Common Urinary Problems in the Elderly
Learn about common urinary problems in the elderly, including causes, symptoms, and management tips to maintain urinary health in older adults.

Written by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes, and the urinary system is no exception. Common urinary problems in the elderly are a frequent concern, affecting millions of seniors and often impacting their quality of life, independence, and dignity. From occasional leaks to persistent infections, these issues are widespread but often under-discussed due to embarrassment. However, understanding these conditions is the first step toward effective management and treatment. This guide will walk you through the most prevalent urinary tract issues affecting older adults, explaining their causes, symptoms, and the wide range of solutions available today. Remember, while these problems are common, they are not an inevitable part of ageing, and help is always available.
Why Ageing Increases Urinary Tract Risks
The ageing process brings about natural changes that can make the urinary system more vulnerable. It's not just one factor but a combination of physiological shifts that contribute to urinary issues in seniors.
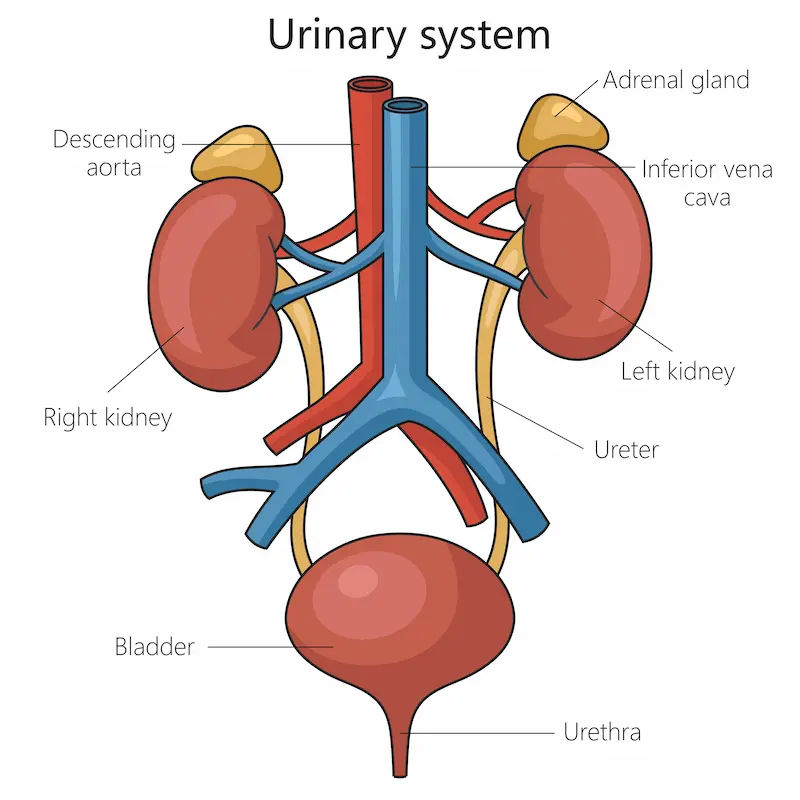
Physiological Changes in the Bladder and Kidneys
With age, the bladder wall changes. It becomes less elastic and may hold less urine than before. The kidneys also become less efficient at concentrating urine, especially at night, leading to increased urine production. Additionally, the muscles supporting the bladder can weaken, making it harder to control urination.
The Role of Weakened Pelvic Floor Muscles
The pelvic floor muscles act like a hammock, supporting the bladder, urethra, and other organs. Over time, especially in women after childbirth and menopause, these muscles can stretch and weaken. This loss of support is a primary contributor to stress incontinence.
Impact of Underlying Health Conditions
Chronic conditions prevalent in older adults, such as diabetes (which can damage nerves), neurological disorders like Parkinson's or stroke, and mobility-limiting arthritis, can significantly interfere with bladder control and function.
Consult a Urologist for the best advice
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): A Leading Concern
UTIs are one of the most common infections in the elderly, but they can present differently than in younger adults, making them harder to spot.
