Cervical Cancer Signs; Recognising Early Warning Symptoms
Learn to recognise the early warning signs of cervical cancer, from abnormal bleeding to unusual discharge, and understand the importance of prevention and regular screening.

Written by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
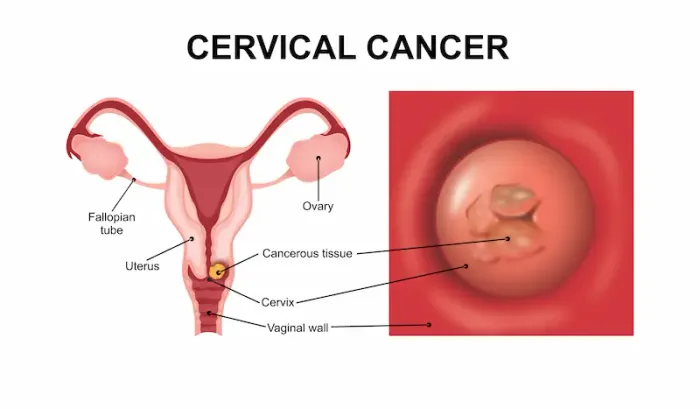
Introduction
Cervical cancer develops in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. While the word "cancer" can be alarming, it's crucial to know that cervical cancer is one of the most preventable and treatable gynaecologic cancers when detected early. The key lies in understanding the signs your body may be sending and taking proactive steps through regular screening. This article will guide you through the often subtle early warning signs of cervical cancer, the symptoms of more advanced stages, and the vital role of prevention. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, reduce anxiety, and emphasise that paying attention to changes in your body is the first and most important step towards safeguarding your health. Remember, many of these symptoms can be caused by conditions other than cancer, but they always warrant a conversation with a healthcare professional.
What is Cervical Cancer? A Brief Overview
Cervical cancer begins when healthy cells in the cervix develop mutations in their DNA. These mutations cause the cells to grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a mass called a tumour. These cancerous cells can invade nearby tissues and may eventually spread (metastasise) to other parts of the body. The vast majority of cervical cancer cases (over 95%) are linked to long-term infection with specific types of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted infection. It's important to understand that while HPV is extremely common, only a small fraction of women with HPV will actually develop cervical cancer, as the immune system typically clears the virus. The problem arises when a high-risk HPV infection persists for many years, leading to pre-cancerous changes that can, if left untreated, progress to cancer.
The Critical Link: HPV and Cervical Cancer
To truly understand the signs of cervical cancer, one must first understand its primary cause: the human papillomavirus. HPV is so common that nearly all sexually active people will get it at some point in their lives, often without ever knowing. There are over 100 types of HPV, but only about 14 high-risk types are known to cause cancer. Types 16 and 18 are responsible for approximately 70% of all cervical cancers and pre-cancerous cervical lesions.
How HPV Leads to Cellular Changes
The virus infects the cells on the surface of the cervix. In most cases, your immune system clears the infection naturally. However, when a high-risk HPV infection lingers for many years—typically a decade or more—it can cause these cells to become abnormal. These abnormal cells are not yet cancerous, and this stage is known as dysplasia or a squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL). This is a pre-cancerous condition. With continued persistence of the virus, these pre-cancerous cells can gradually acquire more genetic damage and eventually transform into invasive cancer cells. This slow progression is precisely why regular screening is so effective; it can detect these pre-cancerous changes long before they become a serious threat.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
The most challenging aspect of early-stage cervical cancer is that it often produces no signs or symptoms at all. This is why relying on symptoms alone is not a safe strategy. When symptoms do appear, they are easily mistaken for common conditions like menstrual irregularities or infections. Here are the key early warning signs to be aware of.Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: The Most Common Red Flag
This is the most frequent symptom of cervical cancer. "Abnormal" bleeding can manifest in several ways:
• Bleeding after menopause: Any vaginal bleeding after you have gone through menopause is a significant red flag and should be evaluated immediately.
• Bleeding after intercourse: Also known as postcoital bleeding, this can occur because the cancerous tissue is fragile and easily irritated.
• Bleeding between periods: Spotting or bleeding that occurs outside your regular menstrual cycle.
• Heavier or longer menstrual periods: A noticeable change in your typical period flow or duration.
If you experience any unusual bleeding, it is essential not to dismiss it. If symptoms like abnormal bleeding persist, consulting a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation is a prudent first step.
Unusual Vaginal Discharge: What to Look For
While vaginal discharge is normal and varies throughout your cycle, changes in its character can be a sign of a problem. Discharge related to cervical cancer may be:
• Watery or bloody: Often described as having a pinkish tinge.
