Understanding How Dengue Spreads
Explore how dengue spreads through mosquito bites, its transmission cycle, and key factors that increase risk. Learn how to break the chain of infection and stay protected.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 23rd Jul, 2025

Introduction
Dengue is a viral illness that affects millions of people worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with dengue or is concerned about the disease, understanding how it spreads can help you take the right precautions. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about dengue transmission, symptoms, prevention, and when to seek medical help.
What Is Dengue?
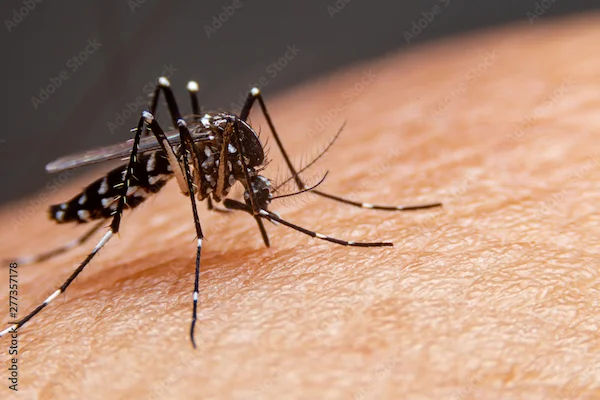
Dengue is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, primarily Aedes aegypti. These mosquitoes are most active during the day, especially in the early morning and late afternoon. Dengue can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, it can lead to life-threatening complications like dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS).
How Does Dengue Spread?
Dengue spreads mainly through mosquito bites, but it can also be transmitted through human-to-mosquito contact and, in rare cases, from mother to child or through blood transfusions:
1. Mosquito Bites – The Primary Cause
The main way dengue spreads is through the bite of an infected female Aedes mosquito. Here’s how the cycle works:
Step 1: A mosquito bites a person who already has dengue.
Step 2: The virus enters the mosquito’s body and multiplies.
Step 3: The infected mosquito then bites another person, passing the virus into their bloodstream.
Unlike malaria-carrying mosquitoes, Aedes mosquitoes breed in clean, stagnant water - commonly found in containers, flower pots, discarded tires, and water storage tanks.
2. Human-to-Mosquito Transmission
A person infected with dengue can transmit the virus to mosquitoes if they are bitten during the first week of infection (when the virus is active in their blood). This is why isolating patients and preventing mosquito bites is crucial to stopping further spread.
3. Rare Cases: Mother-to-Child & Blood Transmission
In very rare cases, dengue can spread:
From a pregnant mother to her baby.
Through blood transfusions or organ transplants from an infected donor.
However, these modes of transmission are uncommon compared to mosquito bites.
Symptoms of Dengue
Symptoms usually appear 4–10 days after being bitten and may include:
High fever (104°F or higher)
Severe headache
Pain behind the eyes
Muscle and joint pain (often called "breakbone fever")
Nausea and vomiting
Skin rash
Mild bleeding (nose or gum bleeding)
In severe cases, symptoms may worsen, leading to:
Persistent vomiting
Severe abdominal pain
Rapid breathing
Bleeding gums or nosebleeds
Fatigue and restlessness
If you or a loved one experience these severe symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
How to Prevent Dengue?
Since there is no specific cure for dengue, prevention is the best approach. Here’s how you can protect yourself and your family:
1. Eliminate Mosquito Breeding Sites
Remove stagnant water from containers, flower pots, and coolers.
Cover water storage tanks properly.
Clean gutters regularly to prevent water accumulation.
Consult Top Specialists
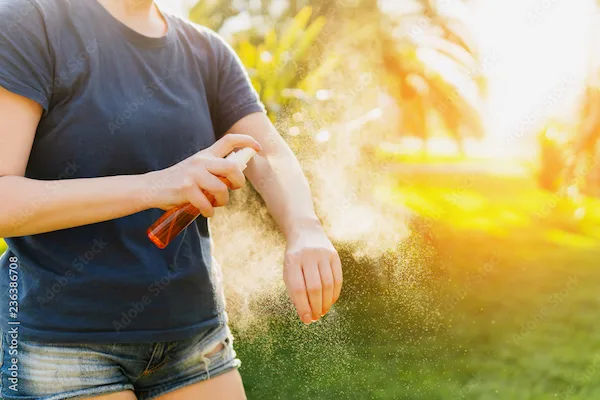
2. Protect Yourself from Mosquito Bites
Use mosquito repellents (containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus).
Wear long-sleeved clothing to reduce exposed skin.
Use mosquito nets while sleeping, especially for infants and elderly individuals.
Install window and door screens to keep mosquitoes out.
3. Community Efforts
Spread awareness about dengue prevention in your neighbourhood.
Support local fogging and sanitation drives to reduce mosquito populations.
What to Do If You Have Dengue?
If you suspect dengue:
1. Consult a doctor: Early diagnosis helps in better management.
2. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids (water, coconut water, oral rehydration solutions).
3. Rest: Avoid strenuous activities.
4. Monitor symptoms: Watch for warning signs like severe pain, bleeding, or persistent vomiting.
Avoid self-medication, especially aspirin or ibuprofen, as they can increase bleeding risk.
When to Seek Emergency Care?
Go to the hospital immediately if you notice:
Difficulty breathing
Blood in vomit or stool
Severe dehydration (dry mouth, dizziness, low urine output)
Extreme fatigue or confusion
Can Dengue Be Treated?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue. Doctors focus on:
Managing fever and pain with paracetamol (acetaminophen).
Ensuring proper hydration.
Monitoring blood platelet levels in severe cases.
Most people recover within 1–2 weeks, but severe cases may require hospitalisation.
Conclusion
Dengue is a serious but preventable disease. By understanding how it spreads and taking simple precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk. If you live in or are travelling to a dengue-prone area, stay vigilant and protect yourself from mosquito bites.
If you or a family member experience dengue-like symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. Early detection and care can prevent complications. For expert medical advice or to book a dengue test, you can schedule a consultation through Apollo 24|7—your trusted partner in health.
Consult Top Specialists
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Syed Ismail Ali
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr D M Karthik
General Practitioner
4 Years • MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus, Advance certificate in Diabetes Mellitus, Derma Nutrition Certification
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam

Dr. M L Ezhilarasan
General Practitioner
6 Years • MBBS
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Mohammed Kamran
General Practitioner
5 Years • MBBS, FIDM
Nashik
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Maharashtra, Nashik

Dr. D Bhanu Prakash
General Practitioner
10 Years • MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad