Cervical Cancer: Recognising Early Signs and Knowing When to See a Doctor
Learn to recognise early signs of cervical cancer, understand symptoms, and know when to consult a doctor for timely screening and prevention.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Mohammed Kamran MBBS, FIDM
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
.webp?tr=q-80,f-webp,w-350,dpr-2,c-at_max 700w)
Introduction
Cervical cancer was once a leading cause of cancer death for women, but thanks to widespread screening, its impact has significantly decreased. However, it remains a serious health concern. The key to successful treatment lies in early detection, and that starts with knowing what to look for. This article will guide you through the potential signs of cervical cancer, from early, subtle changes to symptoms of more advanced disease. More importantly, we’ll clarify a critical point: early-stage cervical cancer often presents no symptoms at all. This is why understanding screening and prevention is just as crucial as recognising symptoms. We’ll empower you with the knowledge to take charge of your health, discuss when it’s time to consult a doctor, and outline the powerful preventive measures available today.
Understanding Cervical Cancer: The Role of HPV
Before diving into symptoms, it's essential to understand what cervical cancer is and what causes it. This knowledge provides context for the signs that may develop.
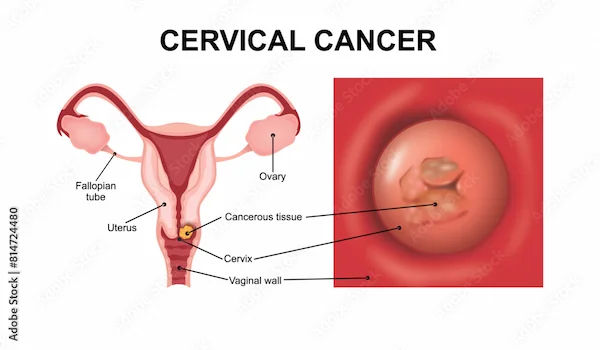
What is the Cervix and What is Cervical Cancer?
The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Cervical cancer occurs when the cells lining the cervix begin to grow uncontrollably. These changes typically happen slowly, over many years, first progressing through a pre-cancerous stage known as dysplasia or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
The HPV-Cervical Cancer Connection: What You Need to Know
Over 99% of cervical cancer cases are linked to long-term infection with high-risk types of Human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is an extremely common virus spread through intimate skin-to-skin contact; most sexually active people will get it at some point. In the majority of cases, the immune system clears the virus naturally. However, when a high-risk HPV infection persists, it can cause cellular changes that may eventually lead to cancer. This strong link is why HPV vaccination and testing are central to modern prevention strategies.
Consult a Gynaecologist for the best advice
Early Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
When early symptoms of cervical cancer do appear, they are often easy to dismiss or attribute to other conditions like menstrual irregularities or infections. Paying close attention to your body is vital.
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: The Most Common Red Flag
This is the most frequent symptom. It’s crucial to understand what "abnormal" means. It can present in several ways, including the following:
- Bleeding between periods: Spotting or bleeding that occurs outside your regular menstrual cycle.
- Bleeding after menopause: Any bleeding after you have stopped having periods.
- Bleeding after sex: Also known as postcoital bleeding.
- Heavier or longer periods: Menstrual bleeding that is unusually heavy or lasts longer than usual.
“Any unexpected vaginal bleeding warrants a discussion with your doctor. While it’s often due to less serious issues, it’s the primary sign we look for.”
Unusual Vaginal Discharge: What to Look For
Changes in vaginal discharge can be another indicator. While normal discharge varies, be concerned if you notice:
- Increased amount: A significant increase in the volume of discharge.
- Foul odour: A strong, unpleasant smell.
- Unusual colour: It may be watery, brown, or tinged with blood.
Pain During Sex (Dyspareunia): A Symptom Not to Ignore
Pain during or after intercourse can be a sign that cancer has grown on the cervix or surrounding tissues. While there are many benign causes for pain during sex, if it is a new or persistent issue, it should be evaluated.
Symptoms of Advanced Cervical Cancer
When cervical cancer grows and spreads (metastasizes) to nearby tissues or organs, it can cause a different set of symptoms.
Pelvic and Back Pain
As the tumour enlarges, it can press on nerves or organs in the pelvis, causing a persistent ache. This pain can also radiate to the lower back. This type of pelvic and back pain is typically constant and not related to your menstrual cycle.
Urinary and Bowel Changes
If the cancer spreads to the bladder or rectum, it can cause:
- Difficulty urinating or pain during urination.
- Blood in the urine (haematuria).
- Constipation or blood in the stool.
Systemic Symptoms: Fatigue, Weight Loss, and Leg Swelling
Advanced cancer can affect the whole body, leading to:
- Unexplained fatigue that doesn't improve with rest.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Swelling in one or both legs if the cancer blocks lymphatic vessels.
Key Point: Early-Stage Cervical Cancer Often Has No Symptoms
This point cannot be overstated. Pre-cancerous changes and very early-stage cervical cancers typically cause no noticeable signs. This silent nature is precisely why regular screening is non-negotiable. Relying solely on symptoms means a potential diagnosis could be delayed until the cancer is more advanced and harder to treat. Screening tests are designed to find abnormal cells before they become cancerous or at the earliest, most treatable stage.
When to Consult a Doctor: A Clear Guide
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially abnormal vaginal bleeding, it is essential to seek medical advice. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation. Don't wait for your next scheduled appointment. It’s always better to take action early to stay on the safe side. A doctor can help determine if your symptoms are related to a common infection, a benign condition, or if further investigation for cervical cancer is needed.
It’s Not Always Cancer: Other Conditions with Similar Symptoms
It's important to remember that the symptoms listed can be caused by numerous other, more common conditions. These include:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Vaginal or cervical infections (e.g., yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis)
- Polyps on the cervix or endometrium
A proper medical evaluation is necessary to determine the true cause.
The Power of Prevention: Screening is Your Best Defense
The most effective way to combat cervical cancer is through prevention and early detection. Screening programs have been incredibly successful in reducing cervical cancer rates.
The Pap Test (Pap Smear): A Life-Saving Routine
A Pap test (or Pap smear) involves collecting cells from the cervix to check for precancerous changes. If these changes are found, they can be treated long before they turn into cancer. Guidelines vary, but generally, women should start Pap tests at age 21 and continue every 3-5 years depending on age and previous results.
The HPV Test: Detecting the High-Risk Virus
The HPV test checks for the presence of high-risk HPV strains in cervical cells. It is often done alongside the Pap test (co-testing) for women over 30. A positive HPV test does not mean you have cancer; it means you have an infection that requires monitoring. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for tests like the HPV test, making proactive health monitoring easier.
HPV Vaccination: Preventing Cancer Before It Starts
The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool that protects against the types of HPV that cause most cervical cancers. It is most effective when administered before a person becomes sexually active (typically recommended for ages 9-12), but can be given up to age 45. Vaccination, combined with regular screening, offers the best possible protection.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of cervical cancer empowers you to be an active participant in your health. While the symptoms discussed here are important to recognise, the overarching message is clear: do not rely on symptoms alone. The true heroes in the fight against cervical cancer are routine screening and vaccination. These proactive steps have the proven power to prevent cancer or catch it at a stage where it is highly curable. If you are overdue for a screening or have concerns about any symptoms, take action today. Schedule an appointment with your gynaecologist or book a physical visit to a doctor with Apollo24|7. Your health is worth it.
Consult a Gynaecologist for the best advice
Consult a Gynaecologist for the best advice