• Heavy and foul-smelling: The odour is caused by the necrosis (death) of cancerous tissue.
• Continuous: Unlike discharge associated with a yeast infection, it may not come and go.
Pain During Intercourse: A Symptom Not to Ignore
Pain during sex (dyspareunia) can be a symptom of advanced pre-cancer or early invasive cancer. This pain is typically due to the tumour itself or changes in the cervical tissue that make it more sensitive.
Symptoms of Advanced Cervical Cancer
When cervical cancer grows and spreads beyond the cervix to nearby tissues and organs, it causes more pronounced symptoms.
Pelvic and Back Pain
As the tumour enlarges, it can press on nerves in the pelvic wall or the spine, causing a persistent, dull ache in the pelvis or lower back. This pain is not related to your menstrual cycle.
Urinary and Bowel Changes
If the cancer invades the bladder or rectum, it can lead to:
• Difficulty urinating or pain during urination.
• Blood in the urine (haematuria).
• Constipation or blood in the stool.
Systemic Symptoms: Fatigue, Weight Loss, and Swelling
Advanced cancer can cause body-wide symptoms, including:
• Unexplained fatigue: A profound tiredness that doesn't improve with rest.
• Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without trying.
• Swelling in the legs: This occurs if the tumour blocks lymphatic vessels, causing a buildup of fluid (lymphoedema).
The Power of Prevention: Screening is Your Best Defence
The most important message about cervical cancer is that you don't have to wait for symptoms. Regular screening can detect pre-cancerous changes early when they are easiest to treat.
The Pap Smear (Pap Test)
During a Pap smear, cells are gently scraped from the cervix and examined under a microscope for abnormalities. It can detect pre-cancerous cells long before they turn into cancer. Guidelines generally recommend starting Pap tests at age 21 and repeating them every 3 years.
The HPV Test
This test checks cervical cells for the DNA of high-risk HPV types. It is often used in conjunction with the Pap test for women over 30 (co-testing) or as a primary screening tool. A positive HPV test does not mean you have cancer; it means you have a virus that increases your risk, requiring closer monitoring.
For convenient and reliable screening, Apollo24|7 offers home collection for tests like the Pap smear and HPV test, making preventive care more accessible.
What to Do If You Notice Symptoms
If you experience any of the symptoms discussed, the most important action is to see a healthcare provider. Do not panic, as these symptoms are more commonly caused by non-cancerous conditions like infections, polyps, or fibroids. A doctor can perform a pelvic exam and appropriate tests, such as a Pap smear, HPV test, or a colposcopy (a procedure to closely examine the cervix), to determine the cause. If your condition does not improve after trying basic remedies, booking a physical visit to a doctor with Apollo24|7 ensures you get a definitive diagnosis and peace of mind.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of cervical cancer is a powerful component of women's health. While the potential symptoms—from abnormal bleeding to pelvic pain—are crucial to recognise, the true hero of this story is prevention. The slow progression from HPV infection to cancer provides a critical window of opportunity that screening tests like the Pap smear and HPV test effectively exploit. By staying informed about the risks, getting vaccinated against HPV, and adhering to recommended screening schedules, you can dramatically reduce your risk. Your health is in your hands. Listen to your body, be proactive with your care, and partner with your healthcare provider to ensure a healthy future. Taking action today is the best defence against cervical cancer tomorrow.Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
More articles from Cervical Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can you have cervical cancer with no symptoms at all?
Yes, absolutely. Pre-cancerous changes and early-stage invasive cervical cancer often cause no noticeable symptoms. This is why following recommended screening guidelines is essential, as it can detect abnormalities before symptoms even begin.
2. What does cervical cancer discharge look like?
Discharge associated with cervical cancer is often described as watery, bloody, or having a pinkish tinge. It may be heavy and have a foul, unpleasant odour. However, these symptoms are more common in advanced stages.
3. Is bleeding after sex always a sign of cervical cancer?
No, bleeding after intercourse can be caused by many other conditions, such as cervical polyps, infections, vaginal dryness, or inflammation. However, because it is a key symptom of advanced cervical cancer, it should never be ignored and always warrants a check-up with a doctor.
4. How long can you have cervical cancer without knowing?
The progression from a persistent HPV infection to pre-cancer to invasive cancer is typically very slow, often taking 10 to 15 years or even longer. This means a person could have pre-cancerous changes for many years without any knowledge, highlighting the critical importance of regular screening.
5. Can cervical cancer cause bloating and weight gain?
While cervical cancer is not typically associated with bloating and weight gain (which are more common with ovarian cancer), advanced disease can cause weight loss due to systemic effects. Swelling in the legs (lymphoedema) can occur if the cancer blocks lymph flow, which might be perceived as weight gain in the limbs.




