Early Signs of Cervical Cancer: What Every Woman Should Watch For
Learn the early warning signs of cervical cancer, its link to HPV, key symptoms, and why regular screening and vaccination are essential for prevention.

Written by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula
Reviewed by Dr. Mohammed Kamran MBBS, FIDM
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Introduction
Cervical cancer was once a leading cause of cancer death for women, but thanks to increased awareness and routine screening, its impact has significantly decreased. However, it remains a serious health concern. The key to successful treatment lies in early detection, and that starts with knowing what to look for. Many women are unsure about the specific signs of cervical cancer, often confusing them with more common gynaecological issues. This guide will walk you through the potential symptoms, from the subtle early warnings to the more pronounced signs of advanced stages. We’ll demystify the crucial link between cervical cancer and the human papillomavirus (HPV), explain why regular screenings are your best defence, and outline the clear steps to take if you have any concerns. Knowledge is power, and understanding these signs can empower you to take charge of your health.
Understanding Cervical Cancer and Its Link to HPV
Before diving into the symptoms, it's helpful to understand what cervical cancer is and what causes it. This knowledge provides context for why certain signs appear and underscores the importance of prevention.
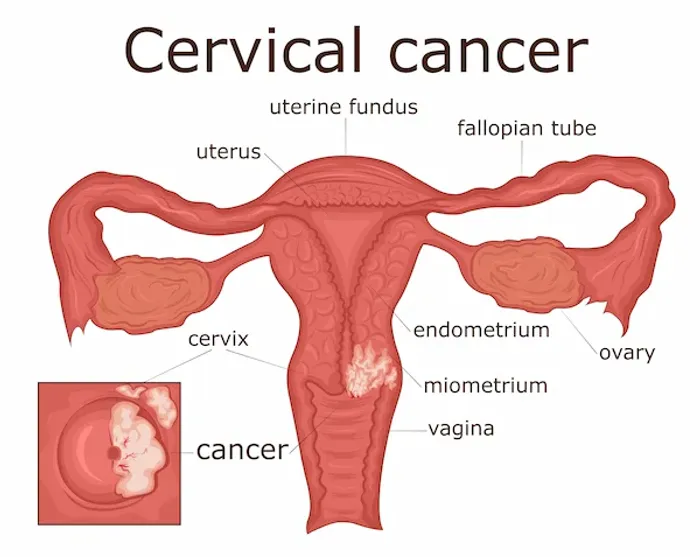
What is the Cervix and What is Cervical Cancer?
The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Cervical cancer occurs when the cells lining the cervix begin to grow out of control. These changes don't happen overnight. They usually develop slowly over many years, starting as precancerous cells (a condition called dysplasia). If these precancerous changes are not found and treated, they can evolve into cervical cancer.
The HPV-Cervical Cancer Connection: A Crucial Link
Virtually all cases of cervical cancer are caused by a persistent infection with a common virus called the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is so common that nearly all sexually active people will get it at some point in their lives, often without ever knowing. In most cases, the body's immune system clears the virus naturally. However, when certain high-risk types of HPV linger in the body for many years, they can cause changes in the cervical cells that may lead to cancer. This is why regular Pap tests and HPV tests are critical—they can detect these cell changes long before they turn into cancer.
The Critical Challenge: Early-Stage Cervical Cancer Often Has No Signs
This is the most important point to remember: precancerous changes and early-stage cervical cancer typically cause no signs or symptoms whatsoever. There is often no pain, no unusual bleeding, and no noticeable discharge. This silent nature is why relying on symptoms alone is not a safe strategy. The disease can progress significantly before any warning signs become apparent. This underscores the non-negotiable importance of routine screening, which can detect abnormalities at a stage when they are highly treatable.
Key Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer to Never Ignore
When cervical cancer does begin to cause symptoms, they are often related to the tumour growing and affecting nearby tissues. If you experience any of the following, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation. Remember, these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions like infections or fibroids, but they should never be ignored.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor's speciality: Oncology
Text: Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: The Most Common Red Flag
This is the most frequently reported symptom of cervical cancer. Any bleeding that is outside your normal menstrual pattern warrants attention.
Bleeding After Menopause
Any vaginal bleeding after you have gone through menopause is a significant red flag and should be investigated immediately by a doctor.
Bleeding After Sex (Postcoital Bleeding)
Bleeding after intercourse can occur because the cancerous tissue on the cervix is fragile and can be easily irritated or disrupted by contact.
Bleeding Between Periods or Heavier Periods
Unusually heavy menstrual bleeding or spotting that occurs at random times between your periods can also be a sign of advanced cell changes or cancer.
Unusual Vaginal Discharge: Changes in Colour, Smell, or Consistency
While vaginal discharge is normal and changes throughout your cycle, be alert to persistent changes. Discharge related to cervical cancer may be:
Watery, pink, or brown: Often described as looking like "watery coffee grounds."
Foul-smelling: A strong, unpleasant odour that doesn't go away.
Heavy and continuous: Unlike cyclical discharge, it may be constant.
Pain and Discomfort: When to Be Concerned
Pain is generally a symptom of more advanced cervical cancer, as the tumour grows larger and affects surrounding organs and nerves.
Pelvic Pain Not Related to Your Menstrual Cycle
A persistent ache or pain in the pelvis that is not associated with your period can be a warning sign.
Pain During Sex (Dyspareunia)
This can occur as the cancer progresses, causing discomfort deep within the pelvis during or after intercourse.
Symptoms of Advanced or Recurrent Cervical Cancer
If cervical cancer spreads (metastasises) to other parts of the body, it can cause additional symptoms.
Leg Pain or Swelling: If the cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the pelvis, it can block the flow of fluid, causing swelling (lymphoedema) in one or both legs.
