Aplastic Anaemia: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Know about Aplastic anaemia, what it is, causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options. Learn about living with aplastic anaemia.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Aplastic anaemia is a rare but serious blood disorder that affects the body’s ability to produce enough blood cells. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with this condition, it’s natural to feel concerned. However, understanding the disease, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you manage it better.
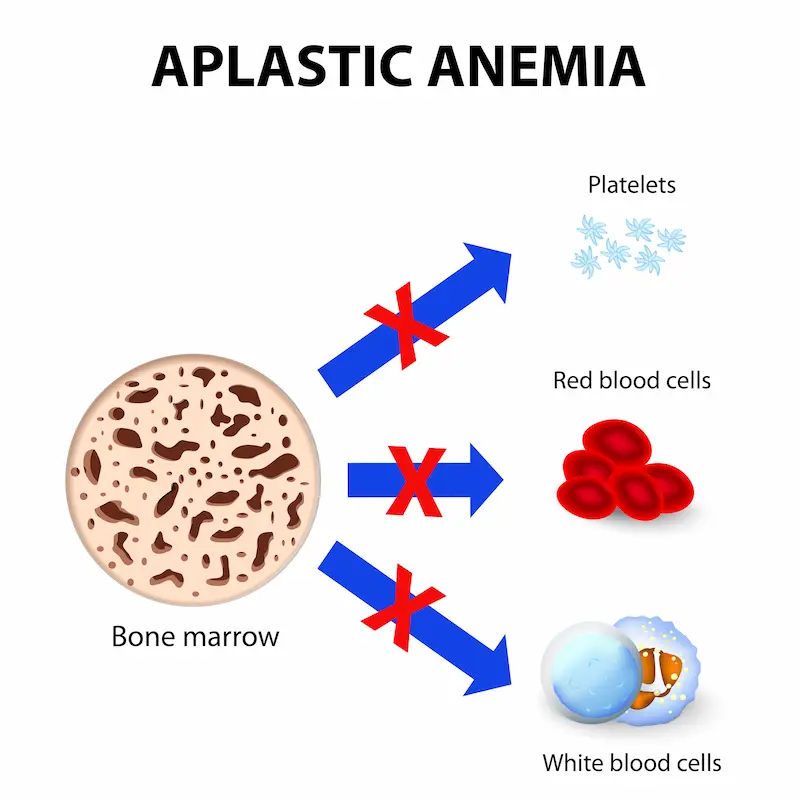
What is Aplastic Anaemia?
Aplastic anaemia occurs when the bone marrow—the spongy tissue inside bones—fails to produce enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This leads to:
Fatigue and weakness (due to low red blood cells).
Increased risk of infections (due to low white blood cells).
Easy bruising or bleeding (due to low platelets).
Unlike other types of anaemia (like iron deficiency anaemia), aplastic anaemia is caused by bone marrow damage rather than a lack of nutrients.
Consult the Best General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Symptoms of Aplastic Anaemia
The symptoms vary depending on which blood cells are most affected:
1. Low Red Blood Cells (Anaemia):
Fatigue and weakness
Pale skin
Shortness of breath
Dizziness or lightheadedness
2. Low White Blood Cells (Neutropenia):
Frequent infections
Fever
Slow healing of wounds
3. Low Platelets (Thrombocytopenia):
Easy bruising
Nosebleeds or bleeding gums
Prolonged bleeding from cuts
If you experience these symptoms persistently, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
What Causes Aplastic Anaemia?
In many cases, the exact cause is unknown (idiopathic aplastic anaemia). However, some known triggers include:
Autoimmune disorders (where the immune system attacks bone marrow).
Exposure to toxins (like pesticides, benzene, or chemotherapy drugs).
Viral infections (such as hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus, or HIV).
Radiation or chemotherapy treatments.
Certain medications (like some antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs).
Inherited conditions (such as Fanconi anaemia).
How is Aplastic Anaemia Diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects aplastic anaemia, they may recommend:
1. Blood tests – To check blood cell counts.
2. Bone marrow biopsy – A small sample of bone marrow is taken to examine under a microscope.
3. Additional tests – To rule out infections or genetic disorders.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anaemia
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Mild Cases
Blood transfusions – To temporarily boost red blood cells and platelets.
Medications – Such as immunosuppressants (to stop the immune system from attacking bone marrow).
2. Severe Cases
Bone marrow transplant (Stem cell transplant) – The most effective cure, especially for younger patients with a matching donor.
Immunosuppressive therapy (IST) – Drugs like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine help stimulate bone marrow function.
3. Supportive Care
Avoid infections – Wash hands frequently, avoid crowds, and stay updated on vaccinations.
Prevent bleeding – Use a soft toothbrush, avoid contact sports, and be cautious with sharp objects.
Healthy diet – Eat iron-rich foods (leafy greens, beans) and foods that support immunity (fruits, nuts).
Living with Aplastic Anaemia
Managing aplastic anaemia requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments:
Follow your doctor’s advice – Take prescribed medications regularly.
Monitor symptoms – Report any new or worsening signs to your doctor.
Stay active (but safely) – Light exercises like walking can help with fatigue.
Eat a balanced diet – Focus on nutrient-rich foods to support blood cell production.
Avoid infections – Stay away from sick people and practice good hygiene.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience:
Unexplained fatigue or weakness
Frequent infections or prolonged fever
Excessive bruising or bleeding
Seek medical help immediately. Early intervention can improve outcomes.
Need Expert Advice?
If you suspect aplastic anaemia or need a consultation, Apollo 24|7 offers expert haematologists who can guide you through diagnosis and treatment. You can book an online consultation or schedule a blood test easily from home.
Final Thoughts
Aplastic anaemia is a challenging condition, but with proper treatment and care, many people lead healthy lives. If you or someone you know is affected, stay informed, follow medical advice, and take steps to protect your health
Consult the Best General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Consult the Best General Practitioner for Personalised Advice

Dr. Mainak Baksi
General Practitioner
13 Years • MBBS , MD (MPH)
Howrah
Mainak Baksi Clinic, Howrah
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Rajib Ghose
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
25 Years • MBBS
East Midnapore
VIVEKANANDA SEBA SADAN, East Midnapore

Dr. Rohinipriyanka Reddy
General Practitioner
9 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad
Dr Nivethitha Sivakumar
General Practitioner
1 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 247 Virtual Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Imtiyaz Khan
General Practitioner
6 Years • MD (Physician), Fellowship in Critical Care,AFIH
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru