Ovarian Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment & More
Learn about ovarian cancer diagnosis, risk factors, symptoms, genetic testing, and treatment options. Discover early detection and prevention strategies to improve outcomes and support better survivorship care.

Written by
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
Among all types of gynaecological cancers, ovarian cancer is one of the hardest to detect and treat. This is because its symptoms are often more subtle and resemble those of common ailments, resulting in later-stage diagnoses and bad prognoses. Thus, awareness and understanding of ovarian cancer and its diagnostic pathway are crucial for better outcomes.
Keep reading this guide to understand the intricacies of confirming ovarian cancer, covering the diagnostic tools, risk factors, and methods for early detection.
Who is at Risk of Ovarian Cancer?
Typically, the risk of ovarian cancer is higher in the presence of the following factors:
Genetic Disposition: Mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 (Breast Cancer Gene 1 and 2) genes are strongly correlated with ovarian cancer.
Family History: Having a family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer makes one more susceptible.
Age: Most cases are in women over 50 years, with peak incidence in the 60s and 70s.
Reproductive History: Never giving birth or having the first child after age 35.
Hormone Therapy: Long-term treatment with estrogen replacement therapy increases risk.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
The general signs of early ovarian cancer can be nonspecific and dismissed as gastrointestinal or benign problems. These include:
Abdominal swelling or bloating
Pelvic or abdominal pain
Loss of appetite or feeling full after a few bites
Urinary urgency or frequency
As the disease advances, more noticeable symptoms may appear:
Persistent fatigue
Changes in bowel habits, like constipation
Unexplained weight loss
Ascites (fluid build-up in the abdominal cavity)
Pain during intercourse
Diagnostic Procedures for Ovarian Cancer
Diagnosis starts with a full physical examination, including a pelvic examination, to identify abnormalities in the ovaries or surrounding tissues. A thorough medical history assessment can help identify risk factors and symptoms.
The role of imaging in the assessment of ovarian anomalies is also critical:
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): It is usually the first-line imaging modality used to evaluate ovarian masses and offers high-resolution images of the ovaries.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: Used to assess the extent of disease spread and to plan biopsies.
CA-125 Test and Other Markers: The CA-125 blood test looks for the presence of a protein that can be elevated in women with ovarian cancer.
It is helpful in monitoring treatment response and recurrence. Depending on the suspected type of ovarian cancer, other markers, e.g., Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) and Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP), may be assessed.
Get Your Heart Health Checked
Biopsy and Histopathological Confirmation of Ovarian Cancer
Healthcare providers may also use a biopsy to diagnose ovarian cancer. Some of the common procedures include:
Needle Biopsy: This is done by imaging to take a tissue or fluid sample.
Laparoscopic Sampling and Staging: A minimally invasive surgical process for abdominal cavity inspections, sample tissue collection, and determining the stage of cancer.
Histopathological examination confirms both the type and grade of cancer, which are vital for conceptualising treatment avenues. The pathologist evaluates tissue samples for malignant type and subtype, which is crucial for prognosis.
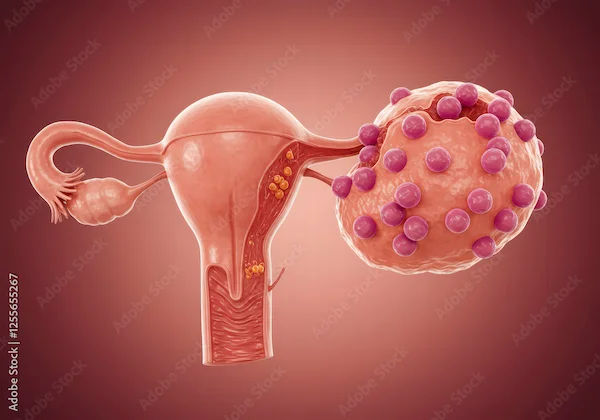
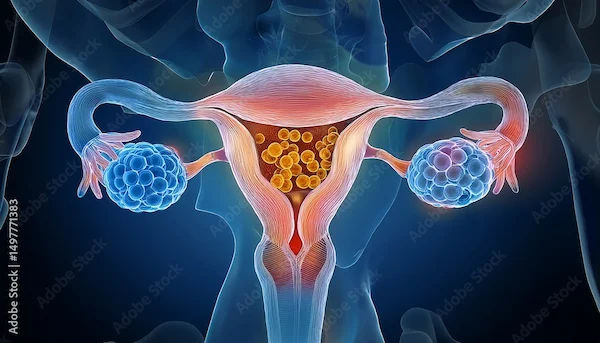
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer staging uses the FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) system to categorise the disease from Stage I (limited to the ovaries) to Stage IV (distant metastasis).
Prognosis is strongly dependent on the stage of diagnosis. Cancers in early stages have far better survival rates than in advanced stages. The staging also helps device treatment plans and predict outcomes.
Genetic Testing and Counseling of Ovarian Cancer
Certain mutations to the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 greatly increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer. Genetic testing can detect these mutations, influencing preventive and treatment decisions.
In this regard, genetic counselling assists patients in understanding their risk. It helps them make informed decisions regarding genetic testing and prophylactic options, including risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes).
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cancer
Doctors usually recommend surgery for managing ovarian cancer. The procedures depend on the stage and spread and may include:
Debulking Surgery: Removing as much of the tumour as possible.
Hysterectomy and Oophorectomy: Removal of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
Chemotherapy, usually involving platinum-based drugs, is routine for most stages of ovarian cancer. PARP (Poly ADP-Ribose Polymerase) inhibitors, for example, are a type of targeted therapy currently available for patients with certain genetic mutations.
Clinical trials are exploring immunotherapy and new drug combinations, bringing the promise of better results.
Consult Experts for Personalised Treatment
Living with Ovarian Cancer
Any type of cancer and its treatments can take a toll on the patient, emotionally and physically. Support groups, counselling services and palliative care services are essential resources for patients and families alike.
Survivorship care involves monitoring for recurrence at regular follow-up visits. These might include imaging, blood tests, and symptom assessments.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Although it may not always be possible to prevent ovarian cancer, a healthy lifestyle may reduce the risk. Moderation in diet, exercise, and abstaining from smoking are often advised.
Additionally, previous studies have found associations between oral contraceptive use and breastfeeding in reducing ovarian cancer risk. Consider visiting a healthcare provider for proper recommendations.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is a serious medical condition that can be hard to detect due to its nonspecific symptoms. However, better diagnostic tools as well as advances in treatment, are bringing hope. Positive outcomes depend on early discovery, genetic screening, and a multidisciplinary approach. By remaining updated and vigilant, people can overcome the complexities of this disease.
Consult Top Gynaecological Oncologists
Get Your Heart Health Checked
₹1550(₹3875)60% off
Consult Experts for Personalised Treatment

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Amit Choraria
Surgical Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MS (Surgery) Fellow, Surgical Oncology, Tata Medical Center (FSO) Fellow, European Board of Surgery (Surgical Oncology) (FEBS) Fellow, Minimal Access Surgery (FMAS) Fellow, Indian Association of Gastrointestinal Endosurgeons (FIAGES) UICC Fellow, Royal Marsden NHS, London, UK Visiting Scholar, Plastic Reconstructive Surgery, CGMH, Taiwan Fellow, Robotic Surgical Oncology, Vattikuti Foundation, USA
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata

Dr. Pakhee Aggarwal
Gynaecological Oncology & Robotic Surgery
18 Years • MBBS, MS, MRCOG (UK), FICOG, MIPHA, UICC Robotic Gynae-Oncology Fellowship (Canada), Commonwealth Gynae-Oncology Fellowship (Oxford, UK)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Priyanka Srivastava
Medical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS, MD, DrNB Medical Oncology, Fellowship (Medical Oncology) , PMCC, UOT Canada.
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad

Dr Bhawna Garg
Gynaecological Oncologist
26 Years • MBBS, MS, (PGI MS ROHTAK) FELLOWSHIP GYNECOLOGY ONCOLOGY, (CANCER INSTITUTE CHENNAI)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Consult Top Gynaecological Oncologists

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Amit Choraria
Surgical Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MS (Surgery) Fellow, Surgical Oncology, Tata Medical Center (FSO) Fellow, European Board of Surgery (Surgical Oncology) (FEBS) Fellow, Minimal Access Surgery (FMAS) Fellow, Indian Association of Gastrointestinal Endosurgeons (FIAGES) UICC Fellow, Royal Marsden NHS, London, UK Visiting Scholar, Plastic Reconstructive Surgery, CGMH, Taiwan Fellow, Robotic Surgical Oncology, Vattikuti Foundation, USA
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata

Dr. Pakhee Aggarwal
Gynaecological Oncology & Robotic Surgery
18 Years • MBBS, MS, MRCOG (UK), FICOG, MIPHA, UICC Robotic Gynae-Oncology Fellowship (Canada), Commonwealth Gynae-Oncology Fellowship (Oxford, UK)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Priyanka Srivastava
Medical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS, MD, DrNB Medical Oncology, Fellowship (Medical Oncology) , PMCC, UOT Canada.
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad

Dr Bhawna Garg
Gynaecological Oncologist
26 Years • MBBS, MS, (PGI MS ROHTAK) FELLOWSHIP GYNECOLOGY ONCOLOGY, (CANCER INSTITUTE CHENNAI)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

.webp)
.webp)