Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Concerned about fatty liver disease? Learn about symptoms, causes, and how to improve liver health. Understand your treatment options. Read more.

Written by
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Introduction
Fatty liver disease is a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. This build-up can affect the liver's ability to function properly, leading to a variety of health problems. Fatty liver disease is more common than many realise, and it can range from a mild condition to a serious disease that can lead to liver damage and other complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatments available is crucial for anyone who may be at risk of developing this condition.
What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat builds up in liver cells, beyond what is typically considered normal. The liver is an essential organ responsible for filtering toxins, producing bile to help digest food, and storing energy. However, when too much fat accumulates in the liver, it can impair these functions and lead to liver damage.
There are two primary types of fatty liver disease:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): As the name suggests, NAFLD occurs in individuals who do not consume excessive alcohol. This is the most common form of fatty liver disease. It is closely associated with metabolic conditions like obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. In its early stages, NAFLD may cause no symptoms, making it difficult to detect.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): AFLD, as the name implies, results from heavy alcohol consumption. The liver can only process a certain amount of alcohol at a time, and excessive drinking leads to an overload of fat in liver cells. If left untreated, this form of fatty liver disease can progress to more severe liver damage, including alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Both forms of fatty liver disease can range from simple fat accumulation (steatosis) to more serious liver damage, such as inflammation and scarring (fibrosis), potentially leading to liver failure.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fatty Liver Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. It is crucial to be aware of the underlying conditions and lifestyle choices that increase the risk of developing the disease.
1. Obesity and Overweight
Obesity is one of the primary risk factors for fatty liver disease, particularly NAFLD. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can increase the amount of fat that is stored in liver cells. The risk of fatty liver increases with the degree of obesity, and it is often linked to insulin resistance, a key feature of metabolic syndrome.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes are at higher risk of developing fatty liver disease. The body's inability to effectively use insulin leads to higher blood sugar levels, which in turn can result in fat buildup in the liver. The relationship between insulin resistance and fatty liver disease is well established.
3. High Cholesterol and Triglycerides
High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood contribute to fat deposits in the liver. These fats can accumulate in liver cells and cause inflammation, which can eventually damage the liver if left unaddressed.
4. Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity is another key risk factor for fatty liver disease. Regular exercise helps control weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces triglyceride levels. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain and poor metabolic health, increasing the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
5. Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a role in the development of fatty liver disease. Some people may be genetically predisposed to accumulating fat in the liver, even without other risk factors. A family history of fatty liver disease or liver-related illnesses may increase the risk of developing the condition.
6. Age and Gender
Age also affects the risk of developing fatty liver disease, with the condition being more common in people over 50 years old. Hormonal changes, especially in women after menopause, may also increase the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. However, men are generally at higher risk of developing AFLD due to the direct effects of alcohol on the liver.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
In the early stages, fatty liver disease may not present with any obvious symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, it can cause a range of symptoms that might indicate liver damage.
Common symptoms include:
Fatigue or tiredness
Unexplained weight loss
Abdominal discomfort or pain in the upper right side
