Guide to Jaundice Preventable Disease
Learn about jaundice as a preventable disease, including its causes, symptoms, prevention tips, and treatment options for better liver health and well-being.

Written by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
Reviewed by Dr. J T Hema Pratima MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

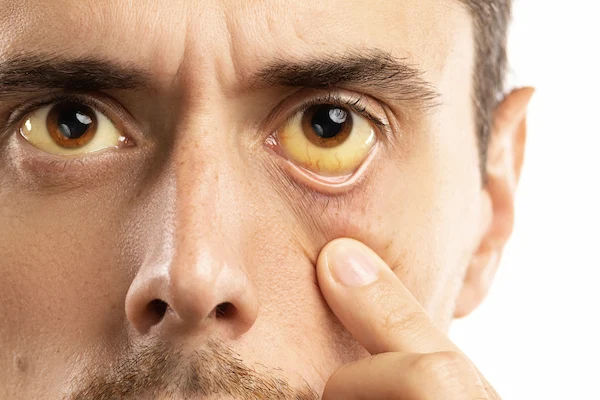
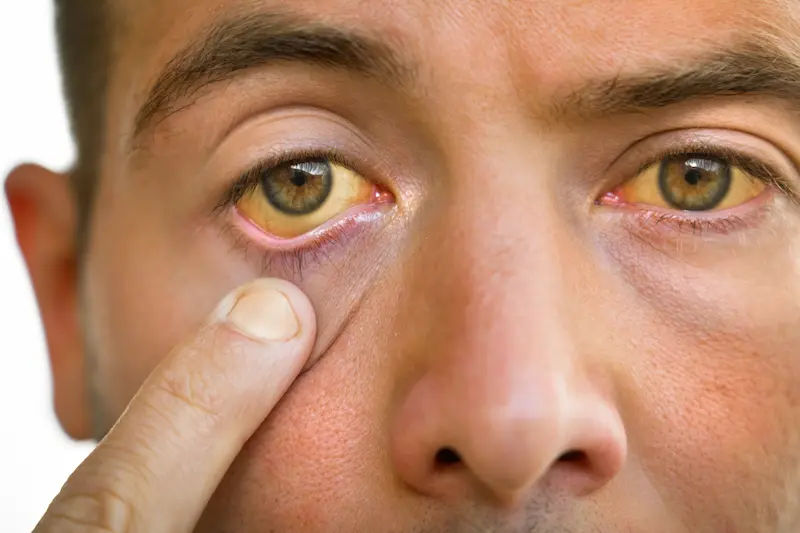
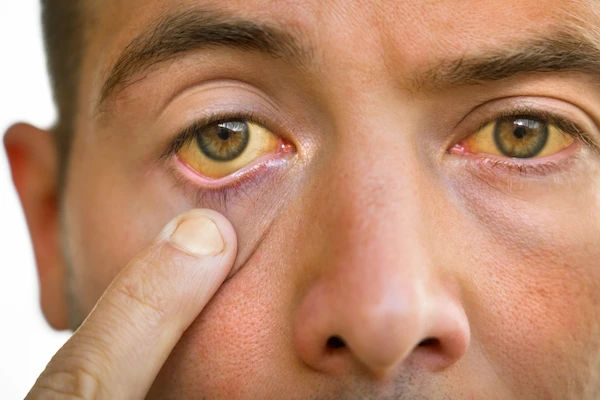
Before we dive into prevention, it's crucial to understand what jaundice is. It's a clinical sign, not a final diagnosis. Think of it as your body's "check engine" light, specifically for your liver and blood. The yellow color manifests when a yellow-orange pigment called bilirubin accumulates in your bloodstream.
Common Causes of Jaundice: Which Ones Can You Prevent?
Many conditions leading to jaundice are, to a large extent, within your control. Let's break down the most common preventable causes of jaundice.
Viral Hepatitis: A Leading Preventable Cause
Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) caused by viruses is a major global health issue.
Hepatitis A: Spread through contaminated food or water. It is highly preventable with a vaccine and good hygiene.
Hepatitis B: Spread through contact with infected blood, semen, or other body fluids. It can become a chronic condition leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The hepatitis B vaccine is over 95% effective and is a cornerstone of prevention.
Hepatitis C: Primarily spread through blood-to-blood contact (e.g., sharing needles). While there is no vaccine yet, modern antiviral treatments can cure over 95% of cases, preventing long-term liver damage and jaundice.
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Chronic, excessive alcohol consumption is toxic to liver cells. It can cause fat buildup (steatosis), inflammation (alcoholic hepatitis), and permanent scarring (cirrhosis). Each stage impairs the liver's function and can lead to jaundice. This is one of the most straightforward jaundice preventable diseases; moderating or eliminating alcohol intake drastically reduces risk.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is the buildup of extra fat in the liver not caused by alcohol. It's closely linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol. As the prevalence of these conditions rises, so does NAFLD, making it a rapidly growing preventable cause of liver dysfunction and, eventually, jaundice.
Gallstones and Blocked Bile Ducts
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. If a stone travels into and blocks the common bile duct, it can prevent bile (and bilirubin) from being excreted, causing obstructive jaundice. While not all gallstones are preventable, maintaining a healthy weight and a diet low in cholesterol and high in fiber can reduce your risk.
Medication-Induced Liver Injury
Certain prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications (like acetaminophen in high doses), and herbal supplements can be harmful to the liver. Always follow dosage instructions and inform your doctor of all medications and supplements you are taking to prevent drug-induced jaundice.
Consult a Top Specialist
Top Strategies for Preventing Jaundice
Now for the actionable part. Here’s how you can actively protect your liver and prevent jaundice.
Get Vaccinated: Your First Line of Defense
Vaccination is the single most effective way to prevent viral hepatitis. The Hepatitis A and B vaccines are safe, effective, and often administered together. The CDC recommends them for all children and at-risk adults. If you're unsure of your vaccination status, ask your doctor.
Embrace a Liver-Healthy Diet
What you eat directly impacts liver health. Focus on:
Fiber-rich foods: Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help maintain digestive health and weight.
Lean proteins: Fish, chicken, and plant-based proteins like lentils are easier on the liver than fatty red meats.
Healthy fats: Those found in nuts, avocados, and olive oil.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps the liver flush out toxins.
Practice Safe Habits to Avoid Infection
Protect yourself from hepatitis viruses by:
Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before handling food.
Practicing safe sex using barrier methods like condoms.
Avoiding sharing personal items like razors, toothbrushes, or needles that might have trace amounts of blood.
Drink Alcohol Responsibly (or Not at All)
The dietary guidelines define moderate drinking as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. However, for optimal liver health, abstaining is best. If you have existing liver concerns, avoid alcohol completely.
Manage Your Weight and Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity helps combat obesity and insulin resistance, the key drivers of NAFLD. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This is a powerful way to prevent fatty liver disease and its complications.
Use Medications Wisely and Review Them Regularly
Always take medication as prescribed. Be particularly cautious with acetaminophen (Tylenol); never exceed the recommended dose and be aware it's hidden in many cold and flu remedies. Discuss all supplements with your doctor, as some, like kava and comfrey, are known to be hepatotoxic.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Liver Trouble
Catching liver issues early is a form of prevention. Jaundice is a later sign; earlier symptoms can include:
Unexplained fatigue and weakness
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal pain and swelling
Dark-colored urine (like tea or cola)
Pale-colored stools
When to See a Doctor Immediately
If you notice any signs of jaundice (yellow skin/eyes), coupled with abdominal pain, fever, or dark urine, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis of the underlying condition is critical for effective treatment and preventing long-term damage.
Conclusion
Jaundice is often a sign of underlying liver or blood-related issues, but with timely care, a healthy lifestyle, and preventive measures, it can be effectively managed or even avoided. Recognizing symptoms early, seeking medical advice, and adopting habits that support liver health are key to preventing complications and ensuring overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Preventing Jaundice
Below are few FAQs
1. Can you completely prevent jaundice?
Not all forms of jaundice are preventable (e.g., some genetic or autoimmune conditions). However, you can dramatically reduce your risk by addressing the major preventable causes like viral hepatitis, alcohol misuse, and fatty liver disease through vaccination and healthy lifestyle choices.
2. What are the best foods to eat for liver health?
Focus on antioxidant-rich and anti-inflammatory foods. Some great choices include coffee (in moderation), leafy greens, berries, nuts, fatty fish like salmon, olive oil, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts.
3. Is jaundice itself contagious?
No, jaundice is a symptom and is not contagious. However, some of the underlying conditions that cause it, like Hepatitis A or B, can be highly contagious.
4. How quickly can jaundice develop from alcohol?
Alcohol-related jaundice typically appears after years of heavy drinking, as it takes time for significant liver damage (like alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis) to develop. However, in cases of extreme binge drinking, it can sometimes occur more acutely.
5. Can weight loss reverse fatty liver disease and prevent jaundice?
Yes, absolutely. For many people, weight loss is the most effective treatment for NAFLD. Losing even 5-10% of your body weight can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis, significantly lowering your risk of progressing to cirrhosis and jaundice.
Consult a Top Specialist
Consult a Top Specialist

Dr. Swaroopa Rani
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Sanjukta Das
General Physician
9 Years • MBBS
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Mary Susan K S
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD INTERNAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Soumen Paul
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
24 Years • MBBS
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Pinaki Mukhopadhyay
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
33 Years • MBBS
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)
 (1).jpg)
 (1).webp)