Angioplasty vs. Angiography: Understanding the Critical Difference
Confused between angioplasty and angiography? Learn the difference, including their purposes, procedures, risks, recovery, and when each is needed for heart health.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Navigating heart health terminology can be confusing, especially when procedures sound as similar as angioplasty and angiography. While their names are often mentioned together, they serve two fundamentally different purposes. One is a detective, meticulously mapping the terrain of your coronary arteries. The other is a repair crew, fixing the problems the detective finds. Understanding the difference between angioplasty and angiography is crucial for anyone seeking clarity on cardiac care. This guide will break down each procedure in simple terms, explaining their purposes, how they are performed, and what to expect, empowering you to have more informed conversations with your healthcare provider about your heart health.
Consult Top Doctors for Personalised Advice
What is Angiography? The Diagnostic Map of Your Arteries
Angiography, often called a coronary angiogram, is a sophisticated diagnostic imaging technique. Think of it as a detailed GPS map for your cardiologist. Its sole job is to find out if your coronary arteries, the vital blood vessels supplying oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle, are narrowed or blocked.
The Primary Purpose of an Angiogram
The main goal of angiography is diagnosis. It answers critical questions such as:
Is there a blockage caused by atherosclerosis or plaque build-up?
Where exactly is the blockage located?
How severe is the narrowing (for example, 50%, 70% or 90%)?
How many arteries are affected?
This information is vital for your doctor to determine the best course of treatment, which could range from medication and lifestyle changes to a procedure such as angioplasty or even bypass surgery.
How is an Angiography Procedure Performed?
Angiography is a minimally invasive procedure performed in a hospital’s catheterisation laboratory (commonly called a cath lab). You are usually awake but sedated.
Step-by-Step: The Angiography Process
To help you understand better, here is how the procedure usually unfolds:
Access: A doctor numbs an area, typically in your wrist (radial artery) or groin (femoral artery).
Catheter Insertion: A very thin, flexible tube called a catheter is gently threaded through the artery up to your heart.
Dye Injection: A special contrast dye is injected through the catheter into your coronary arteries.
X-ray Imaging: As the dye flows through your arteries, X-ray videos are taken. The dye makes the inside of your arteries visible on the X-ray, clearly revealing any narrowings or blockages.
Recovering from a Coronary Angiogram
As a diagnostic test, recovery is typically quick. You will need to rest for a few hours to ensure the puncture site heals properly. Most people can go home the same day or the next morning with instructions to avoid heavy lifting for a short period.
What is Angioplasty? The Treatment to Restore Blood Flow
If angiography is the map, angioplasty is the construction project that fixes the roadblocks it identifies. Angioplasty, formally known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is a therapeutic procedure designed to open a narrowed or blocked coronary artery.
The Primary Purpose of an Angioplasty
The key aim of angioplasty is treatment. It is performed to:
Widen a narrowed artery
Restore healthy blood flow to the heart muscle
Relieve symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath
Minimise damage during or after a heart attack
How is an Angioplasty Procedure Performed? The Role of Stents
Angioplasty often begins in the same way as angiography. In fact, if a significant blockage is found during a diagnostic angiogram, an angioplasty may be performed immediately afterwards.
