Guide to Three Cs And Three Ps First Aid
A comprehensive guide to the Three Cs and Three Ps of first aid. Learn how to Check, Call, Care, and Prevent, Preserve, Protect in emergency situations to provide effective assistance.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Vasanthasree Nair MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
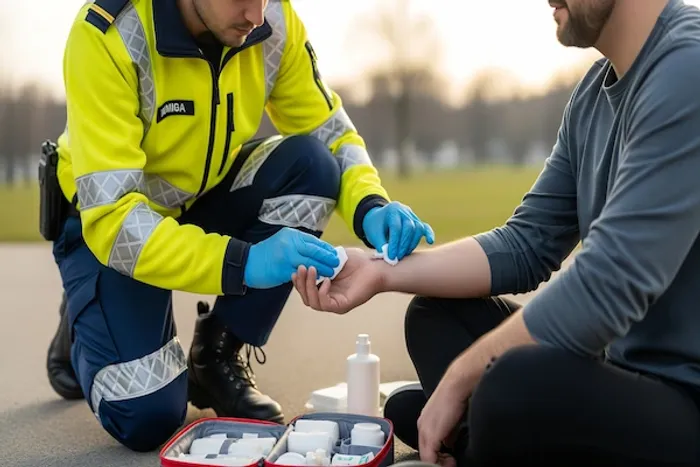

Introduction
In a critical moment, panic can be our biggest enemy. Whether it's a minor cut at home or a more serious accident in public, knowing how to react effectively can make the difference between a quick recovery and a worsened outcome. First aid isn't just for medical professionals; it's a fundamental life skill for everyone. This guide demystifies the core principles of emergency response by breaking down two essential frameworks: the Three Cs of First Aid (Check, Call, Care) and the Three Ps of First Aid (Preserve Life, Prevent Deterioration, Promote Recovery). By understanding these simple yet powerful acronyms, you’ll gain the confidence to assess a situation, prioritize your actions, and provide crucial aid until professional help arrives.
Consult Top Specialists for Personalised Tips
Understanding the Three Cs of First Aid
The Three Cs—Check, Call, Care—provide a clear, sequential action plan. They are your mental checklist to ensure you don't miss a critical step in the heat of the moment. Following this order is vital for your safety and the effectiveness of your help.
1. Check: Assess the Scene and the Person
Before you rush in, you must ensure the environment is safe. Your safety is paramount; you can't help anyone if you become a victim yourself.
Scan the Area: Look for ongoing dangers like traffic, fire, smoke, electrical wires, unstable structures, or violent individuals.
Form an Initial Impression: Quickly assess the number of people involved and the mechanism of injury (e.g., fall, car crash).
Check for Responsiveness: If the scene is safe, approach the person. Gently tap their shoulder and shout, "Are you okay?" Look for any movement or verbal response.
Check for Breathing: If they are unresponsive, look for chest movement, listen for breath sounds, and feel for air on your cheek. This assessment should take no more than 10 seconds.
This step is the foundation of all first aid emergency response and prevents further harm.
2. Call: Summon Professional Help
Once you have assessed the situation, you need to activate the professional emergency medical system.
Dial the Emergency Number: In India, call 108 or 112. If you have specific emergency contacts saved, use them. Clearly state your location, the nature of the emergency, the number of people injured, and the first aid being provided.
Don't Hang Up First: Let the dispatcher tell you when to hang up. They are trained to guide you through life-saving procedures like CPR over the phone.
Delegate if Possible: If others are present, point to a specific person and say, "You, call 108 right now and tell me what they say." This eliminates confusion and ensures the call is made.
3. Care: Provide Necessary Assistance
After ensuring help is on the way, you can focus on providing care based on your level of training.
Follow Priorities: Attend life-threatening conditions first: severe bleeding, stopped breathing, choking.
Use PPE: If available, use gloves or a CPR face shield to protect yourself and the victim from infection.
Comfort and Reassure: Stay with the person, talk to them calmly, and keep them warm and still. Your presence can significantly reduce their anxiety and shock.
For minor wound care at home, this step might involve cleaning a cut and applying a bandage. For major issues, it means maintaining an airway or controlling bleeding until paramedics arrive.
The Three Ps: The Goals of First Aid
While the Three Cs are your actions, the Three Ps define your objectives. They are the "why" behind what you do. Every action you take should align with one of these three goals.
1. Preserve Life
This is the absolute highest priority. Your immediate goal is to prevent death.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): This is the most direct example of preserving life for someone in cardiac arrest.
Clearing an Airway: Performing abdominal thrusts (the Heimlich maneuver) on a choking person preserves life by preventing suffocation.
Controlling Severe Bleeding: Applying direct pressure to a major wound stops blood loss, which is critical for survival.
These interventions are time-sensitive and form the core of basic life support techniques.
2. Prevent Deterioration
This goal is about stopping the person's condition from getting worse. It often involves stabilizing the victim until advanced medical care is available.
Immobilizing Injuries: Telling someone not to move or supporting a suspected broken limb prevents further damage to nerves, blood vessels, and tissues.
Treating for Shock: Laying the person down, elevating their legs (if no spinal injury is suspected), and keeping them warm can prevent shock from progressing.
Cooling Burns: Running cool (not cold) water over a burn for several minutes prevents the burn from deepening and reduces pain.
3. Promote Recovery
This final goal focuses on comfort and the beginning of the healing process. It's about providing compassionate care.
Applying a Bandage: A simple bandage on a scrape protects it from infection and promotes natural healing.
Offering Comfort: Using a calm voice, providing reassurance, and offering a blanket can have a profound psychological effect, which aids physical recovery.
Aftercare Advice: Guiding someone to clean a wound daily or to see a doctor for a tetanus shot promotes full recovery.
How the 3 Cs and 3 Ps Work Together in a Real Scenario
Imagine someone has fallen off a bicycle and is lying on a trail.
1. CHECK: You ensure no cars are coming. You approach and find the person conscious but in pain, holding their arm, with a bleeding cut on their knee.
2. CALL: You ask a bystander to call for help if the injury seems severe (e.g., the arm is clearly deformed). For a minor incident, you may move straight to care.
3. CARE / PRESERVE LIFE: You see the knee is bleeding but not severely. You apply direct pressure with a clean cloth.
4. CARE / PREVENT DETERIORATION: You tell the person not to try and move their injured arm. You support it gently.
5. CARE / PROMOTE RECOVERY: You clean the cut on the knee with water, apply an antiseptic wipe, and bandage it. You stay with them and talk calmly until help arrives or they feel well enough to move.
This integrated approach ensures a structured and effective response, covering both immediate actions and overarching goals.
Quick Takeaways: Your First Aid Priorities
Your safety comes first. Never rush into a dangerous situation.
Remember the mantra: Check, Call, Care. This sequence keeps you organized.
Always summon professional help for serious injuries, even if you think you have it under control.
Focus on the Three Ps: Your job is to preserve life first, prevent the condition from worsening second, and promote recovery third.
Your calm presence is a form of aid. Reassurance can prevent shock.
Only provide care within your knowledge. Don't attempt advanced procedures you're not trained for.
Prepare in advance. Take a certified first aid and CPR course to build confidence.
Conclusion
Mastering the frameworks of the Three Cs and Three Ps doesn't require a medical degree. It requires presence of mind and a willingness to help. These principles empower you to transform from a panicked bystander into a calm, effective first responder. You learn to assess logically, act decisively, and provide compassionate care. Remember, the goal of first aid is not to diagnose or cure but to bridge the critical gap between an emergency and the arrival of professional medical help. By internalizing these steps, you contribute to a safer community for everyone. We encourage you to share this guide with your friends and family. Consider taking a certified first aid course to practice these skills hands-on—it could be the most valuable investment you ever make.
Consult Top Specialists for Personalised Tips