Why the Elderly Are More Susceptible to UTIs
Factors include incomplete bladder emptying due to prostate issues or weakened muscles, a weakened immune system, and, for women, a decline in oestrogen after menopause which changes the protective lining of the urinary tract.
Recognising UTI Symptoms in Seniors (Atypical Signs)
While classic symptoms like burning during urination or fever may occur, seniors often show "atypical" signs. These can include sudden confusion or delirium, agitation, hallucinations, dizziness, falls, or just a general decline in overall condition. This is why any sudden change in behaviour should prompt a check for a UTI.
Complications of Untreated UTIs
If left untreated, a simple UTI can progress to a serious kidney infection (pyelonephritis) or even sepsis, a life-threatening bloodstream infection. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical.
Understanding Urinary Incontinence: It's Not Inevitable
Urinary incontinence in older women and men is a common issue, but it is not a normal part of ageing. It is a medical condition with several types.
Stress Incontinence: Causes and Examples
This occurs when physical movement or activity like coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects puts pressure on the bladder, causing leakage. It's often due to those weakened pelvic floor muscles or a weakened urethral sphincter.
Urge Incontinence (Overactive Bladder)
This is characterised by a sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by an involuntary loss of urine. You may need to urinate frequently, including throughout the night. It's essentially caused by involuntary bladder contractions.
Overflow Incontinence and Functional Incontinence
Overflow Incontinence: You experience frequent or constant dribbling of urine due to a bladder that doesn't empty completely, often linked to urinary retention in elderly men with BPH.
Functional Incontinence: A physical or mental impairment, like severe arthritis or dementia, prevents you from getting to the toilet in time.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Enlarged Prostate in Men
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that affects most men as they age. The growing prostate can squeeze the urethra, like pinching a straw, disrupting urine flow.
How BPH Affects Urination
It causes a host of frustrating symptoms, including a weak urine stream, difficulty starting urination, dribbling at the end of urination, a feeling that the bladder isn't fully empty, and increased frequency and urgency, especially at night (nocturia).
Symptoms and Diagnosis of an Enlarged Prostate
Diagnosis typically involves a discussion of symptoms, a digital rectal exam (DRE), a urine test, and a PSA blood test to rule out prostate cancer. A urinary flow test or ultrasound may also be used to see how well the bladder is emptying.
Other Common Urinary Issues
Besides the main conditions, older adults may face other urinary challenges:
Nocturia: Frequently Waking Up to Urinate at Night
Waking up two or more times per night to urinate is called nocturia. It's a major disruptor of sleep and can increase the risk of falls. Causes range from excess fluid intake before bed and certain medications to more serious conditions like congestive heart failure, sleep apnoea, or untreated diabetes.
Urinary Retention: The Inability to Empty the Bladder
This can be acute (a sudden, painful inability to urinate) or chronic (a persistent difficulty in completely emptying the bladder). Causes include BPH, bladder muscle weakness, nerve damage, or as a side effect of certain medications.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Urinary Problems
Getting a proper diagnosis is crucial. A doctor will likely start with a detailed medical history and may ask you to keep a bladder diary for a few days. This is followed by a physical exam. If your symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation. They may recommend tests like a urinalysis to check for infection, blood tests, or urodynamic testing to measure pressure and flow in the bladder.
Get Your Health Assessed
Treatment and Management Strategies
The good news is that most common urinary problems are highly treatable. Options range from simple lifestyle changes to medical procedures.
Lifestyle Modifications and Bladder Training
This is often the first line of defense. It includes timed voiding, double voiding (waiting a moment and trying again to empty fully), fluid management, and dietary changes (avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods).
Medications for Various Urinary Conditions
Many drugs can help, including antibiotics for UTIs, anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists for overactive bladder, and alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for BPH.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures
For cases that don't respond to other treatments, options include minimally invasive procedures for BPH (like Rezum or UroLift), sling procedures for stress incontinence, or Botox injections into the bladder muscle for severe overactive bladder.
