Signs Of Cervical Cancer
Learn the early signs of cervical cancer, including abnormal bleeding, unusual discharge, and pelvic pain. Understand advanced symptoms, when to see a doctor, and the importance of Pap and HPV screening for prevention.

Cervical cancer was once a leading cause of cancer death for women, but thanks to widespread screening with Pap and HPV tests, its incidence and mortality rates have dropped significantly. However, it remains a critical health concern. The key to successful treatment lies in early detection, and that starts with recognising the potential warning signs. This guide will walk you through the early and advanced symptoms of cervical cancer, explain what's normal and what's not, and empower you with the knowledge to take proactive steps for your health. Understanding your body and its signals is your first line of defence.
Understanding Cervical Cancer: A Brief Overview
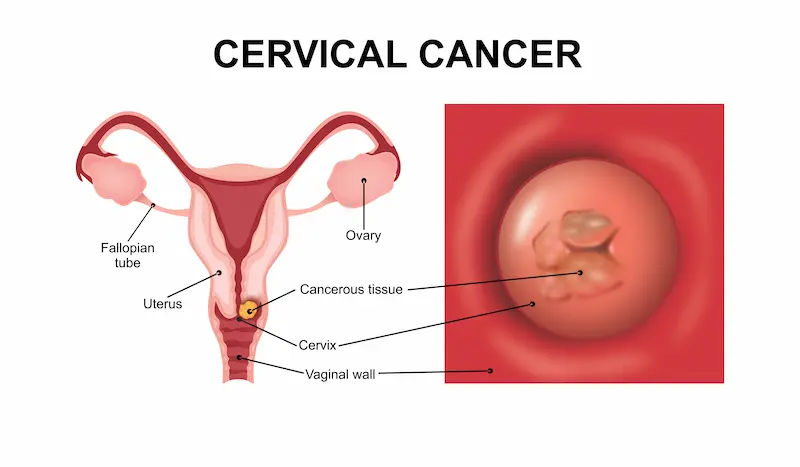
Before diving into the symptoms, it's helpful to understand what cervical cancer is. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by persistent infection with certain high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted infection. While most HPV infections clear on their own, sometimes they can lead to precancerous changes in the cervix's cells. If these changes are not found and treated, they can slowly develop into cancer over many years.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In its earliest, most treatable stages, cervical cancer often causes no signs or symptoms at all. This is why regular screening is so vital. However, as precancerous cells change and a tumour begins to form, symptoms can start to appear. Paying attention to these subtle changes is crucial.
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
This is the most common and often the first noticeable symptom. It's not your typical period. Abnormal bleeding can include:
- Bleeding between menstrual periods.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse (postcoital bleeding).
- Bleeding after menopause.
- Heavier or longer-lasting menstrual bleeding than usual.
- Why it happens: A tumour on the cervix is fragile and has abnormal blood vessels. Irritation, such as during sex, can cause these vessels to break and bleed easily.
2. Unusual Vaginal Discharge
While vaginal discharge is normal and changes throughout your cycle, discharge related to cervical cancer is often
different. Be alert for:
- A discharge that is watery, pink, or brownish.
- A discharge that has a foul or strong odour.
- A discharge that is heavy and continuous.
Why it happens: As cancerous cells die, they can cause an infection or irritate the cervical tissue, leading to this distinct, often malodorous discharge.
3. Pelvic Pain or Pain During Sex
Pain is not a typical early sign but can occur as the cancer progresses. This isn't ordinary menstrual cramping. It may feel like a dull ache or sharp pain in the pelvis, lower back, or appendix area. Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) is a particularly important symptom to discuss with your doctor.
- Why it happens: The cancer may be invading nearby tissues or affecting nerve endings in the cervix and surrounding structures.
Advanced Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
When cervical cancer grows and spreads (metastasizes) to nearby tissues and organs, it can cause more severe symptoms. These indicate a more advanced stage of the disease.
1. Changes in Bladder and Bowel Habits
Blood in the urine (hematuria) or pain during urination.
- Difficulty urinating or a constant feeling of needing to urinate.
- Bowel changes, such as constipation, blood in the stool, or a loss of control over bowel movements (incontinence).
- Why it happens: The cancer has likely spread to the bladder or rectum, which are located very close to the cervix.
2. Leg Swelling and Pain
Swelling in one or both legs can occur if the cancer progresses.
- Why it happens: Advanced tumours can press on nerves in the pelvic wall or block lymphatic vessels and blood flow, causing a buildup of fluid (lymphedema) in the legs.
3. General Health Deterioration
As with many advanced cancers, more systemic symptoms can appear, including:
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue and a general lack of energy.
- Loss of appetite.
- A persistent feeling of being unwell.
When to See a Doctor: Don't Wait
It cannot be stressed enough: do not ignore these symptoms. While they can be caused by conditions other than cervical cancer—such as infections, fibroids, or hormonal changes—only a healthcare professional can determine the cause.
Seek immediate medical advice if you experience:
- Any unexplained bleeding between periods, after sex, or after menopause.
- Unusual discharge that is persistent and foul-smelling.
- Persistent pelvic or back pain that is not related to your menstrual cycle.
Your doctor is not there to judge; they are there to help. Being honest about all your symptoms is the fastest way to get an accurate diagnosis and peace of mind.
The Critical Role of Screening and Prevention
Recognising symptoms is important, but preventing cervical cancer or catching it at a precancerous stage is the ultimate goal. This is achieved through two powerful tools:
- The Pap Test (Smear): This test collects cells from your cervix to check for precancerous changes before they turn into cancer.
- The HPV Test: This test checks for the presence of high-risk HPV strains that can cause these cellular changes.
Following the recommended screening guidelines from organisations like the American Cancer Society is the single most effective thing you can do to protect yourself.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs and symptoms of cervical cancer empowers you to be an active participant in your health journey. While the thought of cancer is frightening, remember that cervical cancer is highly preventable and treatable, especially when caught early. Listen to your body, prioritise your regular well-woman exams, and never hesitate to advocate for yourself if something feels off. Your health is your greatest asset—protect it with knowledge and proactive care. Schedule your screening today and encourage the women in your life to do the same.
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Gopal Kumar
Head, Neck and Thyroid Cancer Surgeon
15 Years • MBBS, MS , FARHNS ( Seoul, South Korea ), FGOLF ( MSKCC, New York )
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Amit Choraria
Surgical Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MS (Surgery) Fellow, Surgical Oncology, Tata Medical Center (FSO) Fellow, European Board of Surgery (Surgical Oncology) (FEBS) Fellow, Minimal Access Surgery (FMAS) Fellow, Indian Association of Gastrointestinal Endosurgeons (FIAGES) UICC Fellow, Royal Marsden NHS, London, UK Visiting Scholar, Plastic Reconstructive Surgery, CGMH, Taiwan Fellow, Robotic Surgical Oncology, Vattikuti Foundation, USA
Kolkata
Apollo Multispeciality Hospitals , Kolkata, Kolkata
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Arvind Raj
Oncologist
5 Years • M.S ( General Surgery), M.Ch ( Surgical Oncology)
Chennai
Lexwell Health Care Multi Speciality Hospital, Chennai

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

.webp)
.webp)
