How to Deal with Acne Pigmentation: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover effective ways to manage acne pigmentation, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Learn about causes, treatments like topical products, chemical peels, and prevention tips for clear, even-toned skin.

Written by Dr Shreya Sarkar
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
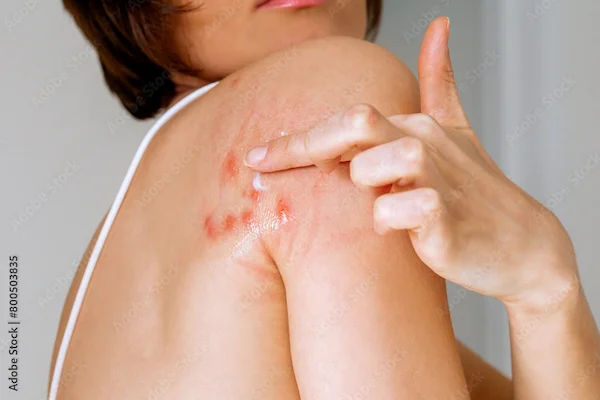
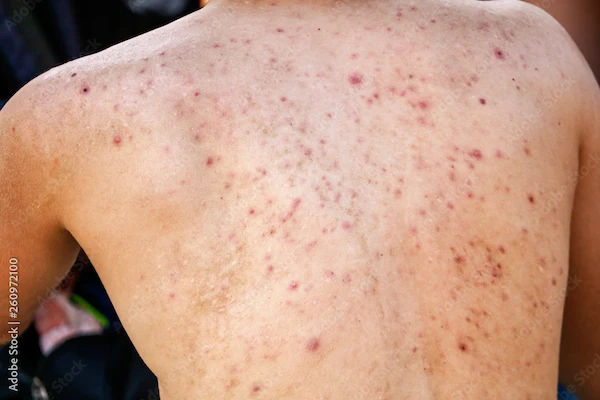
Acne pigmentation, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), is a common concern that often arises after an acne lesion heals. Unlike acne scars, which involve changes in the skin's texture, acne pigmentation is an issue resulting from excessive melanin production during the healing process.
Acne pigmentation typically appears as flat, discoloured spots that can range from light brown to dark brown or even purple, depending on the severity of the inflammation and the individual’s skin tone. These dark spots or patches can take weeks, months, or even years to fade without intervention, impacting both confidence and skin health.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of acne pigmentation, its causes, and effective strategies for management and prevention.
Causes of Acne Pigmentation
Several factors contribute to the development of acne pigmentation. Understanding these causes is key to effectively managing and preventing PIH. Below are the most common causes:
Inflammation: When acne lesions become inflamed, the body's natural response is to produce more melanin as a form of protection. This excess melanin leads to the darkening of the affected area.
Sun Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can exacerbate pigmentation issues by stimulating further melanin production. UV rays penetrate the skin and increase the activity of melanocytes (melanin-producing cells), causing the dark spots to become more pronounced.
Skin Type: While this condition can affect individuals of all skin types and tones, individuals with medium to darker skin tones are more susceptible to PIH due to higher levels of melanin. This makes any increase in melanin production more visible.
Improper Handling: Picking, squeezing, or scratching acne lesions can intensify inflammation and lead to more severe pigmentation. Physical manipulation of acne can cause additional trauma to the skin, worsening the pigmentation.
Underlying Conditions: Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to both acne and the resultant pigmentation. Hormonal changes can trigger acne outbreaks, which in turn can lead to PIH.
How to Manage Acne Pigmentation
There are several effective strategies available to treat and manage acne pigmentation. While some treatments focus on fading existing dark spots, others work on preventing new ones from forming. Here are various helpful options:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are among the most accessible and effective ways to address acne pigmentation. The following ingredients are commonly used to reduce discolouration associated with acne:
Hydroquinone: Often considered the gold standard in treating pigmentation, hydroquinone works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production. However, it should be used under a dermatologist's supervision, as prolonged use can cause irritation or skin sensitivity.
Retinoids: Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin, accelerate skin cell turnover, helping fade pigmentation and improve overall skin texture. Retinoids also help prevent future breakouts.
Vitamin C: As a powerful antioxidant, vitamin C inhibits melanin production and protects the skin from free radical damage. Regular use can brighten the skin and even out discolouration.
Azelaic Acid: This ingredient is ideal for sensitive skin. It lightens dark spots, reduces melanin production, and has anti-inflammatory properties that help control acne.
Kojic Acid and Arbutin: These naturally-derived ingredients are known to lighten pigmentation by targeting melanin production. They are often used in combination with other brightening agents.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of exfoliating acids to remove damaged skin layers, promoting cell renewal and reducing pigmentation. There are different types of chemical peels, including:
Glycolic Acid Peels: Particularly effective for improving skin texture and fading pigmentation.
Salicylic Acid Peels: Ideal for oily and acne-prone skin.
Lactic Acid Peels: Best suited for sensitive or dry skin types.
For optimal results, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist to determine the right type and concentration of peel for your skin type.