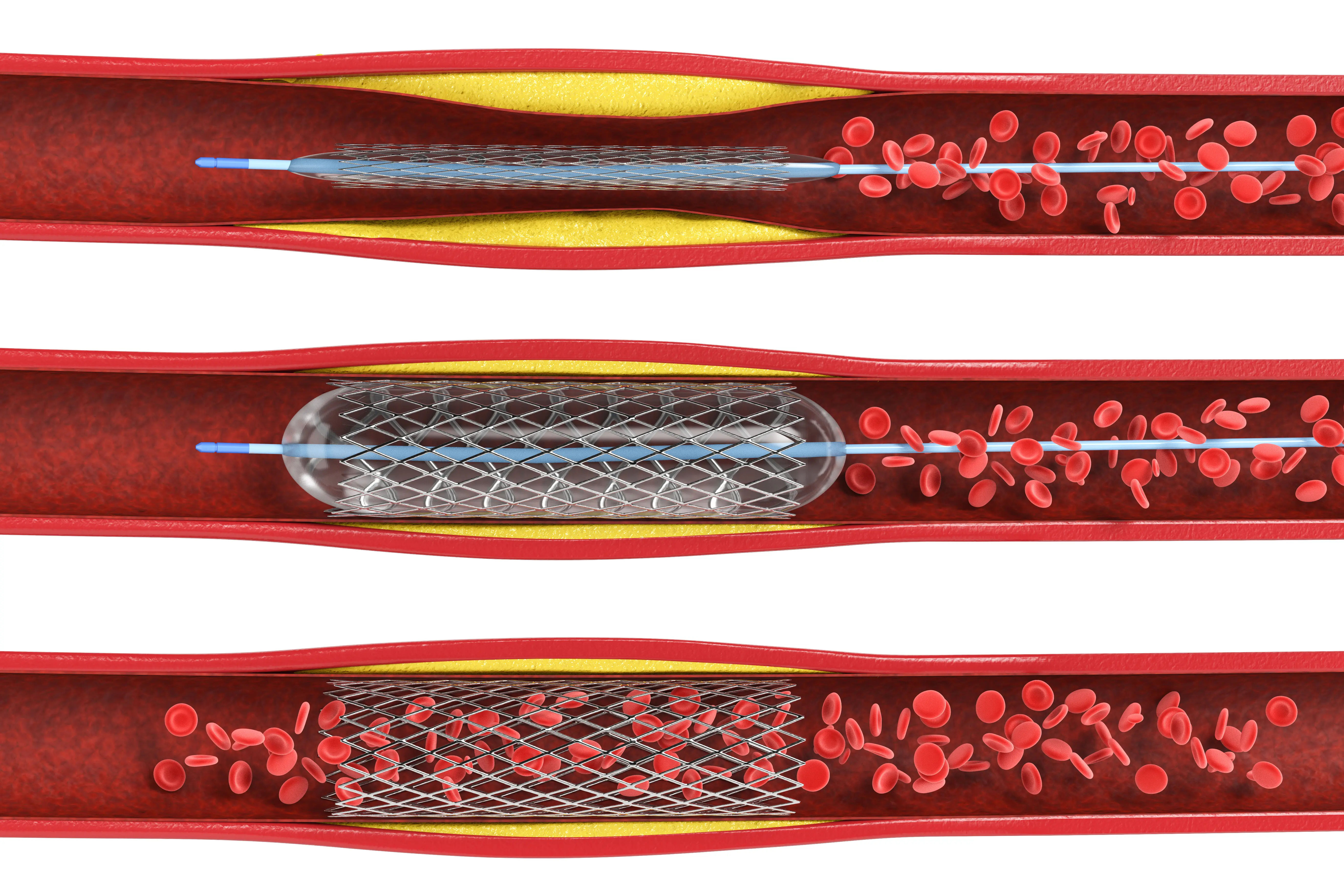
After the blockage is located via angiography, a second catheter with a tiny deflated balloon at its tip is guided to the exact spot.
The balloon is inflated for a short time, compressing the plaque against the artery wall and widening the artery.
In the vast majority of cases, a stent is then deployed.
What is a Stent? The Tiny Scaffold for Your Artery
A stent is a small mesh-wire tube that acts as a scaffold. It is placed over the balloon and expands when the balloon is inflated. The stent remains permanently in the artery to prop it open, significantly reducing the chance of the artery narrowing again (a process called restenosis).
Recovering from an Angioplasty
Recovery from angioplasty is longer than from a diagnostic angiogram. A hospital stay of one to two days is common for monitoring. You will be prescribed blood-thinning medications such as aspirin and clopidogrel to prevent blood clots from forming inside the stent. Cardiac rehabilitation and significant lifestyle changes are often recommended for long-term success.
