Blood Clot in Brain: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Learn about blood clots in the brain, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understand how to recognize signs early and seek timely care.

Written by Dr. M L Ezhilarasan
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
.webp?tr=q-80,f-webp,w-350,dpr-2,c-at_max 700w)
Introduction
A blood clot in the brain is a serious medical emergency that can alter lives in an instant. Often referred to as a stroke when it causes a blockage, this condition occurs when a clot disrupts the vital flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the brain, leading to potential cell death and lasting neurological damage. Understanding what it is, recognizing its warning signs, and knowing how to act can make the critical difference between recovery and disability, or worse. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about a cerebral blood clot, from its various types and subtle symptoms to its leading causes and the advanced treatment options available today. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, because when it comes to a brain clot, every second counts.
What Exactly is a Blood Clot in the Brain?
Not all brain clots are the same. The term broadly covers a few distinct conditions, primarily categorized by where and how the clot forms.
Ischaemic Stroke: The Blockage
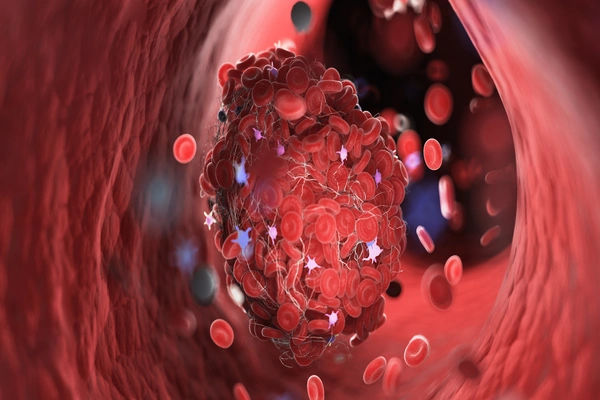
This is the most common type, accounting for about 87% of all strokes. It happens when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in an artery leading to the brain or travels from elsewhere in the body (becoming an embolus) and lodges in a narrower brain artery. This blockage starves brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, causing them to begin dying within minutes.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST): The Rare Type
CVST is a less common but dangerous condition where a clot forms in the brain's venous sinuses, the channels that drain blood from the brain. This blockage can prevent blood from draining out, leading to increased pressure inside the skull and causing haemorrhages or strokes.
Haematomas: Clots from Bleeding
Sometimes, a clot is the result of bleeding, not a cause of it. A head injury can cause blood vessels to rupture, and the pooled blood can form a clot outside the brain tissue but inside the skull (e.g., subdural or epidural haematoma). This mass can press on the brain, causing damaging pressure.
Consult a Neurologist for the best advice
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of a Brain Clot
Speed is everything. Recognizing these symptoms and calling emergency services immediately is crucial.
The FAST Warning Signs
- Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
- Arms: Ask them to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech: Ask them to repeat a simple phrase. Is their speech slurred or strange?
- Time: If you observe any of these signs, call emergency services immediately.
Other Critical Symptoms to Watch For
- Sudden, severe headache often described as "the worst headache of my life."
- Numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Vision problems in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination.
- Seizures without a previous history of epilepsy.
What Causes a Blood Clot to Form in the Brain?
A blood clot can form due to a complex interplay of factors.
Underlying Health Conditions
Conditions like atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat that can cause clots to form in the heart), high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes significantly increase risk. Genetic clotting disorders like Factor V Leiden can also predispose individuals.
Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors
Smoking, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and heavy alcohol use are major contributors. Certain medications, especially birth control pills combined with smoking, can elevate risk.
Trauma and Injury
A significant blow to the head can cause bleeding that leads to a compressive clot (haematoma). It's important to monitor for symptoms like a worsening headache, drowsiness, or vomiting after any head injury.
How is a Brain Clot Diagnosed?
Upon suspecting a stroke, doctors act swiftly.
Immediate Diagnostic Imaging
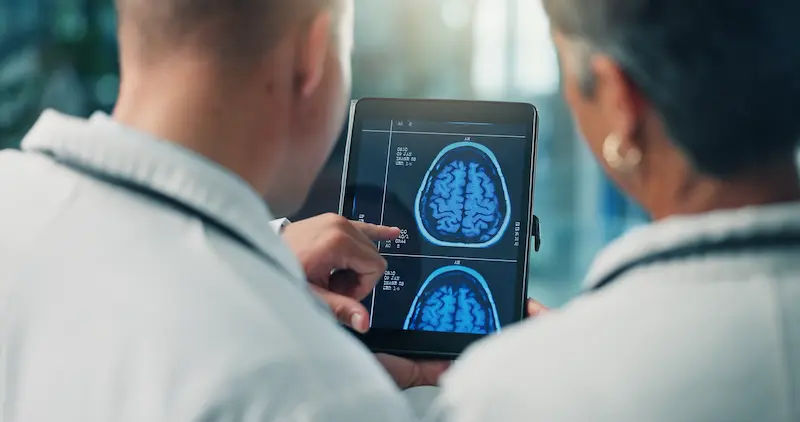
- CT Scan: This is often the first test done. It can quickly show bleeding in the brain and help distinguish between an ischaemic stroke and a hemorrhagic stroke.
- MRI: Provides a more detailed view of the brain and can detect smaller or acute strokes.
Additional Tests and Procedures
- CT or MR Angiography: These scans visualize the blood vessels in the neck and brain to pinpoint the location of the blockage.
- Blood Tests: To check clotting time, blood sugar levels, and other key markers.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart to check for clots that may have traveled from there.
Get Your Health Assessed
Treatment Options: Removing the Clot and Restoring Blood Flow
Treatment depends entirely on the type of clot.
Emergency Medication: Thrombolytics
For an ischaemic stroke, a clot-busting drug called tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) can be administered intravenously. It must be given within a few hours of symptom onset to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow.
Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Surgical Procedure
For larger clots, doctors may perform a thrombectomy. A catheter is threaded through an artery in the groin up to the brain clot. A tiny device at the catheter's tip can physically remove or break up the clot. This procedure can be effective up to 24 hours after symptoms begin for some patients.
Treating CVST and Haematomas
CVST is typically treated with anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting.
Haematomas often require surgical drainage to relieve pressure on the brain.
The Road to Recovery: Rehabilitation and Life After
Recovery is a marathon, not a sprint. The extent of recovery depends on the area of the brain affected and how quickly treatment was received.
The Role of Physical and Occupational Therapy
Rehabilitation is crucial. Physical therapy helps regain strength and coordination. Occupational therapy focuses on relearning daily activities like dressing and eating. Speech therapy assists with language and swallowing difficulties.
Managing Long-Term Effects
Some survivors may experience long-term effects like paralysis, speech difficulties, or emotional changes. A strong support system, ongoing therapy, and sometimes medication are key to managing these challenges and improving quality of life.
Can You Prevent a Blood Clot in the Brain?
While not all clots are preventable, you can drastically reduce your risk.
Controlling Medical Risk Factors
Work with your doctor to manage high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for tests like HbA1c and lipid profiles, making it easier to monitor these critical health metrics. If you have atrial fibrillation, follow your treatment plan diligently.
Adopting a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
This is your first line of defense. Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sodium, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight, avoid smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
Conclusion: Time is Brain
A blood clot in the brain is a dire emergency where immediate action is non-negotiable. The mantra "time is brain" underscores that every minute of delay results in the loss of millions of brain cells. By understanding the symptoms, remembering FAST, and knowing the causes and risk factors, you empower yourself to act quickly and seek life-saving treatment. Recovery is possible, and with advanced medical interventions and dedicated rehabilitation, many survivors go on to lead fulfilling lives. Your health is in your hands; prioritize preventive care and never ignore warning signs.
Consult a Neurologist for the best advice
Consult a Neurologist for the best advice

Dr. Aditendraditya Singh Bhati
Neurosurgeon
21 Years • MBBS(2004), DNB Neurosurgery(2014); MNAMS; Fellow Skull Base Endoscopy (Italy), Fellow Extended Skull Base ( Weill Cornell, USA), Fellow ZAP-X Radiosurgery. Member of American Association of Neurological Surgeons
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr Debnath Dwaipayan
Neurosurgeon
9 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen. Surgery), DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sahaj Agrawal
Neurologist
8 Years • DM Neurology (AIIMS, New Delhi), MD General Medicine, MBBS
Sri Ganganagar
Dr. Sahaj Agarwal, Sri Ganganagar
Consult a Neurologist for the best advice

Dr. Aditendraditya Singh Bhati
Neurosurgeon
21 Years • MBBS(2004), DNB Neurosurgery(2014); MNAMS; Fellow Skull Base Endoscopy (Italy), Fellow Extended Skull Base ( Weill Cornell, USA), Fellow ZAP-X Radiosurgery. Member of American Association of Neurological Surgeons
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr Debnath Dwaipayan
Neurosurgeon
9 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen. Surgery), DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sahaj Agrawal
Neurologist
8 Years • DM Neurology (AIIMS, New Delhi), MD General Medicine, MBBS
Sri Ganganagar
Dr. Sahaj Agarwal, Sri Ganganagar
More articles from Stroke
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a blood clot in the brain be cured?
Yes, especially if treated immediately. With prompt medical intervention like thrombolysis or thrombectomy, the clot can be dissolved or removed, potentially reversing symptoms. However, the term 'cured' must be balanced with the potential for long-term effects that require management and rehabilitation.
What is the survival rate for a cerebral blood clot?
The survival rate varies greatly depending on the type of clot, its location, the patient's age, and how quickly treatment is received. For ischaemic strokes, the 30-day survival rate is around 70-80%. Early treatment is the biggest factor in improving survival odds and reducing disability.
What is the difference between a brain clot and a brain aneurysm?
A brain clot is a mass of coagulated blood that blocks flow. A brain aneurysm is a weak, bulging spot on an artery wall. While an aneurysm itself isn't a clot, if it ruptures, it causes bleeding into the brain (a hemorrhagic stroke), which is a different type of medical emergency.
How long does it take to recover from a blood clot in the brain?
Recovery is highly individual. The most significant gains often occur in the first three to six months, but recovery can continue for years. Continuous rehabilitation is essential for improving function and quality of life.
Can stress cause a blood clot in the brain?
Stress itself does not directly cause a clot. However, chronic stress contributes to risk factors like high blood pressure and can lead to unhealthy behaviors (poor diet, smoking), which indirectly increase the overall risk of a stroke.