Orthopedic Conditions
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Treatment & Complications
6 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 18 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
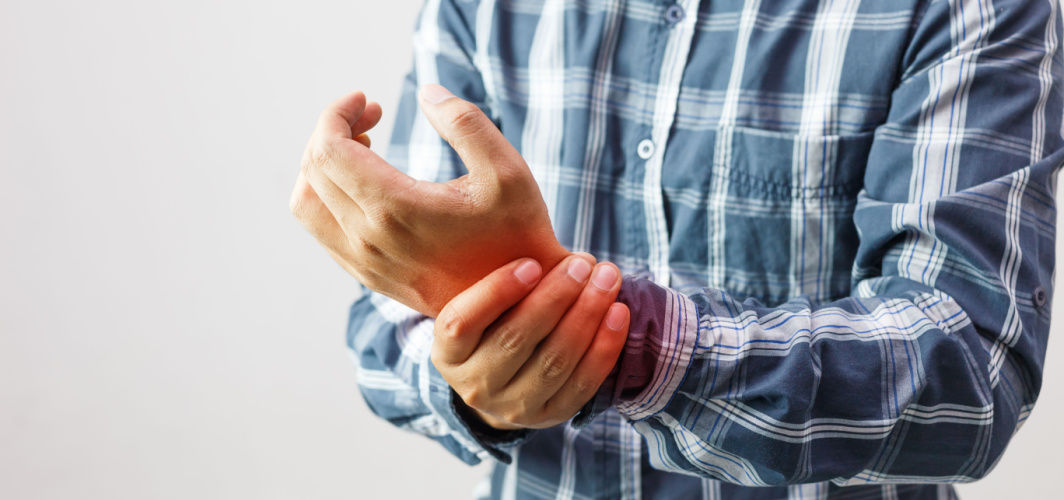

Understanding rheumatoid arthritis is crucial as untreated RA can lead to permanent joint deformity and a decreased quality of life. Early recognition and diagnosis are essential for effective management and improved quality of life for individuals living with RA. Moreover, knowing Rheumatoid Arthritis risk factors can help individuals identify warning signs and take preventive measures promptly. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each aspect of Rheumatoid Arthritis to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of the joints. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks synovium, the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and damage.
Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
It's important to remember that Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms may vary from person to person. If you experience any of these signs and symptoms, seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis.
1. Joint Pain and Stiffness
One of the hallmark Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms is joint pain and stiffness, typically in the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet. The pain is usually worse after periods of inactivity.
2. Swelling and Inflammation in the Joints
Inflamed joints may appear swollen, red, and feel warm to the touch. This inflammation can cause joint deformities if left untreated.
3. Morning Stiffness
Morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour is a common Rheumatoid Arthritis symptom. Performing simple tasks like getting dressed or brushing your teeth may become difficult.
4. Fatigue
People with RA often experience persistent fatigue and a feeling of overall tiredness. This fatigue may be due to the body's immune system being activated, leading to increased energy consumption.
5. Other Symptoms
RA can also affect other parts of the body, leading to symptoms like dry eyes and mouth (due to associated Sjögren's syndrome), nodules under the skin, chest pain with breathing (due to inflammation of the lining around the heart), and eye inflammation (uveitis).
Risk Factors Linked to Rheumatoid Arthritis
Knowledge about Rheumatoid Arthritis risk factors can help individuals make informed decisions and take necessary precautions to minimize their chances of developing this chronic condition
1. Genetic Factors
Rheumatoid Arthritis is known to have a strong genetic component. If you have a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, who has been diagnosed with RA, your risk of developing the condition is higher.
Certain genes, such as the HLA-DRB1 gene, have also been associated with an increased susceptibility to RA.
2. Gender and Age
RA affects women more often than men. Women are two to three times more likely to develop RA than men. Additionally, RA can occur at any age, but most commonly it begins between the age of 30 and 60. However, it can also develop in children and older adults.
3. Lifestyle Choices
Smoking has been strongly linked to an increased risk of developing RA. Furthermore, a sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary choices may increase the risk of developing RA or worsening the symptoms.
4. Other Potential Risk Factors
While the exact cause of RA remains unknown, several other factors including obesity, hormonal changes in women (such as during pregnancy or after menopause), and exposure to certain occupational hazards like asbestos or silica dust have been identified as potential Rheumatoid Arthritis risk factors.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis by taking a multidisciplinary approach. For an appropriate treatment to start, a precise Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosis is necessary. Let's look at various methods used for Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosis:
1. Medical Evaluation and History Taking
Detailed questions about the patient's symptoms and their duration are asked by the healthcare provider to identify the characteristic symptoms of RA, such as joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
The healthcare provider will also inquire about the patient's family history of autoimmune diseases, as RA has a genetic component.
2. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination may include assessing joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. They may also check for any signs of inflammation or deformity in your joints.
3. Lab tests
Blood tests such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are commonly used to identify specific markers associated with RA. These tests can help confirm the Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosis and differentiate it from other forms of arthritis.
4. Imaging techniques
X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may also be used to evaluate joint damage and assess disease progression. These imaging studies can provide valuable information about the extent of joint inflammation, erosion, and other structural changes.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
While there is no cure for RA, proper treatment and self-care can help effectively manage Rheumatoid Arthritis and improve overall quality of life. Let us explore some of these options in detail.
1. Medications for Managing Symptoms and Inflammation
One of the primary goals of RA treatment is to control inflammation and relieve pain.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine are commonly prescribed to control inflammation and relieve pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended for pain relief and reducing inflammation.
- Corticosteroids may also be used for short-term management of severe symptoms.
2. Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
In severe cases where joint damage is extensive and conservative treatment measures have failed, surgery may be considered. Surgical options include synovectomy and joint replacement surgery.
3. Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care for RA Management
In addition to medication and surgery, certain lifestyle changes and self-care practices can help manage RA symptoms and improve overall well-being. These may include:
- Regular exercise and weight management
- Healthy diet
- Stress management
- Heat and cold therapy
Individuals with RA must work closely with their healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.
Complications Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead to various complications beyond joint damage and deformities. In this section, we will provide a brief overview of some of the key Rheumatoid Arthritis complications.
1. Joint Damage and Deformities
Over time, the persistent inflammation caused by RA can erode the cartilage and bone within the joints, leading to irreversible damage. Joint deformities, such as swan-neck deformity or boutonniere deformity in the fingers, can develop as the disease progresses. Individuals with RA should monitor their overall health regularly to manage potential Rheumatoid Arthritis complications.
2. Systemic Effects of RA on Other Organs
RA is not limited to joints alone; it can impact other organs as well. The chronic inflammation associated with this condition can affect various systems in the body, including:
- Heart
- Lungs
- Eyes
- Blood vessels
It increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases like heart attack and stroke. It can also cause lung complications like interstitial lung disease.
3. Emotional Impact of RA
Living with a chronic condition like RA can take a toll on an individual's mental health and emotional well-being. The constant pain, physical limitations, and lifestyle changes associated with RA can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid Arthritis can be challenging to live with, but effective management is possible with the right support and guidance. Remember, early intervention is essential to mitigate the harm caused by RA, so don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for assistance. By seeking medical advice promptly, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and connecting with emotional support networks, you can take control of RA and lead a fulfilling life.
Orthopedic Conditions
Consult Top Orthopaedicians
View AllFrequently Asked Questions
What are the key symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What are the key symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosed?
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosed?
Can lifestyle changes help manage Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Can lifestyle changes help manage Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Can complementary therapies be used alongside conventional treatment for RA?
Can complementary therapies be used alongside conventional treatment for RA?
What complications can arise from Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What complications can arise from Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Orthopedic Conditions
Neck Rotation To Shoulder Shrugs, 7 Effective Exercises For Neck Pain Relief
Neck pain exercises are meant to alleviate pain and discomfort in the neck and shoulder area. These exercises can improve flexibility and strength of the neck and shoulder muscles, thereby, preventing future neck pain.
Orthopedic Conditions
Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery: Procedure and Recovery Time
Learn about the shoulder arthroscopy procedure, what to expect during and after surgery, and the estimated recovery time. Discover the latest advancements and factors that can contribute to a successful outcome.
Orthopedic Conditions
Surprising but True! A Small Wound Can Result In Severe Bone Infection. Know how
Osteomyelitis is a severe bone infection that can destroy bone tissue. It occurs when an open wound exposes the bone to Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Natural Ways to Get Relief from Arthritis
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Orthopedic Conditions
Neck Rotation To Shoulder Shrugs, 7 Effective Exercises For Neck Pain Relief
Neck pain exercises are meant to alleviate pain and discomfort in the neck and shoulder area. These exercises can improve flexibility and strength of the neck and shoulder muscles, thereby, preventing future neck pain.

Orthopedic Conditions
Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery: Procedure and Recovery Time
Learn about the shoulder arthroscopy procedure, what to expect during and after surgery, and the estimated recovery time. Discover the latest advancements and factors that can contribute to a successful outcome.

Orthopedic Conditions
Surprising but True! A Small Wound Can Result In Severe Bone Infection. Know how
Osteomyelitis is a severe bone infection that can destroy bone tissue. It occurs when an open wound exposes the bone to Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria.