Dr. Revathi S Rajan
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
24 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB.FFMM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Renuka Chandran
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
30 Years • MBBS, MD, DGO, Masters in Advanced Ultrasound in Obs & Gynea
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore

Dr. Sreeparna Roy
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS , MS (OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY), Fellowship in Infertility, Endoscopy & Ultrasonography), Fellowship in Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy,DRM
Kolkata
Dr Utsa Basu Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)
Consult a Gynaecologist for the best advice

Dr. Revathi S Rajan
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
24 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB.FFMM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Renuka Chandran
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
30 Years • MBBS, MD, DGO, Masters in Advanced Ultrasound in Obs & Gynea
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore

Dr. Sreeparna Roy
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS , MS (OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY), Fellowship in Infertility, Endoscopy & Ultrasonography), Fellowship in Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy,DRM
Kolkata
Dr Utsa Basu Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)
More articles from Cervical Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
What does cervical cancer discharge look like?
Cervical cancer discharge may be watery, pale, brown, or tinged with blood. It often has a foul odour and may be more persistent and heavy than normal discharge. However, these symptoms are more commonly caused by infections.
Can cervical cancer cause back pain?
Yes, persistent lower back pain can be a symptom of advanced cervical cancer. This occurs if the cancer has spread and is pressing on nerves or organs in the pelvis. It is not typically a sign of early-stage disease.
Is cervical cancer curable if caught early?
Yes. When cervical cancer is detected at an early, localised stage, the 5-year survival rate is very high (over 90%). This highlights the critical importance of regular screening.
How quickly do cervical cancer symptoms appear?
Cervical cancer develops very slowly, often over many years. Pre-cancerous changes usually cause no symptoms. Symptoms typically only appear once the cancer has become invasive and started to grow into surrounding tissues.
At what age should I start getting screened for cervical cancer?
Most guidelines recommend starting Pap tests at age 21. The frequency (every 3 or 5 years) depends on your age and whether you are also getting an HPV test. It's best to discuss a personalised screening schedule with your doctor.