Angioplasty vs. Angiography: The Head-to-Head Comparison
Understanding their differences becomes clearer when set side by side.
| Feature | Angiography (The Diagnostic Test) | Angioplasty (The Treatment) |
| Purpose | To diagnose and locate blockages | To open a blocked artery and restore blood flow |
| Nature | Diagnostic imaging procedure | Therapeutic, interventional procedure |
| Tools Used | Catheter, contrast dye, X-ray | Catheter, balloon, stent (often) |
| Outcome | Provides images of arteries | Physically widens the artery |
| Duration | Shorter (30–60 minutes) | Longer (60–90 minutes or more) |
| Recovery | Quick, often same-day discharge | Requires hospital stay and medication |
The Interconnected Relationship: Why They Often Go Hand-in-Hand
The relationship between the two is sequential and interdependent. A coronary angiogram is almost always the essential first step before an angioplasty. It provides the necessary roadmap. You cannot perform a targeted angioplasty without first knowing the location and severity of the blockage via angiography.
Risks and Complications: What to Be Aware Of
Like all medical procedures, both angiography and angioplasty carry some risks, though these are generally low.
Risks Associated with Angiography
Bleeding or bruising at the catheter insertion site
Allergic reaction to the contrast dye
Minor kidney issues due to the dye, more common in those with pre-existing kidney disease
Very rarely, damage to the artery or a heart attack
Risks Associated with Angioplasty
The risks include all those of angiography, plus:
Blood clots forming within the stent
Re-narrowing of the artery (restenosis), though modern drug-eluting stents have reduced this significantly
Artery damage or rupture (very rare)
Heart attack or need for emergency bypass surgery (very rare)
Which Procedure is Right For You? The Role of Cardiac Diagnosis
Choosing between angiography and angioplasty is not up to the patient; the diagnostic process determines the path. If you experience symptoms such as chest pain, unexplained shortness of breath, or have abnormal stress test results, your cardiologist will likely recommend a coronary angiogram to see what is happening inside your arteries.
Based on the findings:
If no significant blockages are found, the procedure ends at angiography, and other causes for your symptoms are explored.
If a significant blockage is found, your doctor may then proceed directly to angioplasty and stenting to open the artery immediately. This decision is always made in consultation with you or your family where possible.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of heart disease, it is crucial to consult a cardiologist for a proper evaluation. You can book a detailed consultation with an experienced cardiologist online through Apollo 24|7 to discuss your symptoms and determine the right diagnostic path for you.
Conclusion: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Your Heart Health
Understanding the distinct roles of angiography and angioplasty helps demystify an important part of modern cardiology. Angiography is the essential first step, the eyes that allow doctors to see the problem. Angioplasty is the logical next step, the hands that fix the problem, often providing immediate relief and a lifeline during a heart attack. While the names are similar, their functions are complementary. If your doctor recommends either procedure, remember that they are cornerstone techniques in preventing and treating heart disease, helping millions of people live healthier, longer lives. Always follow your doctor’s advice for pre- and post-procedure care and commit to the lifestyle changes needed to protect your heart in the long run.
Consult Top Doctors for Personalised Advice
Consult Top Doctors for Personalised Advice

Dr. Tripti Deb
Cardiologist
40 Years • MBBS, MD, DM, FACC, FESC
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Rakesh Gopal
Cardiologist
22 Years • “ Trained in Trans Aortic Valve Implantation ( TAVI ) from Mehmet Akif Ersoy Hospital Istanbul, Turkey “ & MD (General Medicine), FRCP (Glasglow)DNB( Cardiology), FESC, HICR Cert (Harvard University, USA), Angioplasty Training from Washington Adventist Hospital USA, Asan Medical Centre, Seoul Korea, Board certified in Cardio Oncology, ICOS- USA
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Heart Centre Thousand Lights, Chennai
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Vijayachandra Reddy Y
Cardiologist
27 Years • MD, DM, MRCP, FACC, FCSI, CCDS, FSCAI
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(1250+ Patients)