How To Reduce Fatty Liver?
Understand more about fatty liver and its types. Discover what causes it and how to reduce it with dietary changes, lifestyle modifications and medical treatments to improve liver health. Learn about fatty liver diagnosis and treatment options.

Written by Dr.Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

The liver is the body’s main organ that processes food and waste materials. Fatty liver, also known as steatosis or steatotic liver disease (SLD), occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. It is a common condition that usually doesn’t cause symptoms or serious problems. However, it can sometimes lead to serious health issues like liver inflammation, liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
As mentioned before, fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver. This condition can range from mild to severe, but if left untreated, it may lead to serious health issues and complications. A healthy liver should contain little to no fat. However, excess fat build-up can affect liver function and overall health. Hence, early detection and management are key to preventing future damage. It is common, particularly in people with diabetes or who are overweight. If individuals drink too much alcohol or eat too much food, the body deals with the excess by turning some of the calories into fat. This fat then gets stored in the liver cells. When fat makes up more than 5%-10% of the liver’s total weight, one may get fatty liver. However, for most people, lever damage can be reversed. One can improve or prevent the condition with a healthy diet and lifestyle and reducing alcohol intake.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two types of fatty liver diseases such as:
1. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD occurs in individuals who consume little to no alcohol but have excess fat in their liver. It is commonly linked to obesity, poor diet and insulin resistance.
Causes of NAFLD may include:
Obesity or overweight
Type 2 diabetes
Metabolic syndrome
2. Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
AFLD develops due to excessive alcohol consumption. It can lead to fat build-up and inflammation in the liver. It is the first stage of alcohol-related liver disease.
Causes of AFLD may include:
Obesity or overweight
High levels of cholesterol
Diabetes
Triglycerides in the blood
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver is usually due to a combination of factors over a long period of time.
1. Most common Causes
The most common causes of fatty liver include the following:
Obesity or being overweight, especially around the abdomen.
Having high blood cholesterol or high triglycerides.
Drinking too much alcohol.
Having type 2 diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance.
2. Less Common Causes
The less common causes of fatty liver include the following:
Certain medicines like corticosteroids (like glucocorticoids), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen, high-dose vitamin A, and some antipsychotic and antidepressant medications.
Having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
An underactive thyroid.
3. Diet Options Causing Fatty Liver
Dietary contributors of fatty liver include:
Saturated and trans fats that can contribute to liver fat deposits.
Fructose and refined sugars that can promote fat storage in the liver.
Highly processed foods containing additives and unhealthy fats that can strain liver function.
4. Lifestyle and Other Risk Factors
Lifestyle and other risk factors can contribute to fatty liver.
Poor insulin function can lead to increased fat storage in the liver.
Lack of physical activity or exercise can lead to weight gain and fat accumulation.
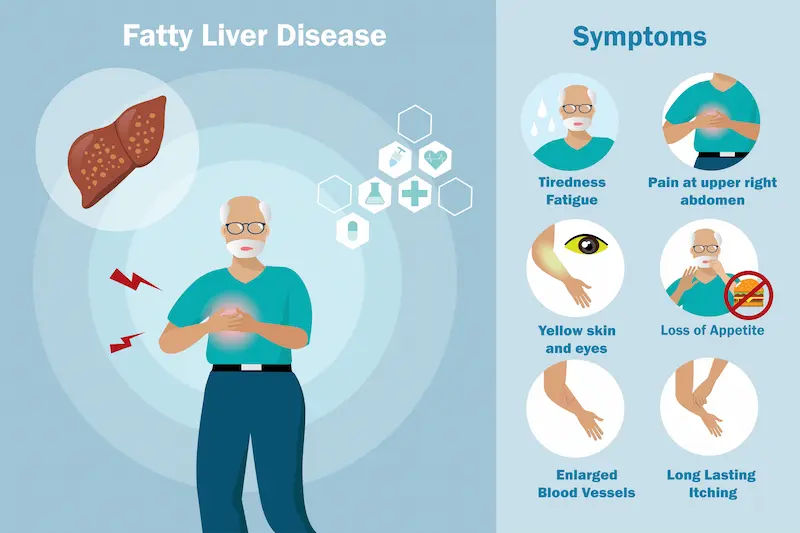
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease can present a few symptoms in its early stages. However, some individuals may experience:
Mild abdominal discomfort or pain in the upper right side.
Unexplained weight loss.
Jaundice, which is the yellowing of the eyes and skin in severe cases.
Fatigue and weakness.
Potential signs that individuals may have more serious fatty liver disease:
Bruising
Swollen tummy
Black stools
Dark urine
Vomiting blood
Itchy skin
Consult Top Doctor For Fatty Liver
Potential Health Risks of Fatty Liver Disease
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can pose severe health conditions, including:
Cirrhosis: This includes severe scarring of liver tissue, which can cause liver failure.
