Understanding Adenoidectomy
Learn about adenoidectomy, including its purpose, procedure, recovery, and potential benefits, to understand this common surgical procedure.

Written by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
Reviewed by Dr. J T Hema Pratima MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Is your child a mouth breather, a constant snorer, or seemingly always battling an ear infection? Have you been told that an adenoidectomy might be the solution? If so, you're likely filled with questions and concerns. This guide is designed to walk you through every aspect of an adenoidectomy, from understanding what adenoids are to navigating a smooth recovery. An adenoidectomy is a common surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, small pads of tissue located at the back of the nasal passage. While often performed on children, adults can benefit from it too. We'll demystify the reasons for this surgery, what the procedure entails, and how to ensure the best possible outcome for you or your child. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, so you can approach this process with confidence and clarity.
What Are Adenoids and What Is an Adenoidectomy?
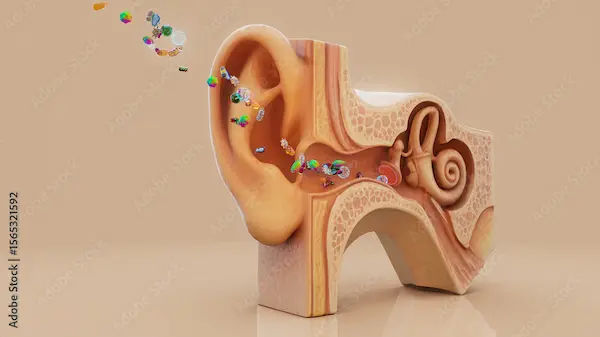
Adenoids are a patch of tissue that sit high in the throat, behind the nose and the roof of the mouth. Unlike tonsils, they are not visible through the mouth without special instruments. They are part of the body's immune system, acting as a first line of defense against inhaled pathogens by trapping germs and producing antibodies.
The Role of Adenoids in the Immune System
In early childhood, adenoids play a significant role in developing immunity. They sample bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose and help the body build defenses. However, this function is most critical in the first few years of life. As a child grows, other parts of the immune system take over, and the adenoids naturally begin to shrink, usually disappearing almost entirely by the teenage years.
When Do Adenoids Become a Problem?
Adenoids become a problem when they are chronically infected or become excessively enlarged. Frequent battles with germs can cause them to swell and remain inflamed, a condition known as adenoiditis. Even after the infection is gone, the tissue might not return to its normal size. This persistent enlargement can block airflow through the nose and trap bacteria, creating a cycle of infection and obstruction that often necessitates an adenoidectomy for chronic issues.
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice
Key Reasons for Needing an Adenoidectomy
The decision to proceed with an adenoidectomy is not taken lightly. ENT specialists typically recommend it when the benefits of removal significantly outweigh the benefits of keeping the tissue, especially when non-surgical treatments have failed.
Chronic Adenoiditis and Recurrent Infections
This is one of the most common reasons. Symptoms include a constantly stuffy nose, thick nasal drainage, sore throat, and swollen neck glands. If a child experiences four or more significant sinus or throat infections in a year, an adenoidectomy may be considered to break the cycle and improve their quality of life.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) in Children
Enlarged adenoids can physically obstruct the airway during sleep. This leads to snoring, restless sleep, and, crucially, pauses in breathing (apnea). This disrupted sleep can cause daytime sleepiness, behavioral issues, and problems with growth and academic performance. An adenoidectomy for sleep apnea is often highly effective in resolving these breathing obstructions.
Persistent Ear Infections and Fluid Buildup
The adenoids are located right near the opening of the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the throat. When enlarged, they can block these tubes, preventing fluid from draining from the ear. This trapped fluid (otitis media with effusion) can lead to recurrent painful ear infections, hearing loss, and potential speech delays. Removing the adenoids can help restore proper Eustachian tube function.
The Adenoidectomy Procedure: What to Expect
Understanding the process can greatly reduce anxiety for both patients and parents.
Pre-Operative Consultation and Preparation
Your ENT doctor will conduct a thorough examination, which may include a nasal endoscopy (a tiny camera inserted through the nose to view the adenoids) and possibly a sleep study or hearing test. You'll receive detailed instructions on fasting before surgery due to the use of general anaesthesia.
Step-by-Step: The Day of Surgery
The procedure itself is relatively short, typically taking about 30 to 45 minutes. The patient is under general anaesthesia, meaning they are completely asleep and feel no pain. The surgeon removes the adenoid tissue through the open mouth using a few different techniques: a special curette (a spoon-shaped instrument), electrocautery (which uses heat to remove tissue and control bleeding), or microdebrider (a powered instrument that shaves the tissue). No external incisions are made.
Adenoidectomy vs. Tonsillectomy: What's the Difference?
While often discussed together, they are distinct procedures. A tonsillectomy removes the tonsils (visible at the back of the throat), and an adenoidectomy removes the adenoids (hidden behind the nose). They are frequently performed together, a procedure called an adenotonsillectomy (T&A), especially for sleep apnea or chronic throat infections. However, if the primary issue is related to nasal obstruction or ear fluid, an adenoidectomy alone may be sufficient.
Navigating Adenoidectomy Recovery: A Timeline
Recovery is a process, and knowing what to expect is key to managing it successfully.
The First 24-48 Hours: Immediate Post-Op Care
The patient will wake up in a recovery room. A sore throat and mild ear pain (referred pain from the surgery site) are common. The primary goals are pain management with prescribed or OTC medications and hydration. Clear, cool liquids like water, apple juice, and ice pops are best. It's normal to see a small amount of blood-tinged saliva.
The First Week: Managing Pain and Diet
Pain often peaks around days 5-7 as the scab at the surgery site naturally sloughs off. Staying on top of pain medication is crucial. The diet should progress to soft, bland foods: mashed potatoes, yoghurt, pudding, scrambled eggs, and well-cooked pasta. Avoiding crunchy, acidic, or spicy foods is essential to prevent irritation and bleeding.
Weeks 2-4: Returning to Normal Activities
Most children can return to school after about one week, though they may still tire easily. Strenuous activity and sports should be avoided for at least two weeks to minimise the risk of bleeding. Full healing of the throat tissue typically takes three to four weeks. If recovery from adenoidectomy is unusually painful, if there is a fever, or if there is any sign of bright red bleeding, it is critical to contact your doctor immediately or seek emergency care.
Potential Risks and Complications of Adenoid Removal
Like any surgery, an adenoidectomy carries some risks, though serious complications are rare.
Common Temporary Side Effects
These include bad breath, throat pain, ear pain, a stuffy nose, and a temporary change in voice (it may sound more nasal). These symptoms almost always resolve as healing progresses.
Rare but Serious Complications
The main serious risk is bleeding, which can occur up to two weeks post-surgery. Infection is another potential risk. In very rare cases, removal can affect the soft palate, leading to velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI), where fluid and air escape into the nose during speech, causing a nasal-sounding voice. This often resolves on its own but may rarely require therapy or further intervention.
Life After an Adenoidectomy: Long-Term Outcomes
The long-term benefits of the procedure are overwhelmingly positive for appropriately selected patients.
Impact on the Immune System
A common concern is whether removal weakens the immune system. Extensive research has shown that the body has plenty of other lymphoid tissue to handle immune responses. Removing diseased adenoids does not lead to an increase in future infections; in fact, it often reduces the frequency of ear, nose, and throat illnesses.
Improvements in Breathing, Sleep, and Health
The most dramatic improvements are often seen in sleep quality and breathing. Children (and adults) who underwent the procedure for sleep apnea typically stop snoring and experience restful, uninterrupted sleep, leading to better focus and behavior. Nasal breathing improves, chronic runny noses often clear up, and recurrent ear infections are significantly reduced.
Conclusion
Deciding to proceed with an adenoidectomy is a significant step, but for those struggling with the chronic issues caused by enlarged adenoids, it can be a life-changing intervention. This guide has outlined the journey from understanding the problem through to a full recovery. The procedure is a well-established, low-risk surgery that effectively resolves obstructive breathing, chronic infections, and ear problems, ultimately leading to better sleep, health, and overall well-being. If you or your child are experiencing persistent symptoms like mouth breathing, loud snoring, or recurrent earaches, it is essential to seek a professional evaluation.
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Nishant Rana
Ent Specialist
8 Years • MBBS. MS ENT
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. D. Naveen Kumar
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MS
Chinagadila
Apollo Hospitals Health City Unit, Chinagadila
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Praveen Sirdesai
Ent Specialist
20 Years • MS
Secunderabad
Apollo Hospitals Secunderabad, Secunderabad

