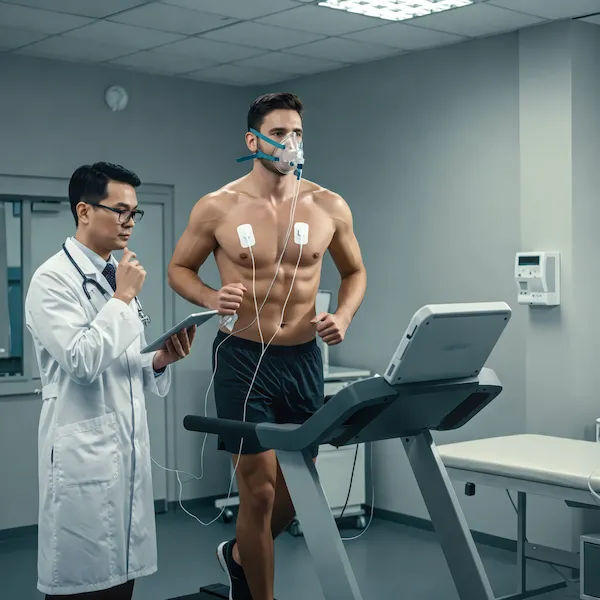
Types of ECG Tests
The types include:
- Resting ECG – Done while lying still (most common type).
- Stress ECG (Exercise ECG) – Records heart activity during physical exercise (treadmill or bike).
- Holter Monitor – A portable ECG device worn for 24-48 hours to detect irregular heartbeats.
- Event Monitor – Used for longer periods (weeks) to record occasional symptoms.
Your doctor will recommend the right type based on your symptoms.
Understanding ECG Results
An ECG produces a graph with spikes and dips called waves. Each wave represents a different part of your heartbeat:
- P Wave – Atrial contraction (upper chambers).
- QRS Complex – Ventricular contraction (lower chambers).
- T Wave – Heart relaxation before the next beat.
- Normal ECG: Shows a steady, regular rhythm (60-100 beats per minute).
- Abnormal ECG: May indicate:
- Fast/Slow heartbeat (tachycardia/bradycardia).
- Irregular rhythm (atrial fibrillation).
- Signs of a heart attack (ST elevation).
- Poor blood flow (ischemia).
Your doctor will explain what your results mean and if further tests (like an echocardiogram or angiogram) are needed.
Tips for a Healthy Heart
While an ECG helps diagnose heart issues, prevention is key. Here are some heart-healthy habits:
- Eat a balanced diet – More fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise regularly – Aim for 30 minutes of walking or cardio daily.
- Manage stress – Try meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
- Avoid smoking & limit alcohol – Both can harm your heart.
- Monitor blood pressure & cholesterol – High levels increase heart disease risk.
- Get regular check-ups – Especially if you have diabetes or a family history of heart disease.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience:
- Severe chest pain or pressure (may indicate a heart attack).
- Fainting spells or extreme dizziness.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat lasting long.
- Sudden shortness of breath.
Don’t ignore these symptoms—seek medical help immediately.
Final Thoughts
An ECG is a safe, quick, and essential test to monitor your heart’s health. Whether you have symptoms or just need a routine check-up, this test provides valuable insights into how well your heart is functioning.
Consult a Cardiologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Cardiologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Krishna N D
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD Physician, Post Graduate Diploma Clinical Cardio Physician
Dibrugarh
Apollo clinic Dibrugarh, Dibrugarh

Dr. Naresh Munot
Cardiologist
5 Years • MBBS, DM in cardiology
Pune
Apollo Hospitals Pune, Pune
(200+ Patients)
Dr. Raghu T R
Cardiologist
30 Years • MD, DM. Cardio, FACC.
Bengaluru
SJICR Hospital, APOLLO SPECIALITY HOSPITAL JAYANAGAR, Bengaluru

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Bhethala Sharan Prakash
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru
Consult a Cardiologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Krishna N D
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD Physician, Post Graduate Diploma Clinical Cardio Physician
Dibrugarh
Apollo clinic Dibrugarh, Dibrugarh

Dr. Naresh Munot
Cardiologist
5 Years • MBBS, DM in cardiology
Pune
Apollo Hospitals Pune, Pune
(200+ Patients)
Dr. Raghu T R
Cardiologist
30 Years • MD, DM. Cardio, FACC.
Bengaluru
SJICR Hospital, APOLLO SPECIALITY HOSPITAL JAYANAGAR, Bengaluru

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Bhethala Sharan Prakash
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru


.webp)