Prevention Tips for Maintaining Urinary Tract Health
Proactive steps can make a significant difference in preventing or minimising urinary issues in seniors.
Hydration and Dietary Choices
Drink adequate water throughout the day (but reduce intake before bedtime). Limit caffeine and alcohol. Eat a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation, which can pressure the bladder.
Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels)
These exercises strengthen the muscles that control urination. Both men and women can benefit from them. Consistency is key.
Smart Bathroom Habits
Take your time to empty your bladder completely when you go. For women, always wipe from front to back to prevent spreading bacteria from the rectum to the urethra.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help
Do not dismiss urinary problems as "just getting old." Seek medical advice if you experience:
Blood in your urine (haematuria)
Painful or burning urination
Incontinence that is new or worsening
A sudden, strong need to urinate frequently
Inability to urinate
Any sudden change in mental status (confusion, agitation)
Conclusion
Navigating common urinary problems in the elderly can feel overwhelming, but it's important to remember that you are not alone and that effective help is available. From understanding the underlying causes like weakened muscles or an enlarged prostate to implementing practical lifestyle changes and exploring medical treatments, there are numerous paths to regaining control and comfort. The most crucial step is to break the silence and speak with a healthcare professional. Addressing these issues proactively can dramatically improve your quality of life, restore your confidence, and help you maintain your independence for years to come. Don't let embarrassment stand in the way of your well-being.
Consult a Urologist for the best advice
Consult a Urologist for the best advice

Dr. Prabir Basu
Urologist
19 Years • MBBS, MS General Surgery, DNB Genito-Urinary Surgery
Jodhpur Park
Dr. Prabir Basu urology clinic, Jodhpur Park
(200+ Patients)
Dr Debanga Sarma
Urologist
10 Years • MBBS, MS (GENERAL SURGERY)M.Ch (UROLOGY)
Guwahati
Apollo Clinic Guwahati, Assam, Guwahati
Dr S K Singhanina
Urologist
25 Years • MBBS/MS/DNB AND MCH UROLOGY
Guwahati
Apollo Clinic Guwahati, Assam, Guwahati
Dr P K Bagchi
Urologist
10 Years • MBBS, MS (Gen. Surgery) M. Ch. (Urology)
Guwahati
Apollo Clinic Guwahati, Assam, Guwahati

Dr. Ramesh H
Urologist
16 Years • MBBS, MS , Mch( Urology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
More articles from Urology Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most common urinary problem in the elderly?
Urinary incontinence and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent issues. In men, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is also extremely common.
2. Can dehydration cause urinary problems in the elderly?
Yes, paradoxically, dehydration can concentrate urine, irritating the bladder and potentially increasing the risk of UTIs. However, overhydration, especially before bed, can worsen incontinence and nocturia. Balanced hydration is key.
3. Are there any effective home remedies for an overactive bladder?
Yes, several behavioural strategies are highly effective. These include scheduled toilet trips (timed voiding), bladder training (gradually increasing the time between bathroom visits), performing pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), and avoiding known bladder irritants like caffeine, artificial sweeteners, and acidic foods.
4. How is a UTI diagnosed in an elderly person with dementia?
Since verbalising symptoms is difficult, doctors rely on observing behavioural changes (e.g., new confusion, agitation) and running diagnostic tests. A urinalysis and urine culture are essential to confirm the presence of bacteria and identify the correct antibiotic. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for these tests, which can be less stressful for the patient.
5. When is urinary incontinence a sign of something serious?
While often not serious on its own, you should seek immediate medical attention if incontinence is sudden in onset, is accompanied by blood in the urine, severe pelvic pain, weakness or numbness in the legs, or changes in bowel function, as these could indicate a more serious neurological or anatomical issue.