Back Pain: This can occur if the cancer presses on nerves or spreads to the spine.
Urinary and Bowel Changes: Difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or changes in bowel habits can happen if the cancer affects the bladder or rectum.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue: These are general symptoms associated with many cancers, as the disease consumes the body's energy.
What to Do If You Experience These Symptoms
If you notice any of the signs mentioned above, the most important step is not to panic but to take action. Schedule an appointment with your gynaecologist. While these symptoms can be caused by less serious conditions, only a medical professional can determine the cause. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation and to discuss whether you need an in-person examination. They will likely perform a pelvic exam and may recommend a Pap test or other diagnostics.
The Best Defence: Regular Screening and HPV Vaccination
Prevention and early detection are far more effective than treating advanced cancer. The two most powerful tools we have are screening and vaccination.
The Pap Test (Smear) and HPV Test
A Pap test (or smear) collects cells from your cervix to check for precancerous changes. An HPV test checks for the presence of high-risk HPV strains. Guidelines vary, but generally, women should start screening at age 21. Talk to your doctor about the right screening schedule for you. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for tests like vitamin D or HbA1c, and while Pap tests require a clinical visit, you can easily book a consultation to discuss your screening needs.
The Importance of the HPV Vaccine
The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against the types of HPV that cause most cervical cancers. It is recommended for both boys and girls, typically between the ages of 9 and 12, but can be given up to age 45. The vaccine is a primary prevention tool that can drastically reduce your risk.
Conclusion
Understanding the potential signs of cervical cancer empowers you to be an active participant in your health journey. While the absence of early symptoms highlights the critical role of routine screenings, knowing the warning signs—like abnormal bleeding, unusual discharge, and persistent pain—allows you to seek timely medical advice. Remember, these signs do not automatically mean you have cancer, but investigating them is a crucial step. The landscape of cervical cancer has been transformed by preventive measures like the HPV vaccine and highly effective screening methods like the Pap test. By staying informed, attending your recommended check-ups, and consulting your doctor about any concerns, you are taking the most powerful steps to protect your well-being. Your health is your priority; if you have any doubts, don't hesitate to book a physical visit to a doctor with Apollo24|7 for a comprehensive evaluation.
FAQs About Cervical Cancer Signs
Can you have cervical cancer with no symptoms at all?
Yes, absolutely. Precancerous changes and early-stage cervical cancer often cause no noticeable symptoms. This is why regular screening is so vital, as it can detect abnormalities before symptoms even begin.
What does cervical cancer discharge look like?
It can vary, but it is often described as watery, pink, or brownish (like "watery coffee grounds") and may have a foul, persistent odour. It's typically different from your normal discharge in consistency, colour, and smell.
Is bleeding after sex always a sign of cervical cancer?
No, bleeding after sex can have other causes, such as cervical polyps, infections, or vaginal dryness. However, it is a common symptom of cervical cancer and should never be ignored. Always see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
At what age do cervical cancer symptoms typically appear?
Cervical cancer is most frequently diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 44. However, it can occur at any age, which is why following age-specific screening guidelines is important.
How quickly do symptoms of cervical cancer develop?
Cervical cancer develops very slowly, often over many years. The cell changes start as precancerous, and if untreated, may progress to cancer. Symptoms usually only appear once the cancer has become more advanced.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor's speciality: Oncology
Text: Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Consult Top oncologist

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Mukti Mukherjee
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
12 Years • MBBS (Hons.), MD (Radiation Oncology), PDCR, CCEPC (Palliative Care) Consultant Oncologist
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata

Dr. Ajay Kumar Shukla
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
9 Years • MD (Radiation Oncology), CCEPC
Lucknow
Apollomedics Super Speciality Hospital, Lucknow

Dr Ashu Abhishek
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD(Radiotherapy)
Chennai
Apollo Proton Cancer Center, Chennai
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr Mukti Mukherjee
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
12 Years • MBBS (Hons.), MD (Radiation Oncology), PDCR, CCEPC (Palliative Care) Consultant Oncologist
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata

Dr. Ajay Kumar Shukla
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
9 Years • MD (Radiation Oncology), CCEPC
Lucknow
Apollomedics Super Speciality Hospital, Lucknow

Dr Ashu Abhishek
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD(Radiotherapy)
Chennai
Apollo Proton Cancer Center, Chennai