3. Laser Treatments
Laser therapy provides a targeted solution for severe or persistent pigmentation. Commonly used lasers include:
Fractional Lasers: These lasers create micro-injuries to stimulate collagen production and skin renewal.
Q-Switched Lasers: Effective for treating pigmentation in darker skin tones, these lasers break down excess melanin.
Laser treatments typically require multiple sessions and should be performed by trained professionals.
4. Microneedling
Microneedling involves creating tiny punctures in the skin using fine needles. This procedure stimulates collagen production and accelerates the fading of pigmentation. Microneedling can be enhanced by combining it with topical serums, such as vitamin C, for better results.
5. Sunscreen
Sun protection is essential when managing acne pigmentation, as UV radiation worsens dark spots. A good sunscreen routine can significantly improve the effectiveness of other treatments. Dermatologists recommend:
Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Protects the skin from both UVA and UVB rays.
SPF 30 or Higher: Ensures adequate protection.
Mineral Sunscreens: Contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, ideal for sensitive or acne-prone skin.
Be sure to reapply sunscreen every two hours when exposed to sunlight for the best protection.
6. Home Remedies
While not as potent as clinical treatments, certain home remedies may complement your skincare routine and help fade pigmentation. These include:
Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, aloe vera may help lighten pigmentation.
Green Tea Extracts: Rich in antioxidants, green tea can reduce melanin production.
Turmeric: It contains curcumin, a natural brightener with anti-inflammatory benefits.
Remember that home remedies may take longer to show results and are best used as supplementary treatments.
Preventing Acne Pigmentation
As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure. By following certain precautions, you can minimise the risk of developing acne pigmentation in the first place. Here are some key strategies for preventing PIH:
Avoid Picking Acne Lesions: The golden rule for acne care is to keep your hands off your face. Picking or squeezing acne lesions can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of pigmentation.
Maintain a Gentle Skincare Routine: Use non-comedogenic, fragrance-free products that cleanse the skin without causing irritation.
Incorporate Exfoliation: Mild exfoliants, such as salicylic acid or lactic acid, can help promote cell turnover and prevent the buildup of dead skin cells that could contribute to pigmentation.
Control Acne: Preventing acne breakouts is the most effective way to reduce the likelihood of developing PIH. Consult a dermatologist for a customised acne management plan.
Use Antioxidants: Antioxidants like Vitamin C protect the skin from damage and can help reduce pigmentation risks.
When to See a Dermatologist
If acne pigmentation does not improve with over-the-counter treatments or if it significantly affects your routine, it may be time to consult a dermatologist. A professional can assess your skin type, identify any underlying conditions, and recommend advanced treatments tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Dealing with acne pigmentation requires a combination of patience, prevention, and targeted treatments. While topical products like retinoids, hydroquinone, and Vitamin C can lighten dark spots, procedures such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling offer quicker results for more severe cases. Protecting your skin from sun damage and avoiding acne triggers are essential for long-term success. Consistency and professional guidance are key to effectively managing acne pigmentation and achieving clearer, more even-toned skin.
Consult Top Dermatologists
Consult Top Dermatologists

Dr. S Madhuri
Dermatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD. DVL, DNB, Fellow (Dermatosurgery & Lasers)
Secunderabad
Apollo Hospitals Secunderabad, Secunderabad
(300+ Patients)

Dr. Himabindu Mamidala
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, DDVL
Hyderabad
DrHIMABINDUS SKIN CLINIC AND LASER CENTRE, Hyderabad
Dr. Gauri Padmawar
Dermatologist
9 Years • MBBS, DDV, Certificate in Aesthetic
Pune
Dr. Aniruddha's advance ortho and polyclinic, Pune
Dr. Kavitha Killaparthy
Dermatologist
23 Years • MBBS,DIPLOMA(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY,LEPROSY)
Hyderabad
JDS Skin & Hair Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Snuhi Bhuiya
Dermatologist
7 Years • MBBS,MD(Dermatology venereology and leprosy)
Kolkata
Dr Snuhi Bhuiya Clinic, Kolkata