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): This is a liver inflammation that may lead to scarring.
Liver Cancer: In severe cases, it can lead to an increased risk of liver cancer.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
To diagnose fatty liver disease, healthcare providers can use a combination of:
Physical Examination: Through physical tests, doctors identify risk factors such as obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Blood Tests: These help in checking liver enzyme levels to detect inflammation.
Additional diagnostic tools include the following:
MRI or CT Scan: This provides a detailed image of the liver.
Ultrasound: This is a non-invasive test to detect liver fat.
Liver Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken for analysis if further assessment is needed.
Medical Treatment Options to Reduce Fatty Liver
In severe cases, medical interventions may be necessary to manage fatty liver disease. Medications and supplements that can be recommended include:
Prescription Medications: These may be prescribed in cases where lifestyle changes haven’t yielded results.
Vitamin E Supplements: These can improve liver function in some individuals.
Besides this, ongoing research explores potential treatments, which may include:
Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Liver-Targeting Medications
Dietary Recommendations to Reduce Fatty Liver
Below are the food options that individuals can include and avoid to reduce fatty liver and promote liver health.
Food options to include in a diet:
Leafy greens like spinach and kale can detoxify the liver.
Nuts and seeds contain healthy fats that can be beneficial for liver function.
Fatty fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help in reducing liver inflammation.
Green tea is rich in antioxidants that improve liver health.
Food options to avoid in a diet:
Sugary beverages and desserts.
Excessive alcohol consumption.
High-fat dairy products.
Processed and fried foods.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Fatty Liver
There are a few lifestyle changes that may be recommended to help reduce fatty liver.
1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial in reducing liver fat. Key recommendations include:
Choose whole grains over refined carbs.
Include lean proteins like legumes and fish.
Increase intake of fruits and vegetables.
2. Physical Activity
Exercise or any physical activity plays an important role in maintaining liver health. The benefits include:
Increased physical activity supports metabolic health.
It improves insulin sensitivity, which helps in regulating blood sugar levels and prevents fat accumulation.
Cardio and strength training can help in reducing overall body fat.
Weight Management to Reduce Fatty Liver
Weight management, particularly weight loss, is considered one of the most effective ways to reduce fatty liver. It can help reduce liver fat and improve liver health. Studies show that even modest weight loss can significantly benefit liver function; a reduction of 5%-10% of body weight is often recommended for optimal results.
Conclusion
Reducing fatty liver requires a holistic approach that focuses on diet, physical activity and healthy lifestyle choices. Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar and alcohol while incorporating nutrient-rich meals can support liver health. For those with underlying health conditions, medical treatments and guidance may be essential. By adopting sustainable habits, individuals can effectively manage and even reverse fatty liver, promoting long-term health and vitality. Early detection and intervention also help in preventing severe complications. Committing to a healthier lifestyle is essential, as it can help improve liver function and overall well-being. Small and mindful changes today can lead to long-term benefits and a healthier future.
Consult Top Hepatologist
Consult Top Doctor For Fatty Liver

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Pukhraj Singh Jeji
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD ( Internal Medicine ), DM ( Gastroenterology ), Consultant - Gastroenterology
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)
Consult Top Hepatologist

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Pukhraj Singh Jeji
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD ( Internal Medicine ), DM ( Gastroenterology ), Consultant - Gastroenterology
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)
 (1).webp)
_0.webp)
