Coeliac Disease Overview and Management
Explore coeliac disease, an autoimmune condition triggered by gluten. Learn about its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and effective management strategies for long-term digestive health.

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Coeliac disease (also spelled celiac) is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the body reacts abnormally to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with coeliac disease consumes gluten, their immune system attacks the small intestine, damaging its lining and preventing proper nutrient absorption.
This condition affects people of all ages, from children to adults, and requires lifelong management through a strict gluten-free diet. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications like malnutrition, osteoporosis, and even certain cancers.
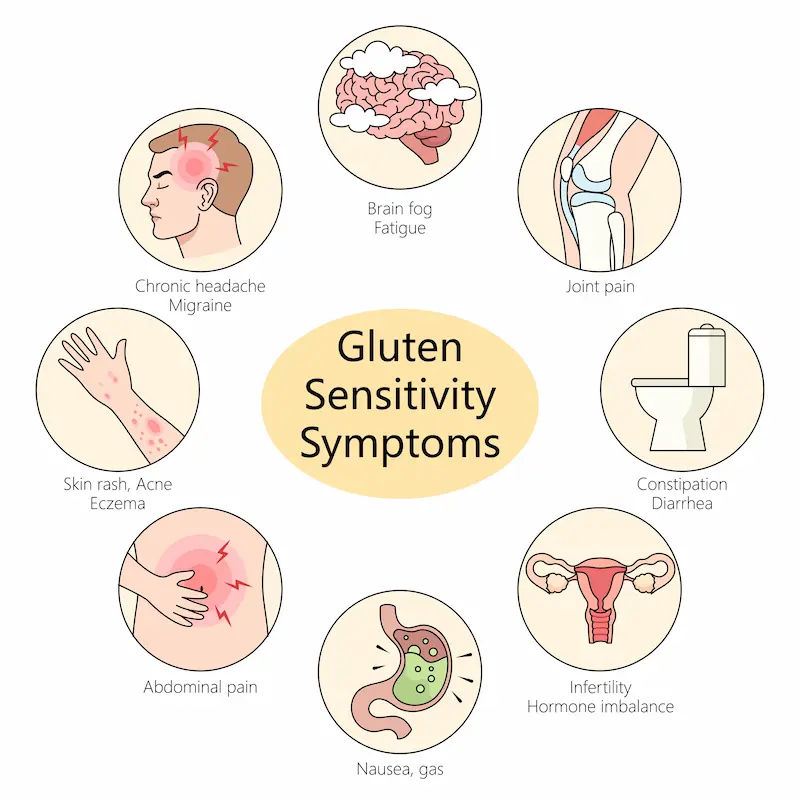
Symptoms of Coeliac Disease
Symptoms vary widely, making diagnosis tricky. Some people experience severe digestive issues, while others have mild or no obvious symptoms. Common signs include:
Digestive Symptoms:
• Diarrhea or constipation
• Bloating and gas
• Stomach pain
• Nausea and vomiting
Non-Digestive Symptoms:
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fatigue and weakness
• Anemia (low iron levels)
• Bone or joint pain
• Skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis)
• Headaches or migraines
• Mood changes (anxiety, depression)
Children with coeliac disease may also experience delayed growth, short stature, or behavioral issues.
Consult a Top Gastroenterologist
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of coeliac disease is unknown, but it involves a combination of:
• Genetics – People with certain genes (HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8) are more likely to develop it.
• Environmental triggers – Infections, gut bacteria changes, or high gluten consumption early in life may contribute.
• Autoimmune response – The immune system mistakenly attacks the intestine when gluten is present.
Risk factors include:
• Family history of coeliac disease
• Type 1 diabetes or thyroid disorders
• Down syndrome or Turner syndrome
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect coeliac disease, consult a doctor. Diagnosis involves:
1. Blood Tests – Checks for antibodies (tTG-IgA) that indicate an immune reaction to gluten.
2. Endoscopy & Biopsy – A small intestine sample is taken to confirm damage.
Important: Do not start a gluten-free diet before testing, as it can lead to false-negative results.
Get Your Health Asseseds
Management and Treatment
The only effective treatment for coeliac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. This means avoiding:
• Wheat (bread, pasta, cereals)
• Barley (beer, malt)
• Rye (rye bread, some cereals)
Safe Foods:
• Rice, quinoa, corn
• Fruits, vegetables, nuts
• Meat, fish, eggs
• Dairy (unless lactose intolerant)
Tips for a Gluten-Free Lifestyle:
• Read labels carefully – Gluten can hide in sauces, soups, and processed foods.
• Use separate kitchen tools – Avoid cross-contamination.
• Dine out cautiously – Inform restaurants about your dietary needs.
• Consider supplements – Some patients need vitamins (iron, calcium, vitamin D).
Potential Complications if Untreated
Ignoring coeliac disease can lead to:
• Malnutrition – Due to poor nutrient absorption.
• Osteoporosis – Weak bones from calcium deficiency.
• Infertility or miscarriages – Linked to untreated coeliac disease.
• Neurological issues – Nerve damage or seizures in rare cases.
• Increased cancer risk – Intestinal lymphoma in severe cases.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent digestive issues, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications.
Need Help?
If you suspect coeliac disease, book a consultation or lab test through Apollo 24|7 for expert guidance and support.
Final Thoughts
Living with coeliac disease can be challenging, but with the right diet and care, you can lead a healthy, symptom-free life. Stay informed, follow medical advice, and connect with support groups if needed.
Consult a Top Gastroenterologist
Consult a Top Gastroenterologist

Dr. Chethan T L
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD, DNB (General Medicine)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS. MD (INTERNAL MEDICINE) DrNB (GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Piyush Vishwakarma
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
11 Years • MBBS, MD, DrNB,
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Sravani Kuppam
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS DNB General Medicine, CCDM (Diabetes)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr Abhishek Tiwari
Minimal Access/Surgical Gastroenterology
15 Years • MBBS, MS, Diabetic Foot Course (Pisa, Italy)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Consult a Top Gastroenterologist

Dr. Chethan T L
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD, DNB (General Medicine)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS. MD (INTERNAL MEDICINE) DrNB (GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Piyush Vishwakarma
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
11 Years • MBBS, MD, DrNB,
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Sravani Kuppam
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS DNB General Medicine, CCDM (Diabetes)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr Abhishek Tiwari
Minimal Access/Surgical Gastroenterology
15 Years • MBBS, MS, Diabetic Foot Course (Pisa, Italy)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi