What Tests Should You Do for Chronic Back Pain?
Suffering from chronic back pain? Discover the essential tests, from X-rays to MRIs, that can help diagnose the cause and guide your treatment. Get the answers you need to find relief.

Written by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula
Reviewed by Dr. Siri Nallapu MBBS
Last updated on 9th Sep, 2025

Chronic back pain affects millions of people around the world and can have a profound impact on quality of life, productivity, and emotional well-being. Unlike acute pain, which usually improves within a few weeks, chronic back pain lingers for three months or more and often resists simple treatments. Its intensity can vary widely, from a persistent ache to sharp, debilitating discomfort, and its causes are just as diverse. That’s why accurate diagnosis is essential to finding lasting relief.
Living with long-term pain can feel overwhelming. It may lead to reduced physical activity, muscle deconditioning, and a cycle of worsening symptoms. The emotional strain can be just as challenging as the physical discomfort. But the good news is that understanding the source of your pain is the first step toward meaningful improvement.
In this article, we’ll explore the common causes of chronic back pain, explain when it’s time to seek medical help, and introduce the diagnostic tests that doctors use to identify the root of the problem. With the right information and support, you can take confident steps toward effective treatment and a better quality of life.
Understanding Chronic Back Pain
Chronic back pain is defined by its duration, lasting for 12 weeks or more, even after an initial injury or underlying cause has been treated. It can affect any part of the back, though the lower back (lumbar region) is the most common site. The spine is a complex structure of bones (vertebrae), discs (cushioning between vertebrae), ligaments, muscles, and nerves, and issues with any of these components can lead to chronic pain.
Common reasons for chronic back pain include:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs between our vertebrae can lose fluid and flexibility, leading to pain and stiffness. This is a natural part of ageing for many, but for some, it can be quite painful.
- Herniated or Slipped Discs: Sometimes, the soft inner material of a disc can push out through a tear in its tougher outer layer, pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, often leading to leg pain, numbness, and weakness in addition to back pain, especially when walking.
- Osteoarthritis: The cartilage that cushions the joints in the spine can wear down, leading to bone-on-bone rubbing, inflammation, and pain.
- Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the one below it, causing pain and instability.
- Muscle or Ligament Strain: While acute strains usually heal, persistent poor posture, repetitive movements, or overuse can lead to chronic muscle tension and pain.
- Skeletal Irregularities: Conditions like scoliosis (a curvature of the spine) or kyphosis (excessive outward curvature of the upper back) can cause long-term back pain.
- Nerve Damage: Sciatica, for instance, is a type of nerve pain caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which originates in the lower back and extends down the leg.
- Non-Spinal Causes: Less commonly, back pain can be referred pain from other conditions like kidney stones, infections, tumours, or inflammatory diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis.
Given the wide array of potential causes, pinpointing the specific origin of chronic back pain requires a thorough and systematic diagnostic approach.
When Should You See a Doctor for Chronic Back Pain?
While short-term back pain often improves with rest, activity modification, or self-care, chronic back pain requires medical evaluation to identify the underlying cause.
You should seek medical advice if your back pain:
- Lasts longer than three months
- Is severe or worsening over time
- Does not improve with rest or position changes
- Radiates into the legs
- Is associated with numbness, tingling, or weakness
- Affects bladder or bowel control
- Is accompanied by unexplained weight loss or fever
- Worsens at night or disrupts sleep
- Follows a significant fall or injury
Avoid delaying care or attempting to self-diagnose, as early evaluation allows for more effective treatment and can prevent the pain from becoming more severe or disabling. Your doctor will consider your history, perform a physical exam, and may recommend diagnostic tests to determine the best course of action.
Key Tests to Help Identify the Cause of Your Back Pain
If you're living with ongoing back pain, getting to the root of the problem is essential for lasting relief. Doctors rely on a variety of diagnostic tests to understand what's going on inside your spine and surrounding tissues. The right test for you will depend on your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination findings. Below are the most commonly used tests to evaluate back pain and why they matter:
1. X-ray
What it is: A quick, painless imaging test that uses a small amount of radiation to capture images of bones.
What it reveals: X-rays are useful for identifying:
- Bone fractures or breaks
- Curvature or alignment issues like scoliosis
- Signs of arthritis, such as bone spurs or narrowed joint spaces
- Some bone-related tumours
Limitations: They do not show soft tissues like muscles, discs, or nerves. So even if your X-ray looks normal, you may still have issues such as disc herniation, causing pain.
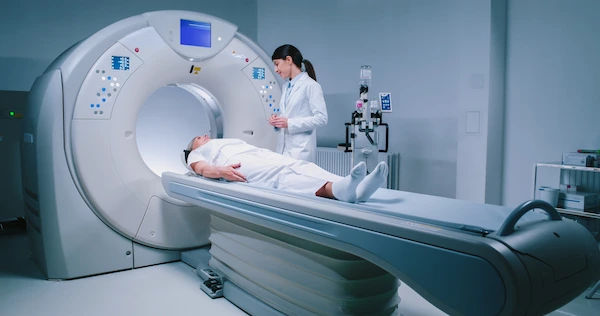
2. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
What it is: An advanced imaging test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues and spinal structures without radiation.
What it reveals: An MRI is ideal for detecting:
- Herniated or degenerated discs
- Nerve compression or inflammation
- Muscle or ligament damage
- Tumours, infections, or inflammatory diseases affecting the spine
When it's used: It is often chosen when nerve issues are suspected or if surgery is being considered.
3. CT (Computed Tomography) Scan
What it is: A more detailed version of an X-ray that combines multiple images to create cross-sectional views of bones and some soft tissues.
What it reveals: CT scans are helpful in spotting:
- Complex fractures
- Bone overgrowth (spurs) pressing on nerves
- Spinal canal narrowing (spinal stenosis)
- Some tumours and infections
When it's used: Recommended when more detail of bone structures is needed, or if an MRI isn’t suitable due to metal implants or other contraindications.
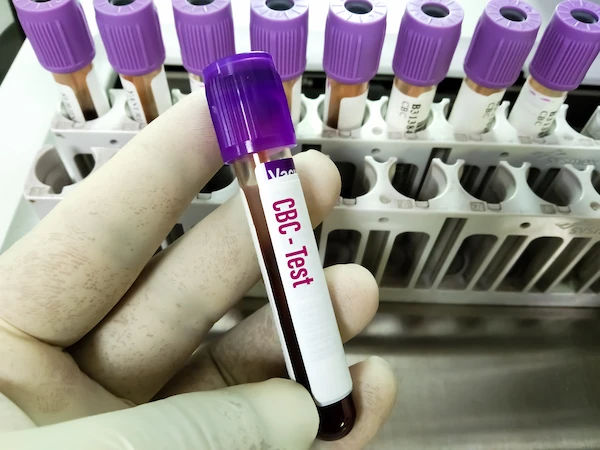
4. Blood Tests
What they are: Simple lab tests that can provide information about underlying infections or inflammatory conditions that might contribute to back pain.
What they reveal:
- Elevated markers like ESR or CRP may suggest inflammation or infection
- A complete blood count (CBC) can point to infection or anaemia
- The presence of the HLA-B27 gene can indicate risk for inflammatory spinal diseases
- Low vitamin D levels may be linked to bone pain and weakness
Limitations: While not diagnostic on their own for most back problems, they can help uncover systemic issues that influence your symptoms.
Get Your Health Assessed Here
5. Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG (Electromyography)
What they are: Tests that measure how well your nerves and muscles are working.
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS): Assess the speed and strength of nerve signals.
- EMG: Involves inserting small needles into muscles to test electrical activity.
What they reveal: These studies are useful for:
- Identifying nerve irritation or damage (such as from a herniated disc)
- Locating pinched nerves
- Distinguishing between spinal and non-spinal nerve problems
When they're used: Recommended if you're experiencing numbness, tingling, weakness, or radiating pain down the legs or arms.
6. Bone Scan
What it is: A nuclear imaging test where a small amount of radioactive material is injected to highlight areas of active bone metabolism.
What it reveals: Bone scans are particularly useful for:
- Detecting stress fractures
- Diagnosing bone infections (osteomyelitis)
- Identifying bone tumours or areas of arthritis
When it's used: It is often used when other tests have been inconclusive or when specific conditions like infection or cancer are suspected.
Get Tested Easily with Apollo 24/7
If your doctor recommends diagnostic tests to investigate chronic back pain, Apollo 24|7 offers a trusted and convenient solution. Through its extensive network of certified laboratories and diagnostic centres, Apollo 24|7 provides access to a wide range of tests, including X-rays, MRI and CT scans, blood tests, and nerve conduction studies.
With Apollo 24|7, you can benefit from:
- Home sample collection for lab tests
- Simple online booking through the Apollo 24|7 website or mobile app
- Secure digital reports delivered directly to your device
- Specialist consultations for expert follow-up and care planning
Final Thoughts
Chronic back pain is a complex condition with many possible causes, and it often requires more than a one-size-fits-all approach. Through a detailed medical evaluation, including a review of symptoms, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can identify the underlying source of your pain. This clarity is essential for developing an effective, tailored treatment plan that addresses the specific issue rather than just masking symptoms. Early diagnosis and targeted therapy not only relieve discomfort but also help prevent further complications, improve mobility, and restore your quality of life. If you've been living with persistent back pain, seeking timely medical guidance is the most important step toward recovery and long-term wellness.