Dr. Tanvi Choubey
Ent Specialist
7 Years • MBBS, MS (ENT). Fellowship in Head Neck Onco Surgery . Consultant - ENT
Rourkela
Apollo Hospitals, Rourkela, Rourkela

Dr. Safina Kauser
Ent Specialist
7 Years • MBBS, MS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Nishant Rana
Ent Specialist
8 Years • MBBS. MS ENT
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. D. Naveen Kumar
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MS
Chinagadila
Apollo Hospitals Health City Unit, Chinagadila
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Praveen Sirdesai
Ent Specialist
20 Years • MS
Secunderabad
Apollo Hospitals Secunderabad, Secunderabad

Dr. Tanvi Choubey
Ent Specialist
7 Years • MBBS, MS (ENT). Fellowship in Head Neck Onco Surgery . Consultant - ENT
Rourkela
Apollo Hospitals, Rourkela, Rourkela

Dr. Safina Kauser
Ent Specialist
7 Years • MBBS, MS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
More articles from Ear infections and earache
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical age for an adenoidectomy?
Adenoidectomies are most commonly performed on children between the ages of 1 and 7, as this is when adenoids are most active. However, older children and adults can also require the procedure if their adenoids did not shrink naturally and are causing problems.
Will my child's voice change after an adenoidectomy?
There might be a temporary, slight change in voice resonance, often making it sound a bit less 'nasal' or 'stopped up.' This is usually a positive change. Any significant or hypernasal voice change should be evaluated by a doctor, as it could indicate a rare complication.
How long does the adenoidectomy surgery take?
The actual procedure is typically very quick, usually taking between 30 and 45 minutes. However, expect to spend several hours at the hospital or surgical center for pre-operative preparation and post-operative recovery.
Is the recovery from an adenoidectomy painful?
There will be a sore throat for 7-10 days, and pain can peak around a week post-op when the scabs fall off. Pain is generally manageable with prescribed medication, acetaminophen, and a soft-food diet. Ear pain is also common but is referred to as pain from the throat.
Can adenoids grow back after being removed?
It is possible, though uncommon, for adenoid tissue to regrow, especially if very small fragments are left behind during surgery. This is more likely if the procedure is done at a very young age (e.g., under 2). Regrowth doesn't always cause problems again, but it might in some cases.