All About Breast Augmentation
Understanding breast augmentation and Learning about its implantation types, procedure, benefits and risks, its clinical implications, psychological impact, costing, recovery and outcome.

Written by Dr. Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Breast augmentation is a cosmetic procedure aimed at changing the size and shape of breasts. Commonly referred to as breast enlargement or augmentation mammoplasty or a boob job, this surgery involves inserting implants either under the breast tissue or the chest muscles to achieve a fuller or more balanced appearance. Individuals pursue breast augmentation for a range of reasons, such as reconstructive surgery following a mastectomy due to breast cancer, as part of gender-affirming procedures, or simply to boost their self-esteem regarding their body image.
Reasons for Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation usually involves silicone or saline implants. The main goal is to improve a patient’s natural proportions, achieving a more symmetrical and visually appealing profile. Each procedure is customised to fit the individual’s requirements.
Women opt for breast augmentation for a variety of reasons, such as:
Restoring breast volume lost after pregnancy and breastfeeding
Gaining confidence in swimwear
Achieving better balance to complement curvy hips
Enhancing self-esteem
Correcting noticeable breast asymmetry or tuberous breast deformities
This procedure may be a good choice if you feel your breasts are small, uneven, or if you wish to alter your appearance after significant weight loss or previous surgeries.
Types of Breast Implants
There are two primary methods for breast augmentation: breast implants and fat transfer augmentation. Each method offers various options based on the desired look and feel of the breasts.
1. Breast Implants
Breast implants are the most commonly chosen option for augmentation and include several types:
Saline Breast Implants: It is filled with sterile salt water. If an implant were to rupture, the saline would be absorbed by the body without harm.
Structured Saline Breast Implants: Similar to saline implants, but with an internal structure designed to provide a more natural sensation.
Silicone Breast Implants: Made from silicone gel, these implants can either keep the gel contained or allow it to leak if damaged. Regular check-ups with a plastic surgeon are often recommended to ensure their integrity.
Form-Stable Breast Implants: Commonly referred to as gummy bear implants, these maintain their shape even if the shell is compromised. They are firmer and require a longer incision for placement.
Round Breast Implants: These typically create a fuller appearance and their shape allows for consistent aesthetics, even if they shift position.
Smooth Breast Implants: Known for their soft feel, these implants often provide a more natural movement.
Textured Breast Implants: Designed to promote scar tissue formation, these implants help secure themselves in place. However, there is a rare association with breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) for textured surfaces.
2. Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation
In this technique, the surgeon uses liposuction to extract fat from another area of the body, which is then injected into the breasts. This approach is typically suitable for individuals seeking a modest enhancement in size. Common areas for fat extraction include: abdomen, flanks (sides and lower back), back and thighs.
What is Procedure of augmentation?
Before your breast augmentation, you'll have a consultation with your surgeon for a medical evaluation to discuss your expectations and receive professional advice. You may need to stop certain medications a few days or weeks prior to surgery.
The procedure can be done as an outpatient, allowing you to go home the same day, or you might stay overnight in hospital if necessary. Surgery typically lasts one to two hours, with general anaesthesia ensuring your comfort throughout.
Key Steps in the Process
Anaesthesia: You'll be under general anaesthesia or intravenous sedation, decided in consultation with your surgeon.
The Incision: Incisions can be made:
Along the crease beneath your breast (inframammary fold)
Around the edge of your areola (periareolar incision)
Through your armpit (transaxillary approach)
Implant Insertion: Implants can be placed either in front of the muscle or behind the pectoral muscle, depending on factors like the implant type and desired size. Discuss the pros of each option with your surgeon.
Closing the Incision: After the implants are in place, your surgeon will stitch the incisions closed. Drainage tubes may be used if necessary. Follow your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, and you'll leave with gauze bandages and possibly a surgical bra.
Risks and Complications of procedure
All surgical procedures involve risks. Among women undergoing breast reconstruction, about 46% with silicone gel implants and 21% with saline implants may require additional surgery within three years. Approximately 8% of saline implant patients and 25% of silicone patients may undergo device removal. Nearly half of those receiving cosmetic breast augmentation experience complications, such as pain, hardening, infection, or further surgery.
