Brain Haemorrhage Overview and Management
Know about the brain haemorrhage, common symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention tips.

Brain Haemorrhage Overview and Management
Introduction
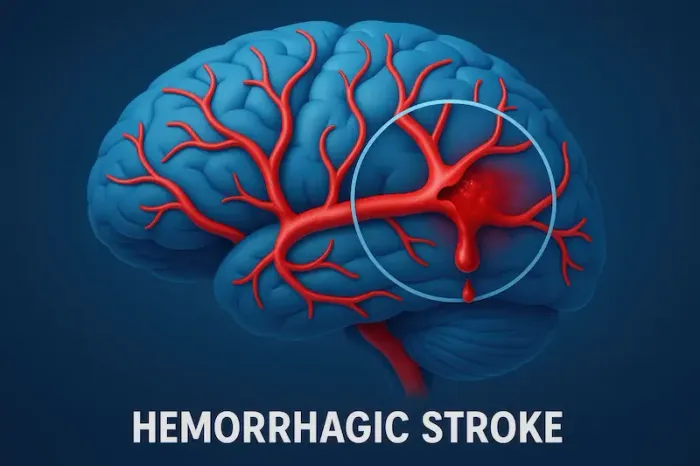
A brain haemorrhage is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding inside or around the brain. This can put pressure on brain tissues, damaging them and affecting vital functions.
Understanding brain haemorrhage—its causes, symptoms, and management—can help you recognise warning signs early and take prompt action.
What is a Brain Haemorrhage?
A brain haemorrhage, also called an intracranial haemorrhage, happens when bleeding occurs within the skull. Depending on the location, it can be classified into different types:
1. Intracerebral Haemorrhage – Bleeding inside the brain tissue.
2. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage – Bleeding in the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it.
3. Subdural Haemorrhage – Bleeding between the brain and its outer covering, often due to head injury.
4. Epidural Haemorrhage – Bleeding between the skull and the brain’s protective layer, usually caused by trauma.
Consult a Neurologist for Personalised Advice
Common Symptoms of Brain Haemorrhage
Recognising the symptoms early can save lives. Seek emergency medical help if you or someone experiences:
• Sudden, severe headache (often described as the "worst headache of life")
• Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg (usually on one side)
• Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
• Vision problems (blurred or double vision)
• Loss of balance or coordination
• Nausea or vomiting
• Seizures
• Loss of consciousness
What Causes a Brain Haemorrhage?
Several factors can lead to a brain haemorrhage, including:
1. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) – The most common cause, that it weakens blood vessel walls over time.
2. Head Trauma – Accidents or falls can rupture blood vessels.
3. Aneurysm – A weak spot in a blood vessel that bulges and bursts.
4. Blood Vessel Abnormalities (AVMs) – Irregular connections between arteries and veins.
5. Blood Disorders – Conditions like haemophilia or sickle cell anaemia increase bleeding risk.
6. Liver Disease – Can lead to clotting problems.
7. Excessive Alcohol or Drug Use – Especially stimulants like cocaine.
How is a Brain Haemorrhage Diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging tests to confirm a brain haemorrhage:
• CT Scan – The fastest way to detect bleeding.
• MRI – Provides detailed images of the brain.
• Angiography – Helps identify abnormalities in blood vessels.
Treatment and Management
Immediate medical care is crucial. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the bleed:
Medical Treatments
• Medications – To reduce swelling, control blood pressure, or prevent seizures.
• Surgery – May be needed to remove blood clots, repair blood vessels, or relieve pressure on the brain.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery varies depending on the extent of brain damage. Rehabilitation may include:
• Physical Therapy – To regain movement and strength.
• Speech Therapy – If communication is affected.
• Occupational Therapy – Helps with daily activities.
Prevention Tips
While not all brain haemorrhages can be prevented, you can reduce the risk by:
• Controlling Blood Pressure – Monitor and manage hypertension with medication and lifestyle changes.
• Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol – Both increase bleeding risks.
• Wearing Helmets and Seatbelts – Protects against head injuries.
• Eating a Healthy Diet – Low in salt and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
• Regular Exercise – Helps maintain cardiovascular health.
When to Seek Help?
If you or a loved one experiences sudden, severe symptoms like an intense headache, weakness, or confusion, call emergency services immediately. Early intervention can prevent severe complications.
Final Thoughts
A brain haemorrhage is a medical emergency, but awareness and timely action can improve outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Consult a Neurologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Neurologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Avinash Gupta
Neurologist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB - Neurology
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Amit Kapoor
Neurosurgeon
18 Years • D.N.B NeuroSurg.
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sarthak Mehta
Neurologist
6 Years • MBBS , MS Mch ( Neuro )
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Jaidev S
Neurosurgeon
10 Years • MBBS, MS ( Genera Surgery), MCH Neurolosurgery
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Indiranagar, Bengaluru
Consult a Neurologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Avinash Gupta
Neurologist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB - Neurology
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Amit Kapoor
Neurosurgeon
18 Years • D.N.B NeuroSurg.
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sarthak Mehta
Neurologist
6 Years • MBBS , MS Mch ( Neuro )
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Jaidev S
Neurosurgeon
10 Years • MBBS, MS ( Genera Surgery), MCH Neurolosurgery
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Indiranagar, Bengaluru




