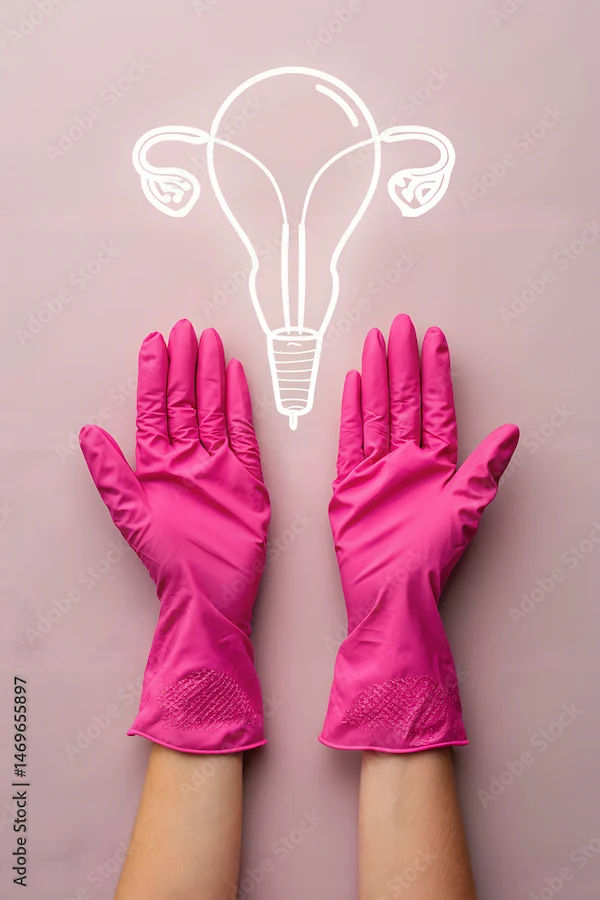
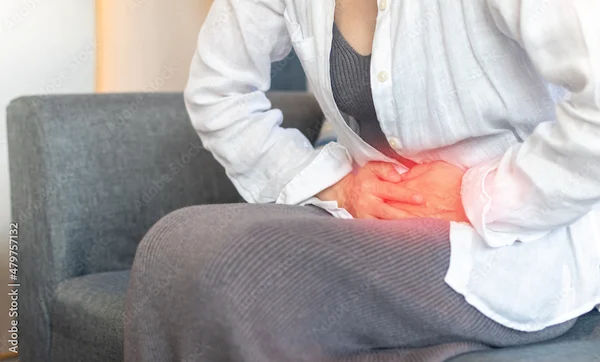
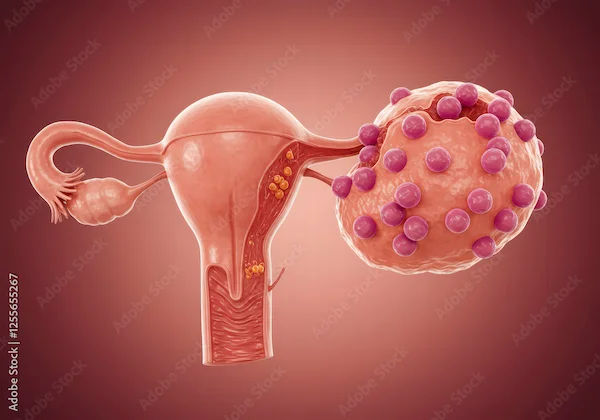
Ovarian Cysts in Unmarried Women Explained
Learn about ovarian cysts in unmarried women—types, symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Discover when to see a doctor and how to manage cyst-related discomfort.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 30th Jul, 2025
Introduction
Ovarian cysts are a common health concern among women, including those who are unmarried. While most cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some may cause discomfort or lead to complications. Understanding what ovarian cysts are, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you manage them effectively.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
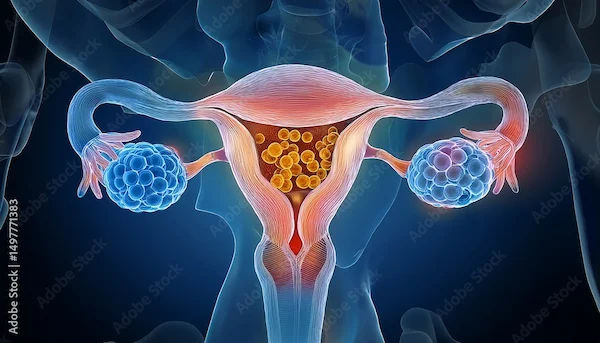
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries. The ovaries are small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus, responsible for producing eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Most ovarian cysts are functional cysts, meaning they form as part of the menstrual cycle and usually disappear without treatment. However, in some cases, cysts can grow larger, cause pain, or lead to complications.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
1. Follicular Cysts: These form when a follicle (a sac that holds an egg) doesn’t release the egg and continues to grow.
2. Corpus Luteum Cysts: After an egg is released, the follicle (now called corpus luteum) may fill with fluid and form a cyst.
3. Dermoid Cysts: These are rare and contain tissues like hair, skin, or teeth.
4. Cystadenomas: These develop from ovarian tissue and can grow large.
5. Endometriomas: Caused by endometriosis, where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus.
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many women with ovarian cysts experience no symptoms, but when symptoms do occur, they may include:
Pelvic pain (dull or sharp, often on one side)
Bloating or swelling in the abdomen
Irregular periods
Pain during intercourse
Frequent urination (if the cyst presses on the bladder)
Nausea or vomiting (if the cyst twists or ruptures)
If you experience sudden, severe pelvic pain, fever, dizziness, or rapid breathing, seek medical help immediately, as this could indicate a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary).
Causes of Ovarian Cysts in Unmarried Women
Ovarian cysts can develop due to:
Hormonal imbalances (common in PCOS -Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
Menstrual cycle changes (delayed ovulation can lead to cyst formation)
Endometriosis
Pelvic infections (though rare)
Genetic factors (family history of cysts)
How Are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
If you experience symptoms, your doctor may recommend:
Pelvic ultrasound: To confirm the presence, size, and type of cyst.
Blood tests: To check hormone levels or rule out cancer (CA-125 test in rare cases).