Common risks include:
Breast pain
Infection
Temporary changes in breast or nipple sensation
Implant rupture or leakage
Bleeding
Fluid accumulation
Capsular contracture, which can harden tissue around the implant and cause discomfort
Visible scarring
Additionally, risks associated with breast implants include:
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), linked to textured implants
Breast implant illness, with symptoms like fatigue and cognitive difficulties
If a saline implant ruptures, it will deflate and be absorbed by the body. Silicone implants can leak silently, known as silent rupture. Breast implants may also complicate breastfeeding.
Recovery Process post procedure
After breast enlargement surgery, you can start moving around soon after. It's advisable to take one to two weeks off work and avoid driving for at least a week.
Surgeons often recommend wearing a sports bra continuously for up to three months, so check with your surgeon. Refrain from heavy lifting and vigorous exercise for at least a month.
1 to 2 weeks: Stitches will usually be removed unless dissolvable.
6 weeks: You can return to most normal activities, and scars will start to fade.
A few months: Your breasts should feel and look more natural.
Your breasts will be covered with gauze, and drainage tubes may be present for a few days. It’s important to rest and manage discomfort with over-the-counter pain relief, as swelling and bruising are common.
Most people can return to work after five to seven days, but wait at least three weeks if your job involves physical activity. Avoid high-intensity activities, including sexual activity, during the first two weeks.
Daily breast massages for the first two weeks may aid healing. By six weeks, you should resume most activities, and after three months, your breasts will appear more natural.
Psychological Implications of surgery
Breast augmentation can enhance the size and shape of your breasts, potentially boosting your body image and self-esteem. However, it's crucial to keep your expectations realistic and avoid the idea of achieving perfection.
Changes in age and weight can impact the appearance of your breasts over time, and if you're dissatisfied with these changes, you might consider additional surgery.
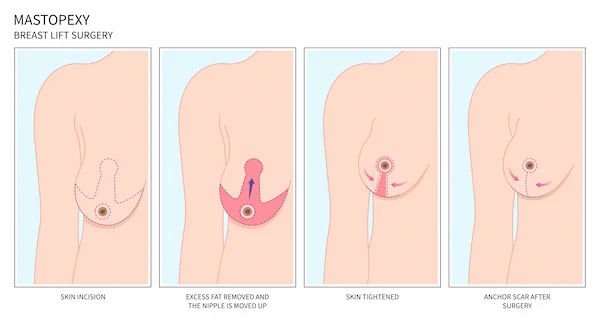
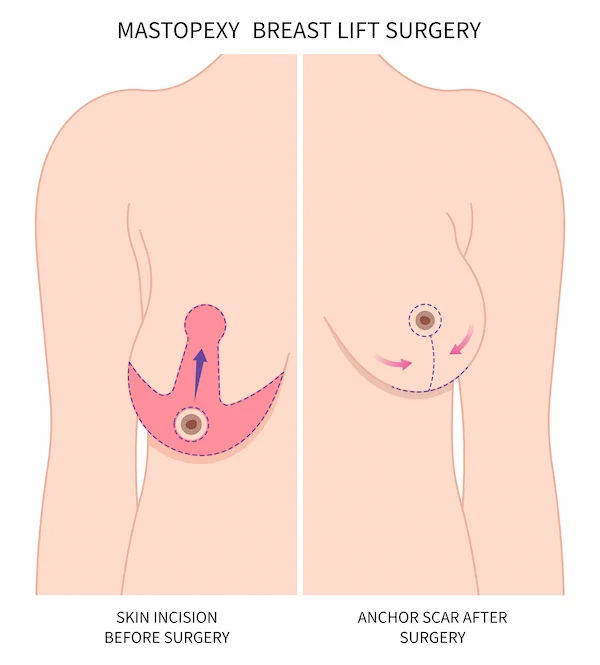
Moreover, breast augmentation alone may not address significant sagging. In such cases, a breast lift may be necessary for a fuller and more elevated appearance. This can often be performed at the same time as the augmentation or as a separate procedure, with advice from your plastic surgeon.
Cost and Insurance Aspects of process
Breast augmentation expenses may include:
Anaesthesia fees
Surgical facility charges
Medical tests
Post-surgery garments
Prescription medications
Surgeon’s fees
Most health insurance policies do not cover cosmetic breast augmentation or related complications, and some may exclude coverage for breast conditions in patients with implants. Since breast augmentation is generally considered elective, insurance typically does not cover the surgery or follow-up appointments, which may lead to higher future premiums. It's advisable to obtain written estimates from your surgeon, especially since insurance may not cover implant removal later.
If the implants are part of reconstructive surgery, there may be some insurance coverage available. Be sure to clarify your insurance details well in advance of your surgery.
Alternatives to Breast Augmentation
Several options are available as alternatives to breast augmentation, including:
1. Breast lift surgery (mastopexy): This procedure raises and reshapes the breasts, effectively reducing sagging and enhancing the overall contour without adding extra volume.
2. Flap reconstruction after mastectomy: This technique involves using skin and tissue from another area of the body, such as the abdomen or back, to construct a new breast, providing a more natural look for those recovering from breast cancer.
3. Padded bras: These can offer a non-surgical way to enhance breast size and shape temporarily. There are various styles and levels of padding available to suit personal preferences.
4. Counselling or therapy: Engaging with a mental health professional can help individuals work through body image issues and boost self-esteem, promoting a greater sense of comfort in their appearance without resorting to surgery.
Conclusion
Breast augmentation is a widely performed procedure that enhances the size and shape of the breasts using saline or silicone implants. While it is generally safe, there are risks involved, making it crucial to select a qualified surgeon and ask thorough questions to achieve the best results. Regular follow-up appointments, especially for silicone implants, are important to ensure their ongoing health.
Consult Top Oncologist
Consult Top Oncologist

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Dr. B Shravanthi Reddy
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
8 Years • MBBS, DNB(Radiation Oncology)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir

Dr. Indranil Ghosh
Oncologist
13 Years • MBBS, MD, DM (Med. Onco.)
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata
(100+ Patients)