Diabetes Management
Eggplants and Diabetes: A Healthy Addition to Your Diet
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 19 September 2023, Updated on - 21 February 2024
Share this article
0
0 like

If you have diabetes, you're likely conscious of what you eat to effectively manage your blood sugar levels. Eggplants, also called brinjal or baingan are known for their rich flavour and versatility in cooking, and can be a nutritious addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. In this blog, we'll explore the benefits of including eggplants in your meals and how they can fit into your diabetes management plan.
What is the Nutritional Value of Eggplants?
Eggplants are low in calories and carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for individuals with diabetes. They are a good source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. 100g raw eggplant contains approximately:
- Calories: 25 Kcal
- Carbohydrates: 6 grams (2% of the Daily Value)
- Dietary Fiber: 3 grams (12% of the Daily Value)
- Protein: 1 gram (2% of the Daily Value)
*The Percent Daily Values are calculated based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your specific daily values may vary, either being higher or lower, depending on your individual calorie requirements
Benefits for Diabetics
Apart from holding a significant amount of nutritional value, here are other benefits of eggplants for individuals living with diabetes:
- Low in Carbohydrates: Eggplants are relatively low in carbs compared to many other vegetables. This means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to other vegetables.
- Rich in Fiber: The fiber content in eggplants can aid in regulating blood sugar. Dietary fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, helping to prevent spikes in blood sugar after meals.
- Antioxidant Properties: Eggplants contain antioxidants, including vitamins C and K, which can help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.
- Heart Health: Maintaining cardiovascular health is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Eggplants are a source of potassium, when consumed in moderation it helps regulate blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart complications often associated with diabetes.
- Weight Management: Due to their low-calorie content and ability to make you feel full, eggplants can be a valuable addition to a weight management strategy, which is often a key aspect of diabetes management.
How to Incorporate Eggplants into Your Diet?
To enjoy the benefits of eggplants while managing diabetes:
- Include grilled or roasted eggplant in salads.
- Make a hearty eggplant stew or curry with plenty of fiber-rich vegetables.
- Experiment with stuffed eggplants filled with lean protein and vegetables.
Conclusion
Remember that portion control is essential, as overconsumption of any food, even low-carb vegetables like eggplants, can impact blood sugar levels. It's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to tailor your diet to your specific diabetes management needs.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Managing Diabetes with a Gluten-Free Diet
Managing both diabetes and celiac disease can be challenging but not unachievable. A strict gluten-free diet is beneficial but requires careful planning and regular monitoring. The presence of healthcare professionals can provide personalised dietary advice and help navigate the complexities of these conditions, ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Diabetes Management
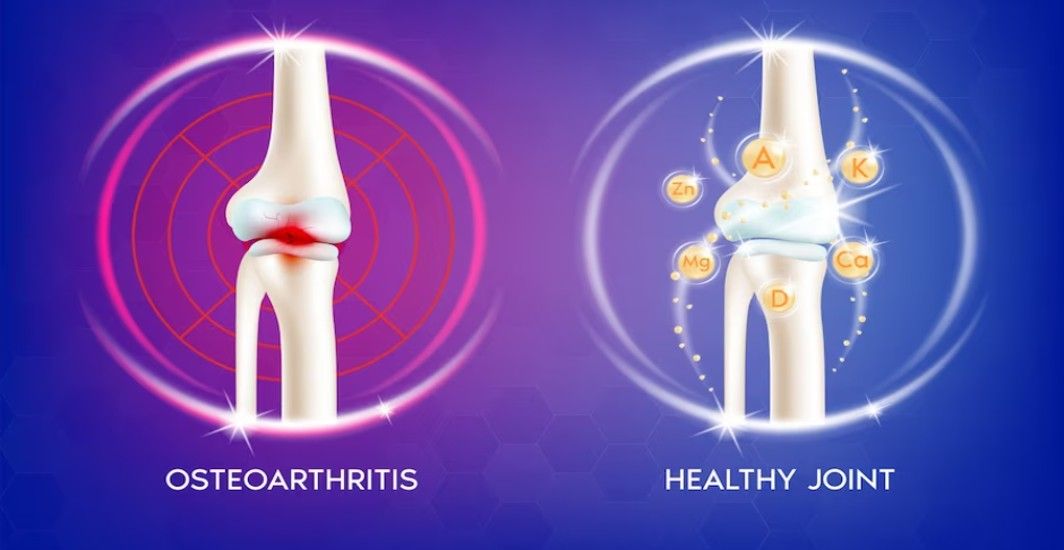
Navigating Osteoarthritis and Diabetes For Better Joint Health
If uncontrolled or poorly managed, diabetes can worsen osteoarthritis. Diabetes can increase inflammation, which exacerbates joint pain and AGEs. These, in turn, cause high blood sugar and speed up joint damage. Effectively managing both conditions involves a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and strict adherence to prescribed medications. This comprehensive approach helps control symptoms and improves overall quality of life.
Diabetes Management
How Type 2 Diabetes May Be Linked to an Unhealthy Gut?
A recent study found that Lactobacillus, a microbe containing numerous bacterial strains and found in probiotics and fermented foods like pickled vegetables and fortified dairy products, can improve metabolism and reduce the risk of diabetes. Another study revealed that individuals consuming a high-fibre diet possess higher levels of indolepropionic acid in their blood. This anti-inflammatory agent, produced by gut bacteria, helps lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Managing Diabetes with a Gluten-Free Diet
Managing both diabetes and celiac disease can be challenging but not unachievable. A strict gluten-free diet is beneficial but requires careful planning and regular monitoring. The presence of healthcare professionals can provide personalised dietary advice and help navigate the complexities of these conditions, ensuring optimal health outcomes.

Diabetes Management
Navigating Osteoarthritis and Diabetes For Better Joint Health
If uncontrolled or poorly managed, diabetes can worsen osteoarthritis. Diabetes can increase inflammation, which exacerbates joint pain and AGEs. These, in turn, cause high blood sugar and speed up joint damage. Effectively managing both conditions involves a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and strict adherence to prescribed medications. This comprehensive approach helps control symptoms and improves overall quality of life.

Diabetes Management
How Type 2 Diabetes May Be Linked to an Unhealthy Gut?
A recent study found that Lactobacillus, a microbe containing numerous bacterial strains and found in probiotics and fermented foods like pickled vegetables and fortified dairy products, can improve metabolism and reduce the risk of diabetes. Another study revealed that individuals consuming a high-fibre diet possess higher levels of indolepropionic acid in their blood. This anti-inflammatory agent, produced by gut bacteria, helps lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.


