Guide to Know About Hernia
Learn what a hernia is, why it happens, symptoms to watch for, and treatment options, including surgery. A clear, patient-friendly guide so you know when to seek a doctor’s help and what to expect.


Introduction
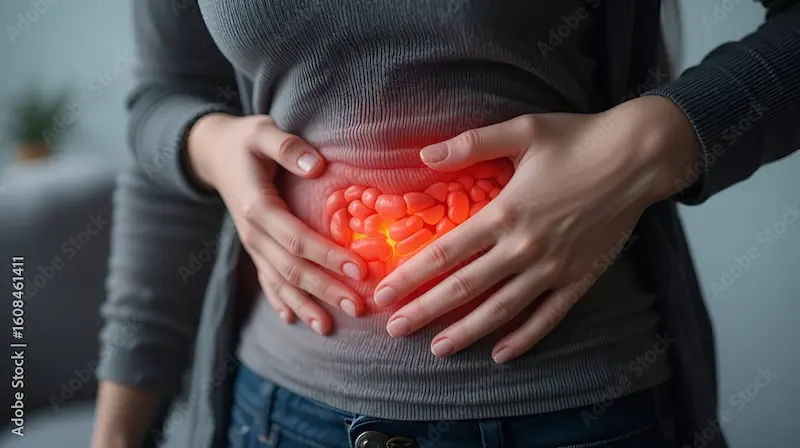
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the muscle or surrounding tissue that normally keeps it in place. While some hernias may appear small or painless at first, they can worsen over time and potentially lead to complications if left untreated. This guide explains the different types of hernias, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and modern treatment options — so you can understand when simple monitoring is safe and when surgery is necessary. A hernia is more common than many people think, and early attention often leads to better outcomes.
What is a Hernia?
This section explains the definition and mechanism of a hernia.
A hernia develops when part of an organ or fatty tissue bulges through a weak area in the muscle or abdominal wall. This bulge may become more noticeable when standing, bending, lifting, or coughing. Hernias often begin small and may not cause discomfort initially, but they typically do not resolve on their own. Over time, the weakness can progress, resulting in a larger bulge and more symptoms. Understanding the basics of how a hernia forms helps patients recognise when to seek medical evaluation.
When the abdominal wall is strong, organs stay securely in place. However, when weaknesses exist — whether from ageing, previous surgery, or increased internal pressure — organs can push outward. Most hernias involve the intestines, but other tissues may also be affected. Importantly, worsening pain, sudden swelling, or difficulty pushing the bulge back in can signal a complication that requires urgent medical care.
Consult a Top Surgeon for Personalised Advice
Types of Hernias
A recap of common hernia types to help you identify potential concerns.
Several types of hernias can occur, depending on where the weakness develops. The major types include:
Inguinal Hernia
This is the most common type, seen more in men. It appears in the groin area when part of the intestine pushes into a
weak spot of the lower abdominal wall. The bulge may extend into the scrotum and becomes more obvious when lifting
heavy objects or coughing.
Femoral Hernia
More common in women, this occurs when tissue pushes through a canal near the upper thigh. Femoral hernias have a
higher risk of complications such as strangulation and often require surgical attention once diagnosed.
Umbilical Hernia
Located near the belly button, this hernia occurs when abdominal tissue pushes through the area where the umbilical cord
once passed. Common in infants, it often resolves naturally in babies but may require surgery in adults.
Incisional Hernia
This appears at the site of a previous abdominal surgery. Weakness along the healed incision line allows tissues to
protrude. It can grow over time, particularly in cases with repeated strain or poor wound healing.
Hiatal Hernia
This involves part of the stomach pushing through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Hiatal hernias often contribute to
reflux symptoms, including heartburn and difficulty swallowing.
Understanding which type you have guides your treatment plan and whether surgery is recommended early or can be
delayed.
Common Causes of Hernias
Why hernias develop and what can increase risk.
A hernia can form due to a combination of muscle weakness and increased pressure inside the abdomen. Some people
are born with weaker muscles in certain areas, while others develop weakness with age or injury.
Factors that may contribute include:
- Heavy lifting or intense physical effort
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Obesity causing strain on abdominal structures
- Pregnancy, which stretches abdominal muscles
- Past surgeries have weakened tissue strength
- Constipation requiring repeated straining
- Smoking, which affects tissue healing
Not all causes are preventable, but reducing modifiable risks can slow progression and prevent new hernias.
Symptoms of a Hernia
How to recognise early signs and seek timely care.
A noticeable bulge is the most common symptom. It may appear during daily activities or be visible only when standing.
Other symptoms can include:
- Aching or discomfort in the affected area
- Heaviness or pressure sensation in the abdomen or groin
- Weakness or burning around the bulge
- Pain that increases with movement, lifting, or straining
Some hernias are silent and discovered during routine exams. If a bulge disappears when lying down, it may be reducible, meaning tissue can be gently pushed back into place — generally a less urgent situation unless symptoms worsen.
Warning Signs of Complications
Recognise symptoms that require immediate medical care.
If the protruding organ becomes trapped (incarcerated) or the blood supply is cut off (strangulated), urgent treatment is
necessary. Warning signs include:
- Sudden, sharp, or worsening pain
- Redness or darkening of the skin over the bulge
- A bulge that does not reduce even when lying down
- Vomiting, nausea, or inability to pass stool or gas
- Fever or rapid heart rate
Strangulation can lead to tissue death and life-threatening complications, so prompt attention is crucial.
