What Makes an Ovarian Cyst Dangerous?
Learn when an ovarian cyst becomes dangerous. Explore symptoms, risks like rupture or torsion, and when to seek medical help. Timely care can prevent serious complications.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 30th Jul, 2025
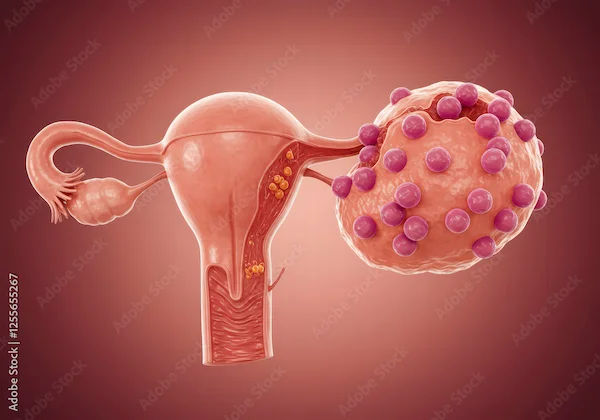
Introduction
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can become dangerous and require medical attention. Understanding when a cyst poses a risk can help you take timely action and prevent complications.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are common in women, especially during their reproductive years. Many women develop cysts at some point, often without even realising it. Most cysts are functional cysts, meaning they form as part of the menstrual cycle and disappear on their own. However, some cysts can grow large, rupture, or twist, leading to serious health concerns.
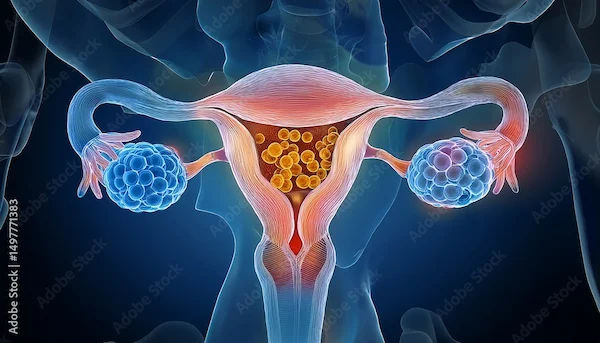
Types of Ovarian Cysts
These are the various types of Ovarian cysts:
1. Functional Cysts: These are the most common and usually harmless. They include:
Follicular cysts (form when an egg follicle doesn’t release an egg).
Corpus luteum cysts (develop after an egg is released).
2. Pathological Cysts: These are less common and may require treatment:
Dermoid cysts (contain tissues like hair, skin, or teeth).
Cystadenomas (filled with watery or mucous-like fluid and can grow large).
Endometriomas (caused by endometriosis, where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus).
When Does an Ovarian Cyst Become Dangerous?
Most ovarian cysts are harmless, but certain factors can make them risky:
1. Large Size
Cysts larger than 5 cm may cause pain, bloating, or pressure.
Very large cysts can lead to complications like rupture or ovarian torsion.
2. Rupture (Bursting of the Cyst)
A ruptured cyst can cause sudden, severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Internal bleeding may occur, leading to dizziness or fainting.
3. Ovarian Torsion (Twisting of the Ovary)
Large cysts can cause the ovary to twist, cutting off blood supply.
This is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgery to save the ovary.
4. Cancerous Cysts
While rare, some cysts can be malignant (cancerous), especially in older women.
Persistent cysts that grow over time should be evaluated.
Symptoms of a Dangerous Ovarian Cyst
Most small cysts don’t cause symptoms, but warning signs of a problematic cyst include:
Severe pelvic or lower abdominal pain (sharp or dull ache).
Bloating or swelling in the abdomen.
Pain during intercourse or bowel movements.
Irregular periods or heavy bleeding.
Nausea, vomiting, or fever (signs of infection or rupture).
Sudden dizziness or weakness (possible internal bleeding).
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist
How Are Dangerous Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
Doctors use the following tests to evaluate ovarian cysts:
Pelvic ultrasound (to check the size and type of cyst).
Blood tests (like CA-125 to rule out ovarian cancer).
MRI or CT scan (for a detailed view if needed).
Treatment Options
1. Watchful Waiting
Small, simple cysts often disappear on their own in a few months.
Doctors may recommend follow-up ultrasounds to monitor changes.
2. Medications
Birth control pills may help prevent new cysts, but won’t shrink existing ones.
3. Surgery
Laparoscopy (minimally invasive surgery to remove cysts).
Laparotomy (open surgery for large or cancerous cysts).
How to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cysts?
While not all cysts can be prevented, you can lower your risk by:
Regular pelvic exams to detect cysts early.
Maintaining a healthy weight (obesity can increase risks).
Managing hormonal imbalances (consult a doctor if you have PCOS or endometriosis).
Avoiding smoking, which can affect ovarian health.
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor if you experience:
Sudden, severe pelvic pain.
Persistent bloating or discomfort.
Unexplained weight loss or fatigue.
Changes in menstrual cycles.
If you suspect an ovarian cyst, Apollo 24|7 offers expert consultations and diagnostic tests to ensure timely care.
Conclusion
Most ovarian cysts are harmless, but some can become dangerous if left untreated. Knowing the warning signs and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent complications. If you have concerns about ovarian cysts, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and care.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist

Dr. Priyanka Surisetty
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS, DGO
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam

Dr Swatika Kumari
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
19 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Nashik
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Maharashtra, Nashik

Dr. Veena H
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
16 Years • MBBS DGO
Bangalore
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Karnataka, Bangalore

Dr. Mona Yadav
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
19 Years • MBBS, MD (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
Dombivli
Nulife multispeciality, Dombivli

Dr. Asha Rani Singh
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
24 Years • MBBS DGO
Delhi
Dr Asha Rani Singh Clinic, Delhi
.webp)
.webp)