Swelling or bloating in the abdomen (ascites)
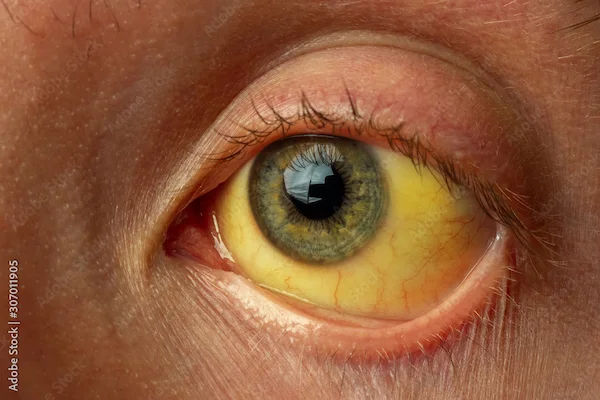
Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
Dark urine and light-coloured stools
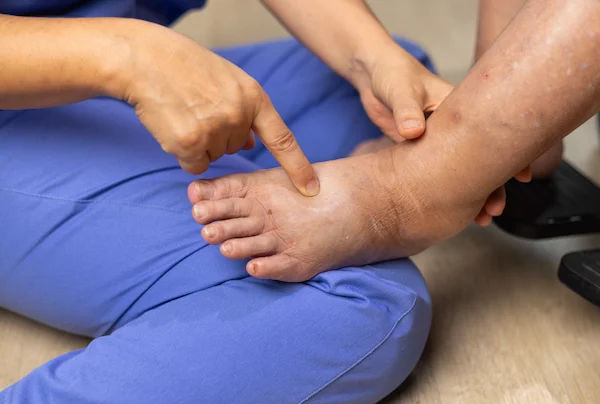
Swollen legs and ankles (edema)
Mental confusion or difficulty concentrating (in severe cases)
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of these symptoms, as they may indicate liver dysfunction or more advanced liver disease.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. The following methods are commonly used:
1. Blood Tests
Blood tests are often the first step in diagnosing fatty liver disease. Elevated liver enzymes such as ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) may indicate liver damage. However, these tests alone cannot confirm the presence of fatty liver disease, so further tests are needed.
2. Imaging Tests
Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are commonly used to visualise the liver and check for signs of fat buildup. These imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis of fatty liver disease and assess the extent of liver damage.
3. Liver Biopsy
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be required to assess the severity of liver damage. This test involves removing a small sample of liver tissue for examination under a microscope. A biopsy is particularly useful in diagnosing NASHand determining whether the liver has developed fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Consult Top Hepatologists
Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease
While there is no specific medication to treat fatty liver disease, lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and prevent further liver damage. Key treatment strategies include:
1. Weight Loss
For individuals who are overweight or obese, losing 5-10% of body weight can significantly reduce fat in the liver and improve liver function. Gradual weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise is recommended to avoid stress on the liver.
2. Healthy Diet
A well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet is crucial for managing fatty liver disease. Focus on eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugarscan help prevent further fat accumulation in the liver.
3. Regular Exercise
Physical activity plays a vital role in reducing liver fat and improving insulin sensitivity. It is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
4. Avoid Alcohol
For individuals with alcoholic fatty liver disease, completely eliminating alcohol from the diet is essential. Even for those with NAFLD, it may be beneficial to limit alcohol consumption, as it can further damage the liver.
5. Managing Underlying Conditions
While there are no medications specifically for fatty liver disease, certain drugs may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, or hypertension. Your doctor may recommend medications to help control these issues, improving overall liver health.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing fatty liver disease involves making healthy lifestyle choices, such as:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Following a balanced diet
Exercising regularly
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
Monitoring and managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a common yet often overlooked condition that can lead to severe liver damage if not managed properly. By understanding the causes, recognising symptoms, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of developing fatty liver disease or reverse its progression. Regular monitoring and medical support are essential for managing this condition and ensuring long-term liver health.
If you suspect you have fatty liver disease or are at risk, it is crucial to consult with your doctor to receive a proper diagnosis and explore the best treatment options for your situation.
Consult Top Hepatologists
Consult Top Hepatologists

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Pukhraj Singh Jeji
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD ( Internal Medicine ), DM ( Gastroenterology ), Consultant - Gastroenterology
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)

Dr U V U Vamsidhar Reddy
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (JIPMER), DM (Hepatology, PGIMER)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)
Consult Top Hepatologists

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Pukhraj Singh Jeji
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD ( Internal Medicine ), DM ( Gastroenterology ), Consultant - Gastroenterology
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(125+ Patients)

Dr U V U Vamsidhar Reddy
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (JIPMER), DM (Hepatology, PGIMER)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)