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Harshendra Jaiswal
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS , MD (General medicine)
Kolkata
108 DHANA DHANVANTARI Clinic, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)

Dr Syed Mateen Pasha
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Aakash Andgi
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
More articles from General Medical Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important thing to remember in first aid?
The absolute most important thing is to ensure your own safety first (the first 'Check' in the Three Cs). You cannot help anyone if you become a casualty yourself.
Should I always 'Call' before 'Care'?
For life-threatening emergencies like cardiac arrest, choking, or severe bleeding, you should shout for help and delegate the 'Call' to someone else immediately so you can begin 'Care' (e.g., CPR) without delay. If you are alone, call first for these specific emergencies.
What if I'm not trained in CPR? Should I still try it?
Yes. For an unresponsive person who is not breathing, it is recommended to perform Hands-Only CPR—push hard and fast in the center of the chest. Any attempt is better than no attempt. The emergency dispatcher can guide you through it.
How can I promote recovery for a minor burn?
Cool the burn under cool running water for at least 10-20 minutes. Cover it loosely with a sterile, non-stick dressing. Avoid applying ice, butter, or toothpaste, as these can worsen the injury.
Where can I get proper first aid training?
Many organizations like the Indian Red Cross Society, St. John Ambulance, and local hospitals offer certified first aid and CPR courses. You can also often find courses through community centers or online platforms with a practical component.



.webp)