Understanding Pancytopenia and Its Management
Know all about the pancytopenia, what it is, causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment options. Learn about the prevention, lifestyle changes and more.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Pancytopenia is a medical condition that affects your blood cells, leading to low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This can impact your overall health, making you feel weak, prone to infections, and at risk of excessive bleeding.
If you have been diagnosed with pancytopenia, it’s natural to have questions and concerns. This article will help you understand the condition, its causes, symptoms, and how to manage it effectively.
What Is Pancytopenia?
Pancytopenia occurs when your bone marrow doesn’t produce enough of the three main types of blood cells:
1. Red blood cells (RBCs) – Carry oxygen throughout the body. Low levels can cause fatigue and weakness (anaemia).
2. White blood cells (WBCs) – Fight infections. A shortage increases the risk of infections.
3. Platelets – Help in blood clotting. Low platelet counts can lead to easy bruising or excessive bleeding.
When all three cell types are low, it can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly.
Consult a General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Common Symptoms of Pancytopenia
The symptoms vary depending on which blood cells are most affected, but common signs include:
• Fatigue and weakness (due to low RBCs)
• Frequent infections (due to low WBCs)
• Easy bruising or prolonged bleeding (due to low platelets)
• Pale skin (a sign of anaemia)
• Shortness of breath
• Dizziness
If you experience these symptoms, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Causes Pancytopenia?
Several factors can lead to pancytopenia, including:
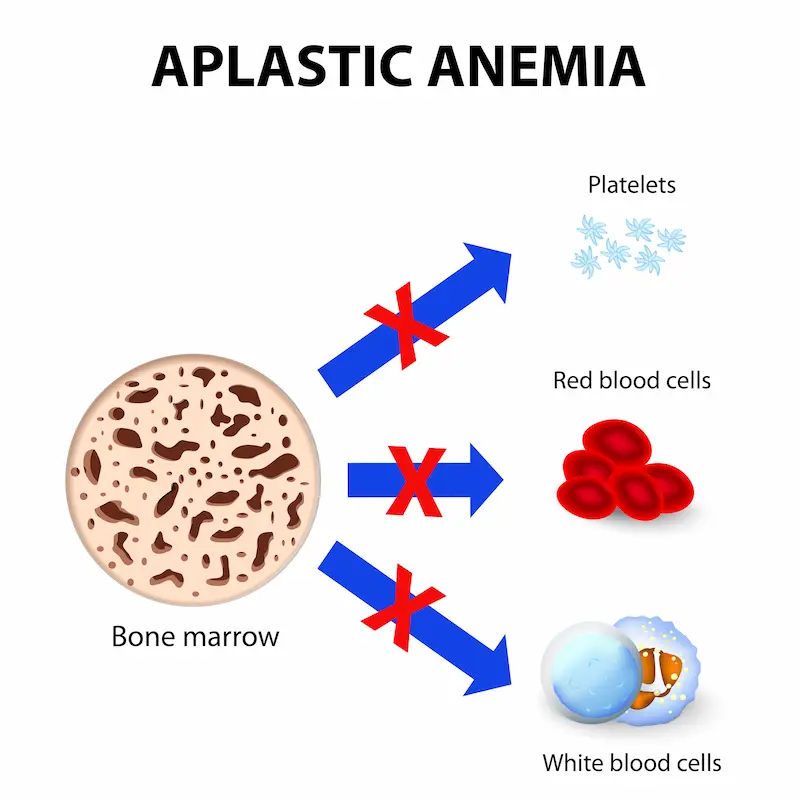
1. Bone Marrow Disorders – Conditions like aplastic anaemia, leukaemia, or myelodysplastic syndromes affect blood cell production.
2. Nutritional Deficiencies – Lack of vitamin B12, folate, or iron can impair bone marrow function.
3. Infections – Viral infections (like HIV or hepatitis) can suppress bone marrow activity.
4. Autoimmune Diseases – Conditions like lupus may attack blood cells.
5. Medications & Chemotherapy – Some drugs can reduce blood cell production.
6. Exposure to Toxins – Chemicals or radiation can damage bone marrow.
Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment.
How Is Pancytopenia Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to confirm pancytopenia:
• Complete Blood Count (CBC) – Measures levels of RBCs, WBCs, and platelets.
• Bone Marrow Biopsy – Checks bone marrow function.
• Additional Tests – Vitamin levels, infections, or genetic tests may be needed.
Get Your Health Assessed
Managing Pancytopenia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, but general management includes:
Medical Treatments
• Blood Transfusions – To replenish low blood cell levels.
• Medications – Such as immunosuppressants or growth factors to stimulate blood cell production.
• Treating Underlying Conditions – Addressing infections, nutritional deficiencies, or bone marrow disorders.
Lifestyle & Dietary Changes
• Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet – Include iron (spinach, lentils), vitamin B12 (eggs, dairy), and folate (leafy greens).
• Avoid Infections – Wash hands frequently, avoid crowded places, and stay updated on vaccinations.
• Prevent Bleeding – Use a soft toothbrush, avoid contact sports, and be cautious with sharp objects.
• Stay Hydrated & Rested – Helps in recovery and energy levels.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek immediate medical help if you experience:
• Severe fatigue or fainting
• High fever (sign of infection)
• Uncontrolled bleeding
Can Pancytopenia Be Prevented?
While some causes (like genetic disorders) can’t be prevented, you can reduce risks by:
• Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
• Avoiding unnecessary exposure to toxins or radiation.
• Following prescribed medication guidelines carefully.
Final Thoughts
Pancytopenia can be challenging, but with proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments, many people manage it effectively. If you suspect any symptoms, consult a doctor and get the necessary tests. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference in recovery.
Consult a General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Consult a General Practitioner for Personalised Advice

Dr. Mainak Baksi
General Practitioner
13 Years • MBBS , MD (MPH)
Howrah
Mainak Baksi Clinic, Howrah
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Rajib Ghose
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
25 Years • MBBS
East Midnapore
VIVEKANANDA SEBA SADAN, East Midnapore

Dr. Utsa Basu
Diabetologist
14 Years • MBBS , MD
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
(75+ Patients)
Dr Nivethitha Sivakumar
General Practitioner
1 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 247 Virtual Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Rupam Chowdhury
Orthopaedician
10 Years • MBBS, DNB (Ortho.)
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
Consult a General Practitioner for Personalised Advice

Dr. Mainak Baksi
General Practitioner
13 Years • MBBS , MD (MPH)
Howrah
Mainak Baksi Clinic, Howrah
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Rajib Ghose
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
25 Years • MBBS
East Midnapore
VIVEKANANDA SEBA SADAN, East Midnapore

Dr. Utsa Basu
Diabetologist
14 Years • MBBS , MD
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
(75+ Patients)
Dr Nivethitha Sivakumar
General Practitioner
1 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 247 Virtual Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Rupam Chowdhury
Orthopaedician
10 Years • MBBS, DNB (Ortho.)
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata