Signs of Liver Cancer Causes, Symptoms, and When to See a Doctor
Know about liver cancer, causes, symptoms, risk factors, and recognising the signs, symptoms. What are the causes, diagnosis, and can it be prevented and more.

Written by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
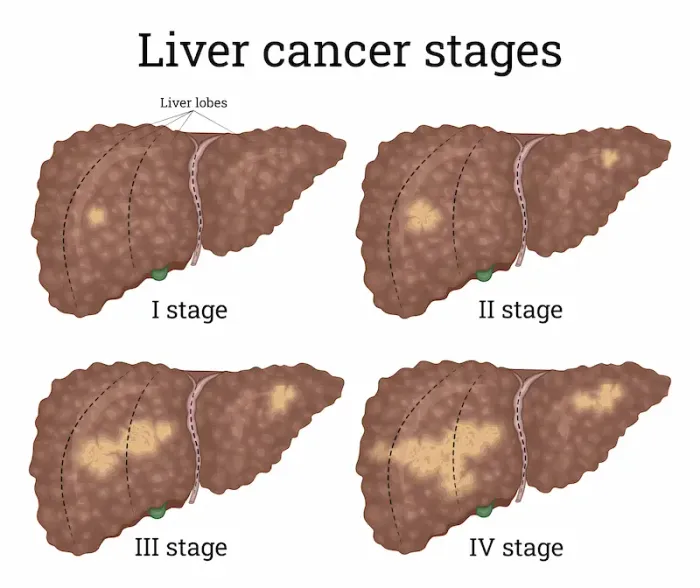
Introduction
Liver cancer is a serious health condition where abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably in the liver. Understanding what leads to the signs of liver cancer is crucial for early detection and effective management. Often, symptoms don't appear until the disease is in its advanced stages, making awareness of risk factors and early indicators vital. This article will demystify the complex journey from underlying causes to the manifestation of symptoms. We will explore the primary risk factors, such as chronic viral hepatitis and cirrhosis, and connect them to the physical signs your body may exhibit. By the end, you'll have a clearer picture of the pathways that lead to liver cancer symptoms and know when it's essential to seek professional medical advice for prompt intervention.
Understanding the Liver and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The Liver's Vital Role in Your Body
The liver is your body's powerhouse, performing over 500 essential functions. It processes nutrients from food, produces bile to digest fats, filters toxins from your blood, and creates proteins necessary for blood clotting. When cancer originates in the liver (primary liver cancer), it disrupts these critical processes, leading to a cascade of health issues. The most common type of primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte).
How Does Liver Cancer Develop?
Liver cancer typically doesn't develop in a healthy liver. It is almost always preceded by long-term damage and scarring, a condition known as cirrhosis. This ongoing injury causes healthy liver cells to become inflamed and die. As the liver attempts to repair itself, it creates scar tissue. Over time, this cycle of damage and repair can lead to genetic mutations in the remaining cells, causing them to grow uncontrollably and form a malignant tumour. This is the fundamental pathway that leads to signs of liver cancer.
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice
Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Chronic Viral Hepatitis: A Leading Cause
Chronic infections with hepatitis viruses are among the top global causes of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
HBV can cause long-term infection that directly damages liver DNA, leading to cancer even without cirrhosis. It is a major risk factor worldwide. The virus integrates its genetic material into the host's liver cells, which can trigger cancerous changes.
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
HCV primarily leads to cancer through the development of cirrhosis. The chronic inflammation caused by HCV over decades results in extensive scarring, creating an environment ripe for cancerous growth. With the advent of effective antiviral treatments, the risk from HCV can now be significantly reduced.
Cirrhosis: The Scarred Pathway to Cancer
Cirrhosis is the end-stage of liver scarring and is the most significant risk factor for HCC. It creates a landscape of continuous cell turnover and genetic instability. Causes of cirrhosis include:
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Long-term, heavy alcohol consumption is a direct toxin to liver cells. It causes fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and ultimately, cirrhosis. This alcohol-induced cirrhosis dramatically increases liver cancer risk factors.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and NASH
With rising rates of obesity and diabetes, NAFLD has become a critical concern. In some, NAFLD progresses to a more aggressive form called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and can lead to cirrhosis and cancer. This is one of the fastest-growing reasons for liver cancer in developed countries.
Other Significant Risk Factors
These include:
1. Aflatoxin Exposure: A toxin produced by mould on poorly stored crops (like corn, peanuts, and tree nuts), aflatoxin is a potent carcinogen, especially in combination with HBV.
2. Genetic Conditions: Hemochromatosis (iron overload), Wilson's disease (copper overload), and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can cause cirrhosis.
3. Type 2 Diabetes: This condition is strongly linked to an increased risk of liver cancer, often due to its association with NAFLD and NASH.
4. Obesity: By promoting NAFLD and NASH, obesity is a significant indirect risk factor.
Recognising the Signs and Symptoms
Early-Stage Symptoms: Often Silent
In its initial stages, liver cancer may cause no noticeable symptoms. This is why screening for high-risk individuals is so important. When early signs do occur, they are often vague and easily mistaken for other, less serious conditions, a phase often referred to as asymptomatic liver cancer.
Advanced-Stage Symptoms
As the tumour grows and liver function declines, more specific signs begin to appear.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite
One of the most common symptoms of advanced liver cancer is losing weight without trying. This occurs as the cancer alters your metabolism and suppresses your appetite.
Abdominal Pain and Swelling
Pain in the upper right abdomen, just below the rib cage, is a frequent complaint. Swelling or a feeling of fullness (ascites) can occur due to fluid buildup caused by the liver's inability to produce albumin and manage fluids.
Jaundice: The Yellow Warning
Jaundice, characterised by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, is a classic sign of liver problems. It happens when the diseased liver cannot process bilirubin, a waste product from broken-down red blood cells.
Other General Symptoms
These include nausea, vomiting, general fatigue and weakness, and white, chalky stools. Some may also experience fever and an enlarged liver or spleen, which a doctor can feel during an examination.
Diagnosis, Prevention, and Action Steps
How is Liver Cancer Diagnosed?
If liver cancer is suspected based on symptoms or risk factors, doctors use a combination of methods:
• Blood Tests: Including tests for liver function (LFTs) and the alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) tumour marker.
• Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs are crucial for visualising tumours.
• Liver Biopsy: Removing a small sample of tissue for analysis is the most definitive way to confirm a diagnosis.
If you are experiencing persistent symptoms like unexplained abdominal pain or jaundice, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation. They can guide you on the necessary diagnostic steps.
Get Your Health Assessed
Can Liver Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all cases are preventable, you can significantly reduce your risk by managing the underlying causes:
1. Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B.
2. Get tested and treated for Hepatitis C.
3. Drink alcohol in moderation, or not at all.
4. Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise to prevent NAFLD.
5. Manage diabetes effectively.
For those with known risk factors like cirrhosis, Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for monitoring tests like liver function tests (LFTs) and AFP, allowing for regular check-ups from the comfort of your home.
Conclusion
Understanding what leads to the signs of liver cancer empowers you to take proactive steps for your health. The journey typically begins with long-term damage, often from viral hepatitis, alcohol, or metabolic syndrome, that progresses to cirrhosis and finally to cancer. The insidious nature of this disease, with its often silent early stages, underscores the importance of awareness, especially if you fall into a high-risk category. By knowing the risk factors and heeding the warning signs like jaundice, unexplained weight loss, and abdominal swelling, you can seek timely medical intervention.
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
Consult an Oncologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Devashish Tripathi
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
20 Years • MBBS, PLAB, MRCP (UK)- General Medicine, FRCR (Oncology), Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT)- Clinical Oncology
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
More articles from Liver Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the first warning signs of liver cancer?
The very first signs are often subtle and non-specific, including fatigue, unexplained weight loss, a loss of appetite, and general malaise. More specific signs like jaundice or right-sided abdominal pain typically appear later.
Q2: Can you have liver cancer with no symptoms?
Yes, absolutely. This is very common, especially in the early stages of the disease. This is why screening through ultrasound and blood tests is recommended for individuals with known cirrhosis or other major risk factors.
Q3: How long can you have liver cancer without knowing?
It's possible to have liver cancer for months or even years without knowing, as the tumour can grow slowly without causing noticeable symptoms until it becomes quite large or begins to affect liver function significantly.
Q4: Does liver cancer spread quickly?
The rate of spread (metastasis) can vary, but liver cancer can be aggressive. It most commonly spreads to the lungs, bones, and lymph nodes. The prognosis is better when the cancer is caught before it has spread.
Q5: Is liver cancer curable if found early?
Yes, early-stage liver cancer offers the best chance for a cure. Treatment options for localised tumours can include surgical resection (removing part of the liver), a liver transplant, or localised therapies like ablation, which can be highly effective.