Preventing Jaundice: Key Steps and Tips
Discover key steps and tips to prevent jaundice, including healthy liver habits, vaccination, proper hygiene, and early medical intervention. Learn how to protect yourself from common causes of jaundice.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 28th Aug, 2025

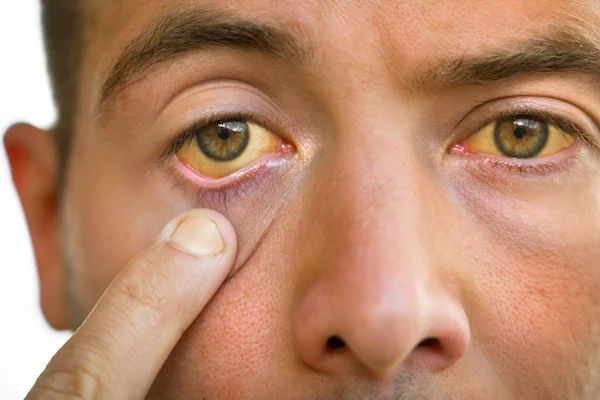
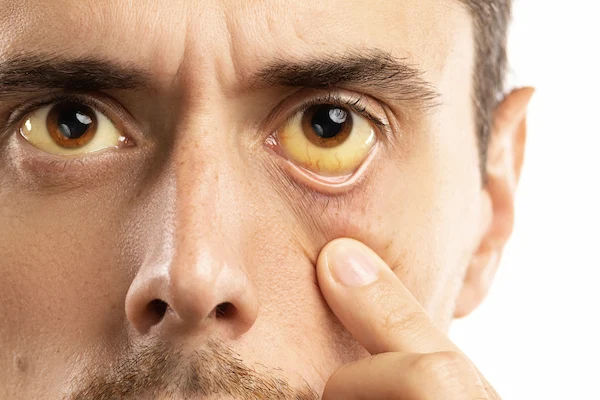
Jaundice is a common condition that causes yellowing of the skin and eyes due to high levels of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced when red blood cells break down. While jaundice itself is not a disease, it is often a sign of an underlying liver or blood-related problem. The good news is that many cases of jaundice can be prevented with simple lifestyle changes and precautions.
In this article, we’ll discuss what causes jaundice, who is at risk, and most importantly how you can take steps to prevent it.
Understanding Jaundice and Its Causes
Jaundice occurs when the liver cannot efficiently process bilirubin, leading to its buildup in the body. Some common causes include:
- Hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E): Viral infections that inflame the liver.
- Alcohol-related liver disease: Excessive alcohol consumption damages the liver.
- Gallstones or bile duct blockage: Prevents bile (which contains bilirubin) from being excreted.
- Hemolytic anemia: A condition where red blood cells break down too quickly.
- Newborn jaundice: Common in babies due to an immature liver.
Consult top Hepatologist
Who Is at Risk?
Certain people are more prone to jaundice, including:
- Newborns (especially premature babies)
- People with liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Heavy alcohol drinkers
- Those with a family history of liver or blood disorders
- Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes or obesity
Key Steps to Prevent Jaundice
Preventing jaundice largely depends on maintaining liver health and avoiding infections. Here are some essential tips:
1. Get Vaccinated
- Hepatitis A & B vaccines are highly effective in preventing viral hepatitis, a leading cause of jaundice.
Ensure children receive vaccinations as per their immunization schedule.
2. Maintain Good Hygiene
- Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after using the restroom.
- Drink clean, filtered water to avoid waterborne infections like Hepatitis E.
- Avoid consuming raw or undercooked seafood, which may carry Hepatitis A.
3. Eat a Liver-Friendly Diet
- Increase fiber intake (whole grains, fruits, vegetables) to aid digestion.
- Limit fatty, fried, and processed foods that strain the liver.
- Stay hydrated to help flush out toxins.
- Include liver-supportive foods like beetroot, garlic, turmeric, and green tea.
4. Avoid Excessive Alcohol
- Alcohol damages liver cells over time, leading to cirrhosis and jaundice.
- If you drink, do so in moderation (1 drink per day for women, 2 for men).
5. Practice Safe Blood and Needle Use
- Avoid sharing needles, razors, or toothbrushes to prevent Hepatitis B and C.
- Ensure medical or tattoo equipment is sterilized.
6. Manage Underlying Health Conditions
- Control diabetes, obesity, and high cholesterol, as they contribute to fatty liver disease.
- If you have hemolytic anemia, follow your doctor’s treatment plan.
7. Be Cautious with Medications
- Some medicines (like paracetamol in high doses) can harm the liver.
- Always take medications as prescribed and avoid self-medication.
8. Protect Against Newborn Jaundice
- Ensure proper breastfeeding (frequent feeding helps flush out bilirubin).
- Monitor babies for yellowing skin or eyes in the first week.
When to See a Doctor
While prevention is key, early detection is crucial. Consult a doctor if you notice:
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Dark urine or pale stools
- Fatigue, nausea, or abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
If you suspect jaundice or have risk factors, consider booking a liver function test (LFT) or consultation with a hepatologist through Apollo 24|7 for expert guidance.
Conclusion
Jaundice is often preventable with healthy habits, vaccinations, and proper hygiene. By taking care of your liver and staying informed, you can significantly reduce your risk. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms, seek medical advice promptly for the best outcomes.
Consult top Hepatologist
Consult top Hepatologist

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Srinivasa Reddy
Hepatologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Hepatology),ASGE
Hyderabad
Myra Liver & Gastro Care, Hyderabad

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(100+ Patients)

Dr U V U Vamsidhar Reddy
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (JIPMER), DM (Hepatology, PGIMER)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)
Consult top Hepatologist

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Srinivasa Reddy
Hepatologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Hepatology),ASGE
Hyderabad
Myra Liver & Gastro Care, Hyderabad

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(100+ Patients)

Dr U V U Vamsidhar Reddy
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (JIPMER), DM (Hepatology, PGIMER)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)
.webp)