MRI or CT scan: For a more detailed view, if needed.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist
Treatment Options
Most ovarian cysts go away on their own within a few menstrual cycles. However, treatment may be needed if the cyst:
Is large (over 5 cm)
Causes severe pain
Doesn’t shrink over time
Shows signs of being cancerous (rare)
1. Watchful Waiting
Doctors may monitor the cyst with follow-up ultrasounds.
2. Medications
Birth control pills: Can help prevent new cysts by regulating hormones.
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter painkillers (like ibuprofen) can ease discomfort.
3. Surgery
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to remove small cysts.
Laparotomy: For larger or suspicious cysts, a larger incision may be needed.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
While ovarian cysts can’t always be prevented, these tips may help manage symptoms:
Warm compresses: Can relieve pelvic pain.
Gentle exercise: Yoga or walking may reduce discomfort.
Healthy diet: Eating fibre-rich foods, reducing processed sugars, and staying hydrated can help.
Stress management: High stress can affect hormones; meditation or relaxation techniques may help.
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor if you experience:
Persistent pelvic pain
Sudden, severe abdominal pain
Unusual bleeding or irregular periods
Unexplained weight loss or bloating
If you suspect an ovarian cyst or have concerns about your reproductive health, you can book a consultation with a gynaecologist through Apollo 24|7 for expert advice and personalised care.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are common and often harmless, but being aware of symptoms and seeking timely medical advice ensures proper care. Most women with ovarian cysts lead healthy lives with minimal intervention. If you have concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for guidance.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist
Get Your Symptoms Checked By A Gynaecologist

Dr. Veena H
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
16 Years • MBBS DGO
Bangalore
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Karnataka, Bangalore

Dr. Priyanka Surisetty
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS, DGO
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam

Dr Swatika Kumari
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
19 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Nashik
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Maharashtra, Nashik

Dr. Abhishek Daga
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
20 Years • MBBS, MS (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
Kolkata
Gynae Care Fertility Centre, Kolkata
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Aaditi Acharya
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
12 Years • MBBS, DGO
New Delhi
WELLNESS CLINIC, New Delhi
(25+ Patients)

.webp)