How Hernias Are Diagnosed
What to expect when seeing a doctor for symptoms.
A doctor usually diagnoses a hernia through physical examination. You may be asked to stand or cough to make the bulge more noticeable. If the hernia is not clearly visible or if complications are suspected, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may help assess the condition. Diagnosis aims to determine hernia type, severity, and whether surgical treatment is required urgently or can be planned.
Treatment Options for Hernias
An overview of available medical and surgical care.
Watchful Waiting
If a hernia is small and without symptoms, monitoring may be recommended. You will be advised to avoid heavy lifting
and manage contributing factors such as constipation or weight gain.
Hernia Truss
Some individuals find temporary relief using a supportive belt to keep the bulge in place. However, this does not repair
the hernia and is not a long-term solution.
Surgical Repair
Surgery is the only definitive treatment. Approaches include:
- Open surgery – A cut is made over the hernia, and the tissue is returned to place while strengthening the muscle wall.
- Laparoscopic surgery – Minimally invasive using small incisions, a camera, and mesh for reinforcement.
Surgical methods aim to prevent recurrence and reduce the risk of complications.
Recovery After Hernia Surgery
What helps with healing and a smoother return to movement?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of hernia and surgical approach. Many patients go home the same day after
laparoscopic procedures. Postoperative advice may include:
- Gradually increasing activity levels
- Avoiding heavy lifting for several weeks
- Managing pain with medicines as prescribed
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce future strain
Following guidance carefully promotes strong healing and lowers recurrence risk.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Understand the right time to get a professional evaluation.
See a healthcare provider if:
- You notice a new bulge in the abdomen or groin
- You experience discomfort or pressure that interferes with daily routines
- Pain or swelling worsens over time
- You have risk factors and notice subtle changes
Urgent care is needed if severe pain, vomiting, or an irreducible bulge develops, as these may indicate strangulation.
Living with a Hernia
How lifestyle adjustments support comfort and safety.
People with small hernias can often live normal lives with certain precautions:
- Avoid lifting heavy objects
- Treat chronic cough or constipation promptly
- Maintain good posture and core support
- Consider weight management if overweight
Even when symptoms are mild, regular monitoring ensures the condition remains safe under medical guidance.
Prevention Tips
Simple habits that may help lower the risk.
While not all hernias can be prevented, strengthening core muscles and reducing strain on the abdomen can help.
Supportive habits include:
- Eating a high-fibre diet to prevent constipation
- Quitting smoking to improve muscle and tissue health
- Using proper lifting techniques during activities
These steps help protect abdominal strength and reduce future risk.
Conclusion
A hernia is a common condition where internal tissue pushes through a weakness in the muscle wall. Although some hernias may remain small or painless for some time, they do not resolve on their own and can progress if untreated. Recognising symptoms, understanding risks, and seeking timely medical evaluation are key to preventing complications. When necessary, surgical repair provides a reliable and lasting solution. Being aware of your body and addressing changes early ensures better long-term comfort and health.
Consult a Top Surgeon for Personalised Advice
Consult a Top Surgeon for Personalised Advice
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Anubhav Chittari
General Surgeon
3 Years • MBBS, M.S GENERAL SURGERY
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Bhethala Sharan Prakash
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Bhumika Lalwani
General Surgeon
4 Years • MBBS MS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru
Dr. Naziya Rahim Bhatia
General Surgeon
7 Years • MBBS ,MS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
Consult a Top Surgeon for Personalised Advice
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Anubhav Chittari
General Surgeon
3 Years • MBBS, M.S GENERAL SURGERY
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Bhethala Sharan Prakash
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Bhumika Lalwani
General Surgeon
4 Years • MBBS MS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru
Dr. Naziya Rahim Bhatia
General Surgeon
7 Years • MBBS ,MS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
More articles from Hernia
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Can a hernia heal without surgery?
No. A true hernia defect in the muscle or fascia does not close on its own. Lifestyle changes can reduce symptoms, but definitive repair requires surgery. For some minimally symptomatic inguinal hernias, watchful waiting is reasonable under medical supervision.
2) How do I know if my hernia is strangulated?
Severe, sudden pain; a firm, tender bulge that won’t reduce; skin color changes; vomiting; and inability to pass gas or stool are warning signs of a strangulated hernia. Seek emergency care immediately.
3) What is the hernia surgery recovery time?
Most people walk the same day. Desk work often resumes in 1–2 weeks after laparoscopic repair and 2–3 weeks after open repair. Heavy lifting typically waits 4–6 weeks, based on your surgeon’s guidance.
4) Are hernia mesh complications common?
Serious mesh complications are uncommon, and mesh repairs generally reduce recurrence compared to tissue-only repairs. Choosing an experienced surgeon and the right mesh and fixation method lowers the risk of chronic groin pain and other issues.
5) What lifestyle changes help a hiatal hernia?
Smaller meals, avoiding late-night eating, elevating the head of your bed, and using acid-suppressing medications help reduce reflux. Weight management and treating constipation/cough lower pressure on the diaphragm. If symptoms persist, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7.